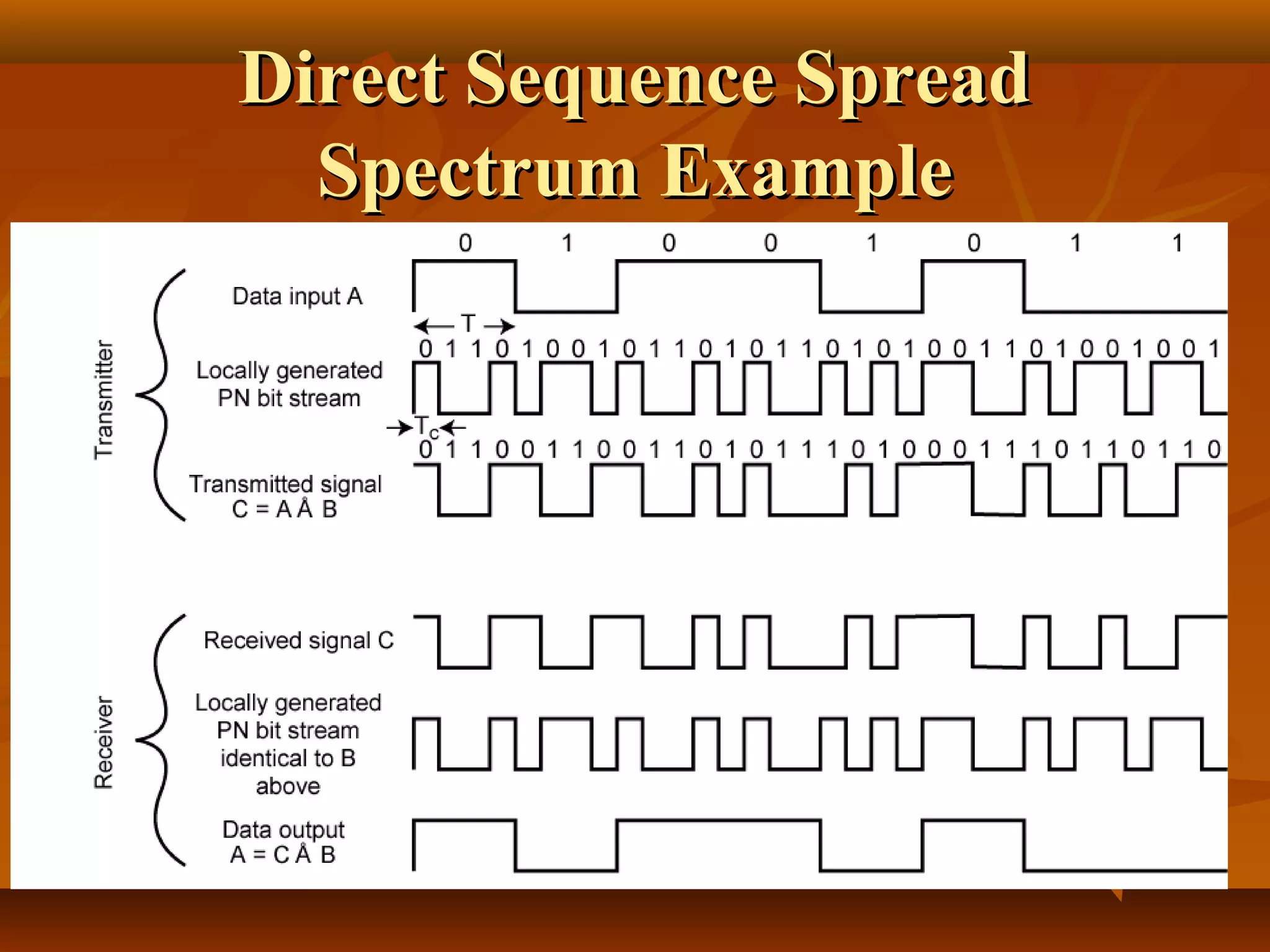
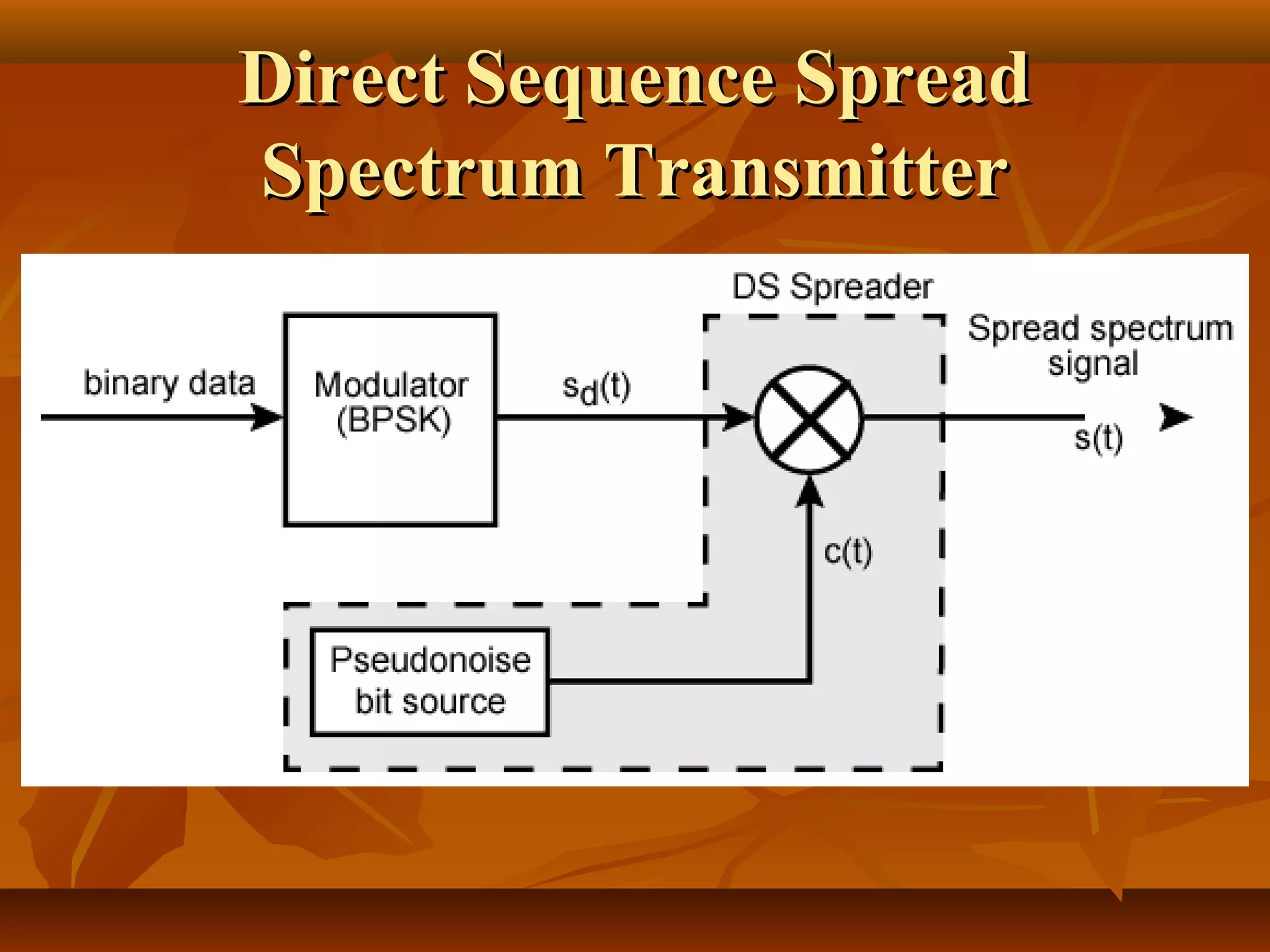
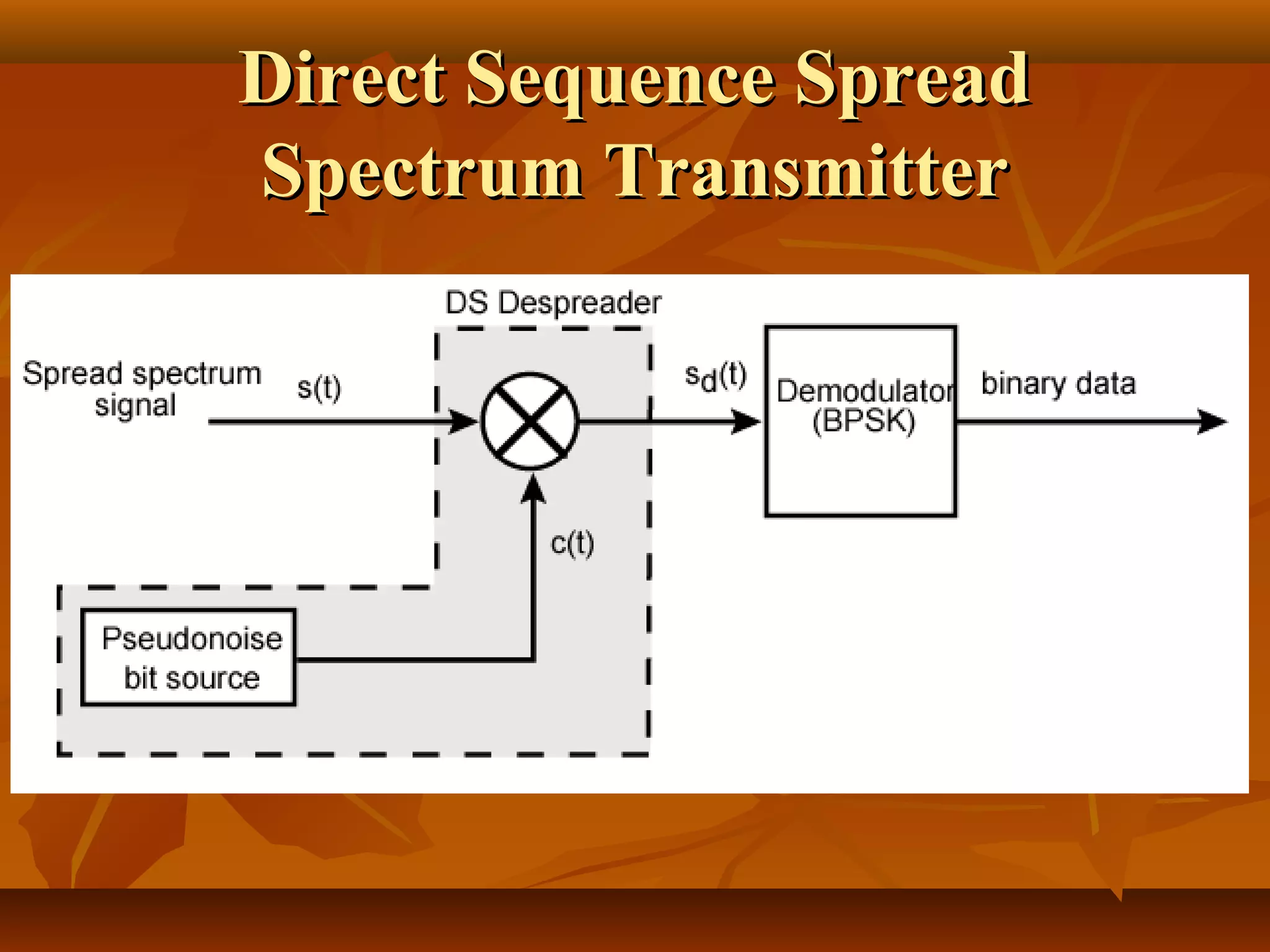
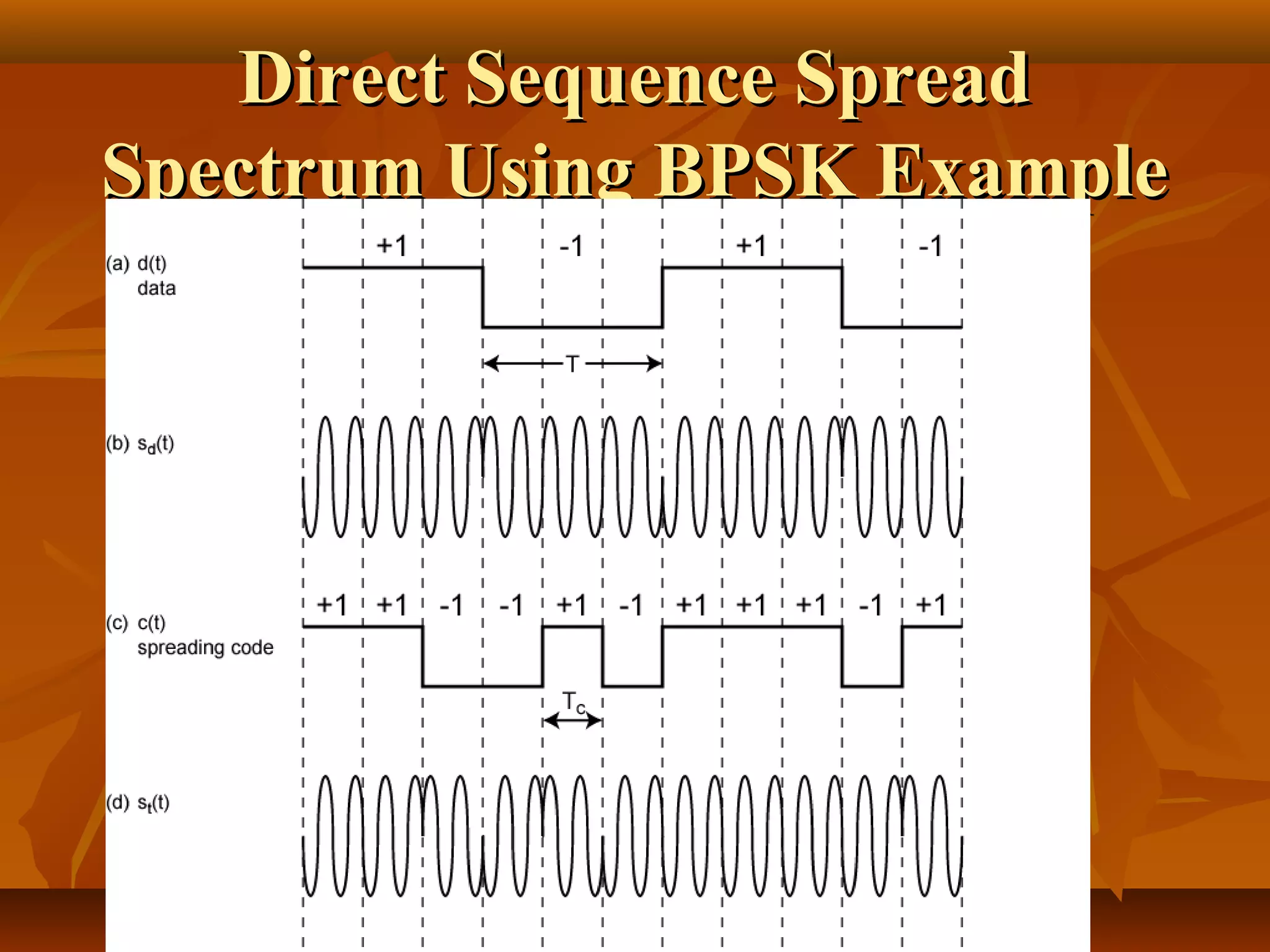
Direct sequence spread spectrum is a technique that spreads signals across a wider bandwidth through the use of pseudorandom number sequences. This decreases interference and allows multiple access and functions. In direct sequence spread spectrum, each bit is represented by multiple bits using a spreading code, spreading the signal across a wider frequency band proportional to the number of bits. It is used in applications like GPS, wireless networks, and communications to increase resistance to interference and jamming while allowing sharing of channels.