This document provides information about Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) including:
- OFDM was first proposed in 1966 and has developed over the years as a popular scheme for wideband digital communication.
- OFDM works by dividing the available spectrum into multiple orthogonal subcarriers that are modulated with low-rate data streams, maintaining total data rates similar to conventional single-carrier modulation schemes.
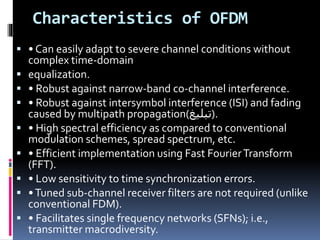
- OFDM has advantages over other modulation techniques in that it can easily adapt to severe channel conditions and is robust against interference and fading.