Embed presentation
Downloaded 36 times


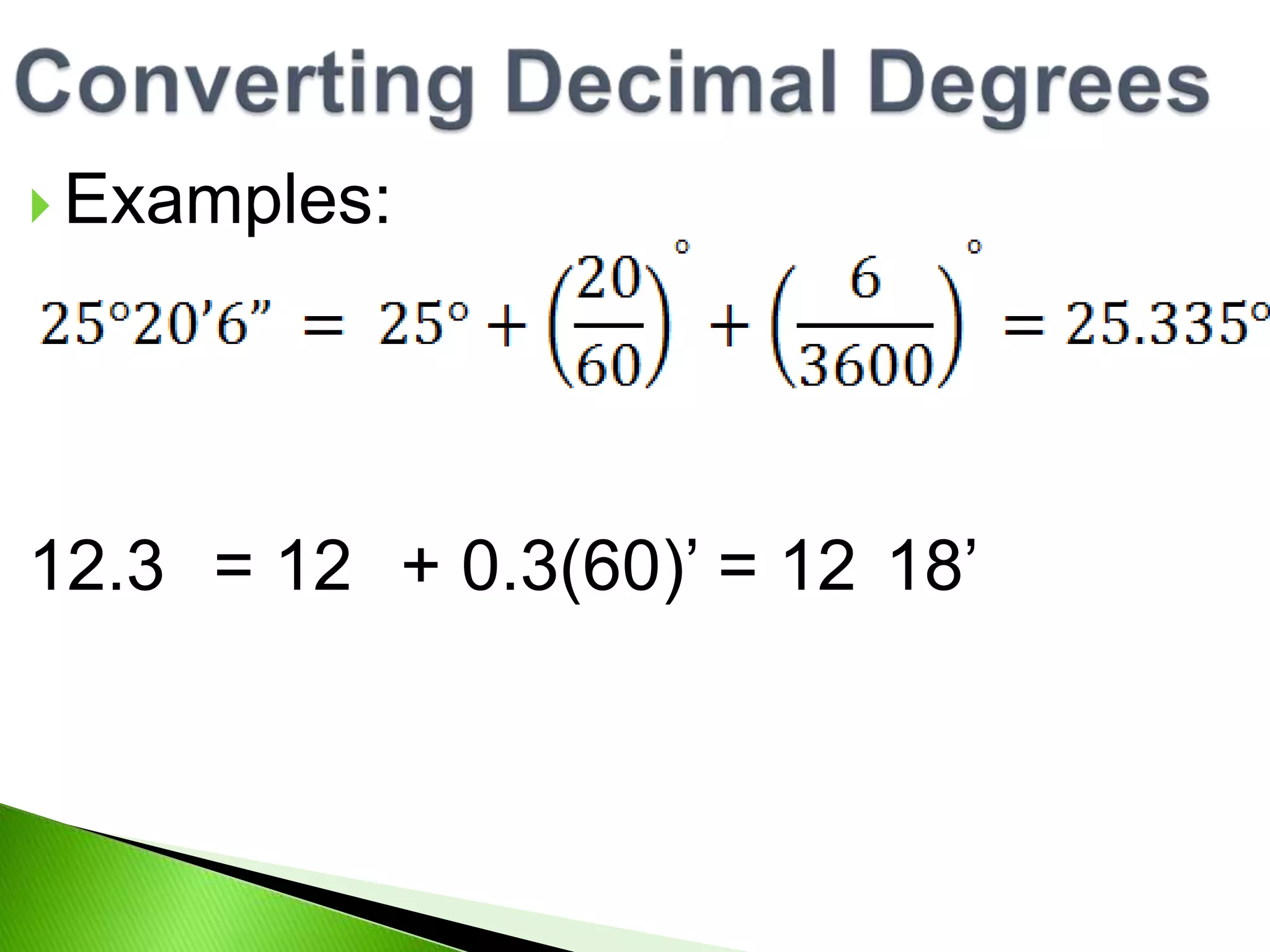






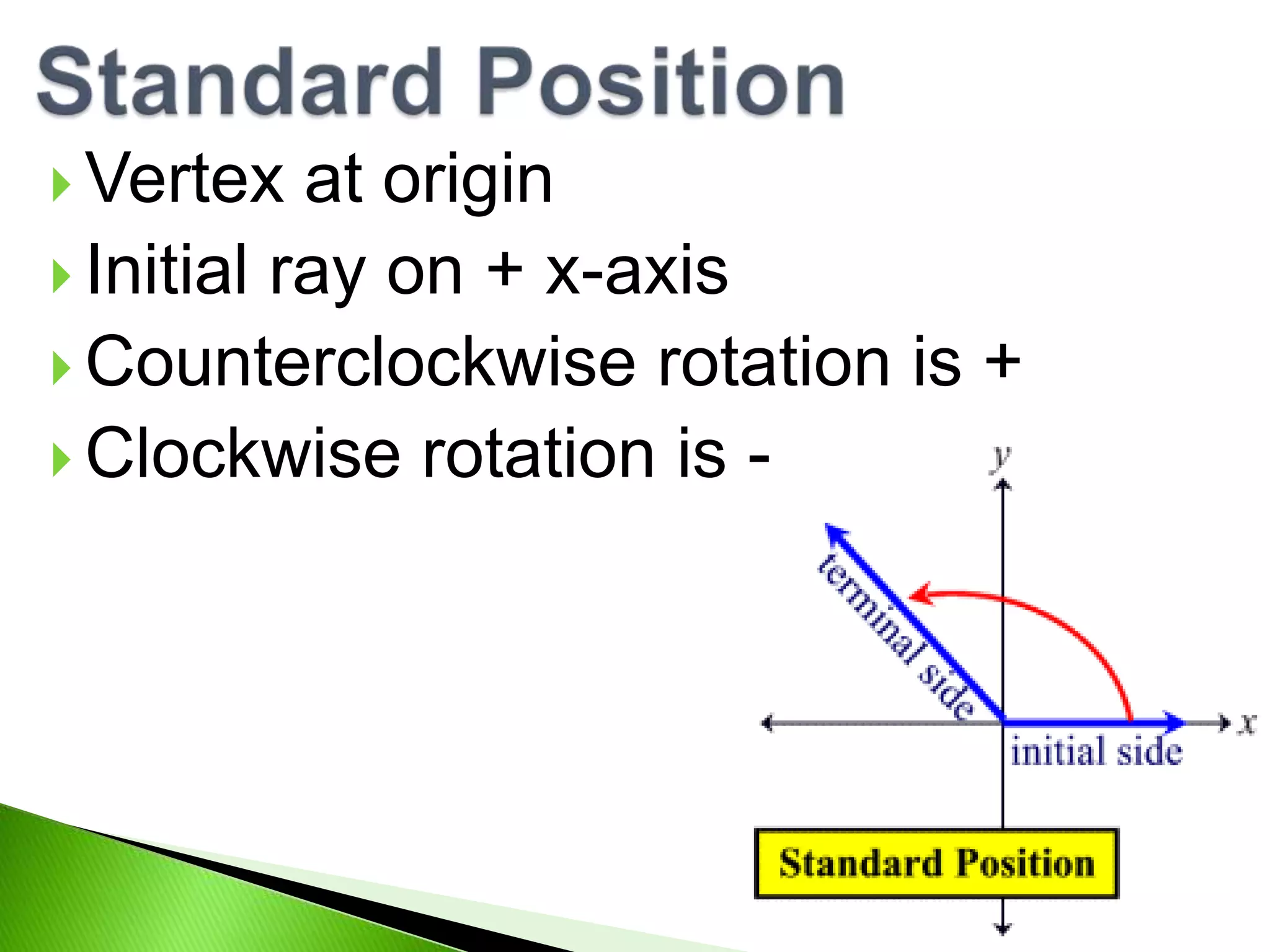
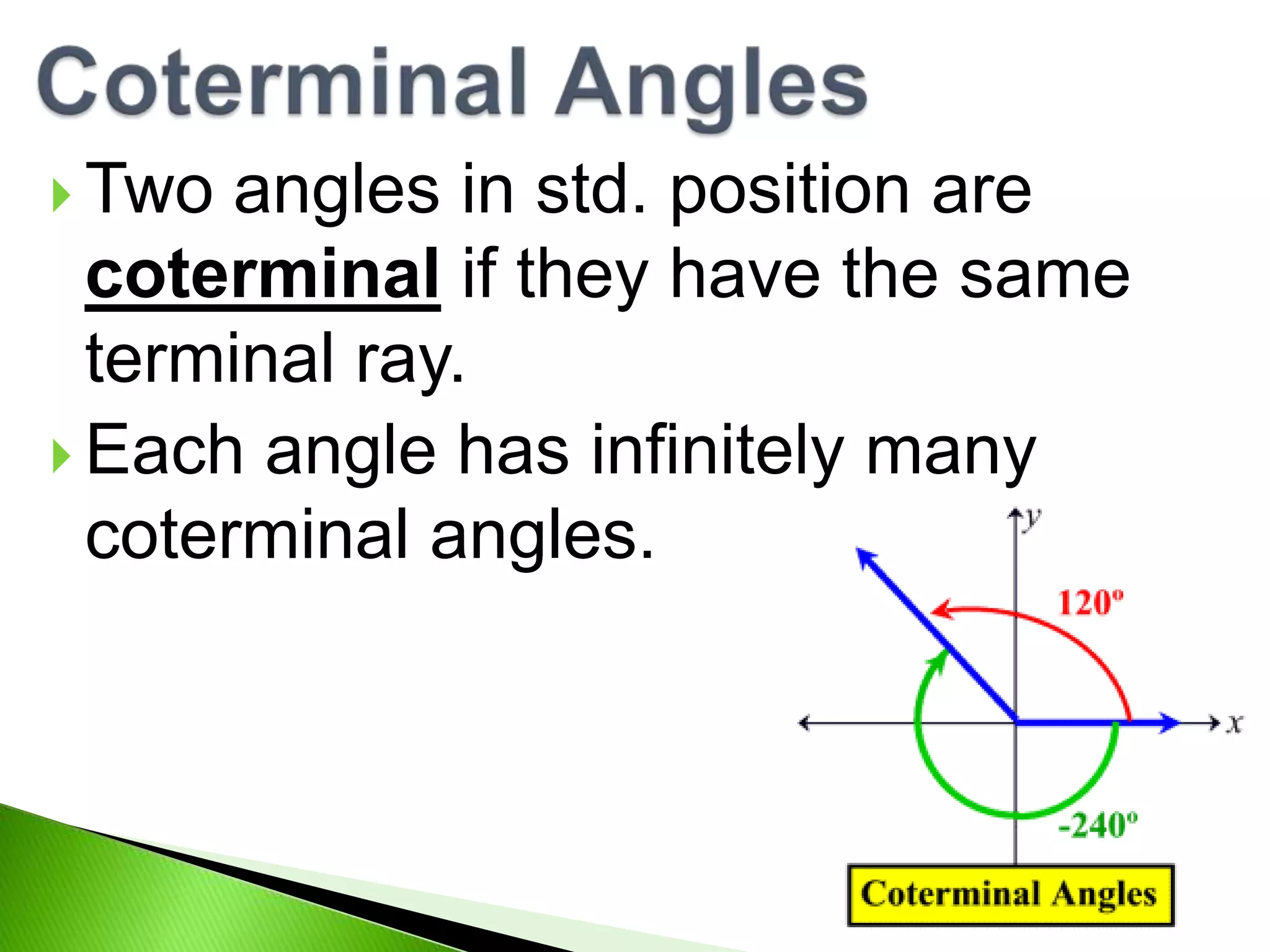


This document discusses trigonometry and angles. It defines angles in degrees and radians, and coterminal angles. Degrees can be divided into minutes and seconds. One radian is defined as the central angle whose arc length equals the radius. Conversions between degrees and radians are provided. Coterminal angles have the same terminal ray but different measures. Examples are given to find coterminal angles of π/4 and 4π/3.














