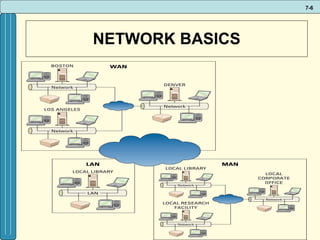
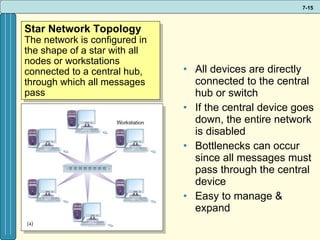
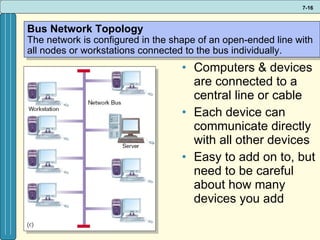
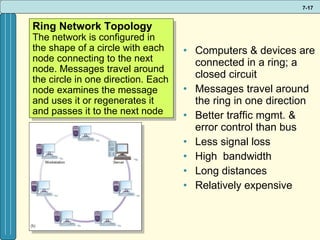
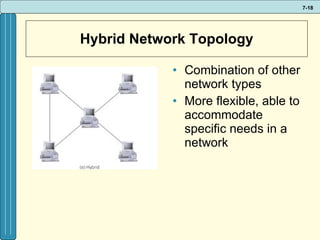
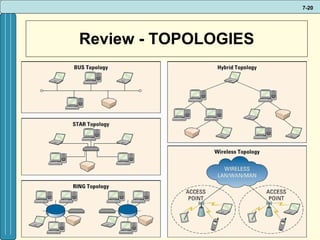
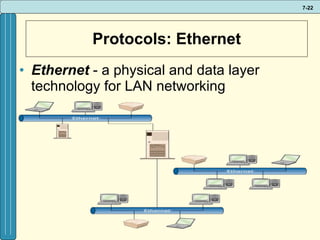
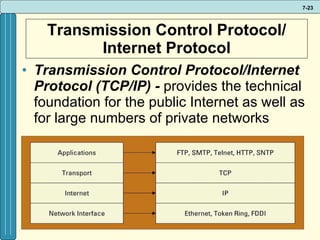
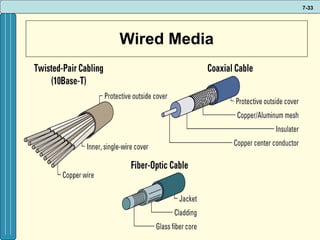
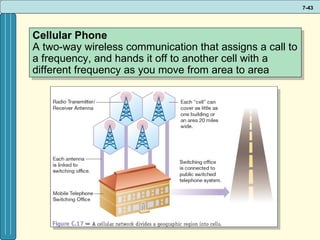
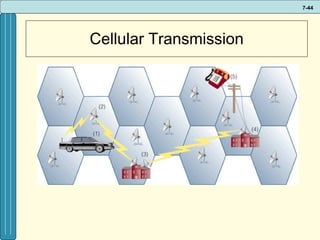
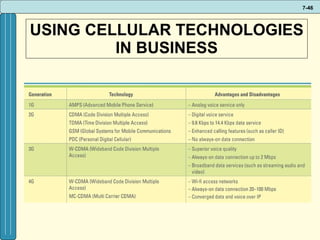
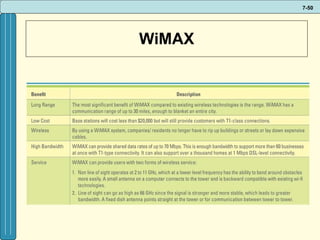
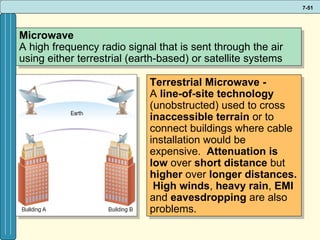
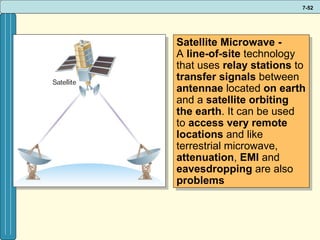
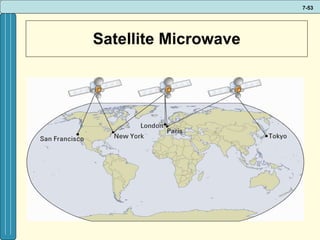
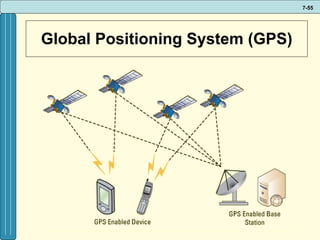
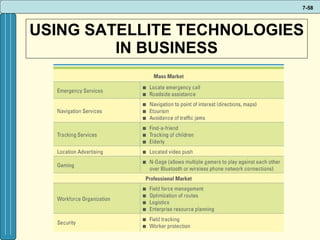
The document discusses various networking, telecommunications, and mobile technologies important for business. It defines different types of networks including LANs, WANs, and MANs. It also covers network basics like architecture, protocols, media, and topologies. Wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, WiMAX, Bluetooth, and cellular are described along with how they enable increased business mobility. Security of business networks is also addressed.