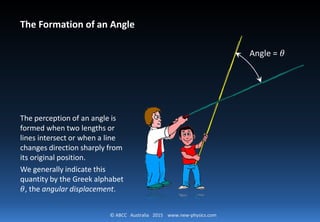
The document discusses the definition and formation of angles, indicating that an angle is created when two lines intersect. It explains how angles are measured in degrees and radians, detailing the conversion between the two systems. Additionally, it presents typical angles and their circular equivalents.
![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
ANGLES & MEASUREMENT
PM [B05]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmb05anglesmeasure-151011170600-lva1-app6891/85/PM-B05-Angles-Measurement-1-320.jpg)





![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
COMPLEX POLAR COORDINATES
To be carried on PM [BO6]:
ABCC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmb05anglesmeasure-151011170600-lva1-app6891/85/PM-B05-Angles-Measurement-8-320.jpg)