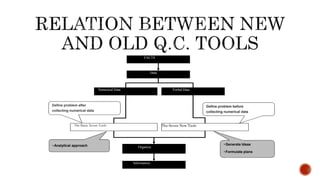
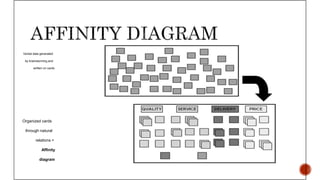
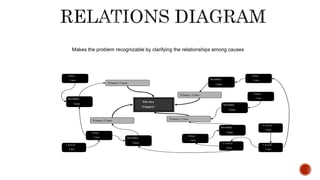
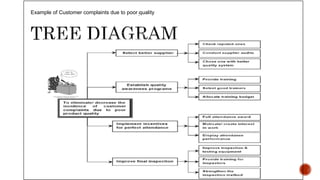
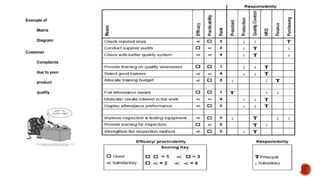
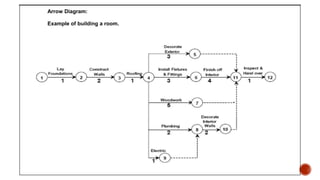
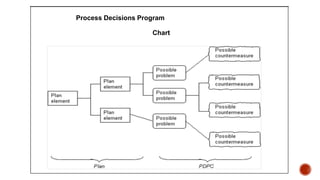
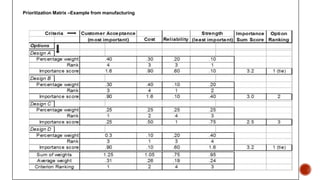
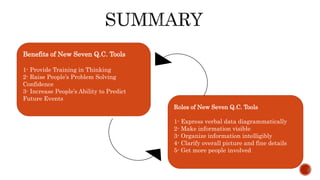
The document discusses the new seven quality tools introduced by the Union of Japanese Scientists and Engineers in 1976, designed for innovation and project planning. These tools, which include the affinity diagram and matrix diagram, help organize verbal data and improve total quality management by identifying problems and facilitating systematic thinking. The document outlines the benefits and applications of these tools in problem-solving and decision-making processes within organizations.