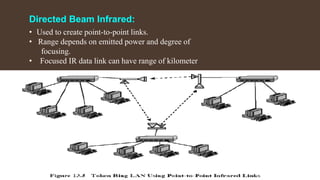
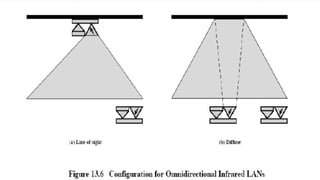
This document provides an overview of infrared radiation and wireless protocols. It begins with definitions of infrared radiation, its history and characteristics. It then discusses infrared technology used in mobiles for wireless connectivity. The document outlines different infrared data transmission techniques and classification schemes. It also covers wireless networks and common network protocols like TCP, IP, HTTP and their standards. The key points covered are the use of infrared for mobile communication, protocols for network communication and wireless network standards.