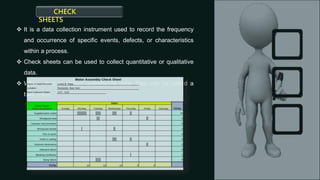
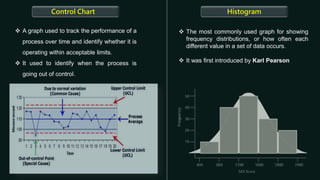
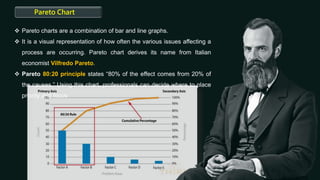
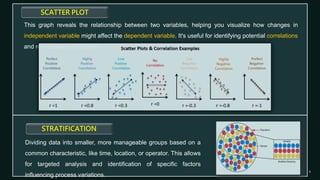
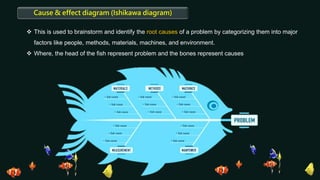
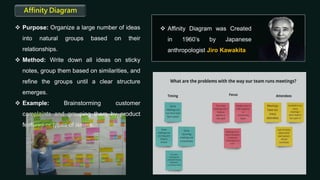
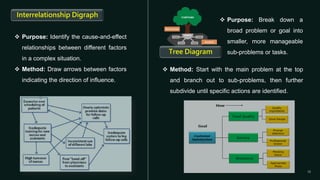
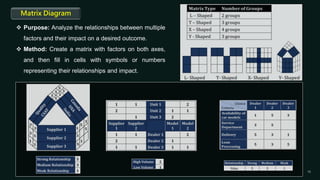
Quality control is a systematic approach to ensure products or services meet standards. It involves activities and inspections throughout production to identify and correct deviations. There are statistical and non-statistical quality control tools. Statistical tools are applied after problems occur for analysis and corrective actions. Non-statistical tools are applied before problems to plan and prevent issues. The document describes 7 basic and 7 new quality control tools, including check sheets, control charts, histograms, Pareto charts, scatter diagrams, stratification, Ishikawa diagrams, affinity diagrams, relationship diagrams, tree diagrams, matrix diagrams, PDPC, activity network diagrams, and prioritization matrices.