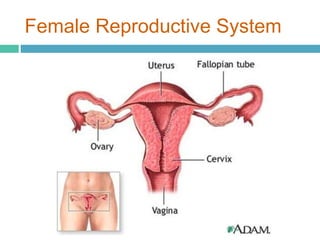
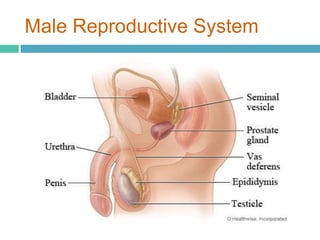
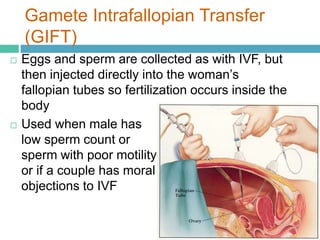
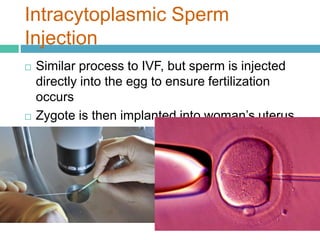
Infertility affects approximately 15% of couples in North America due to issues like low sperm counts, hormone imbalances, or damage to eggs or sperm. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) allow many infertile couples to conceive, including artificial insemination (AI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. IVF involves collecting eggs and sperm and fertilizing the egg in a petri dish before implanting the embryo in the woman's uterus, while GIFT and intracytoplasmic sperm injection directly inject gametes or embryos in the body. ART can help couples conceive when natural conception is impossible due to issues with the