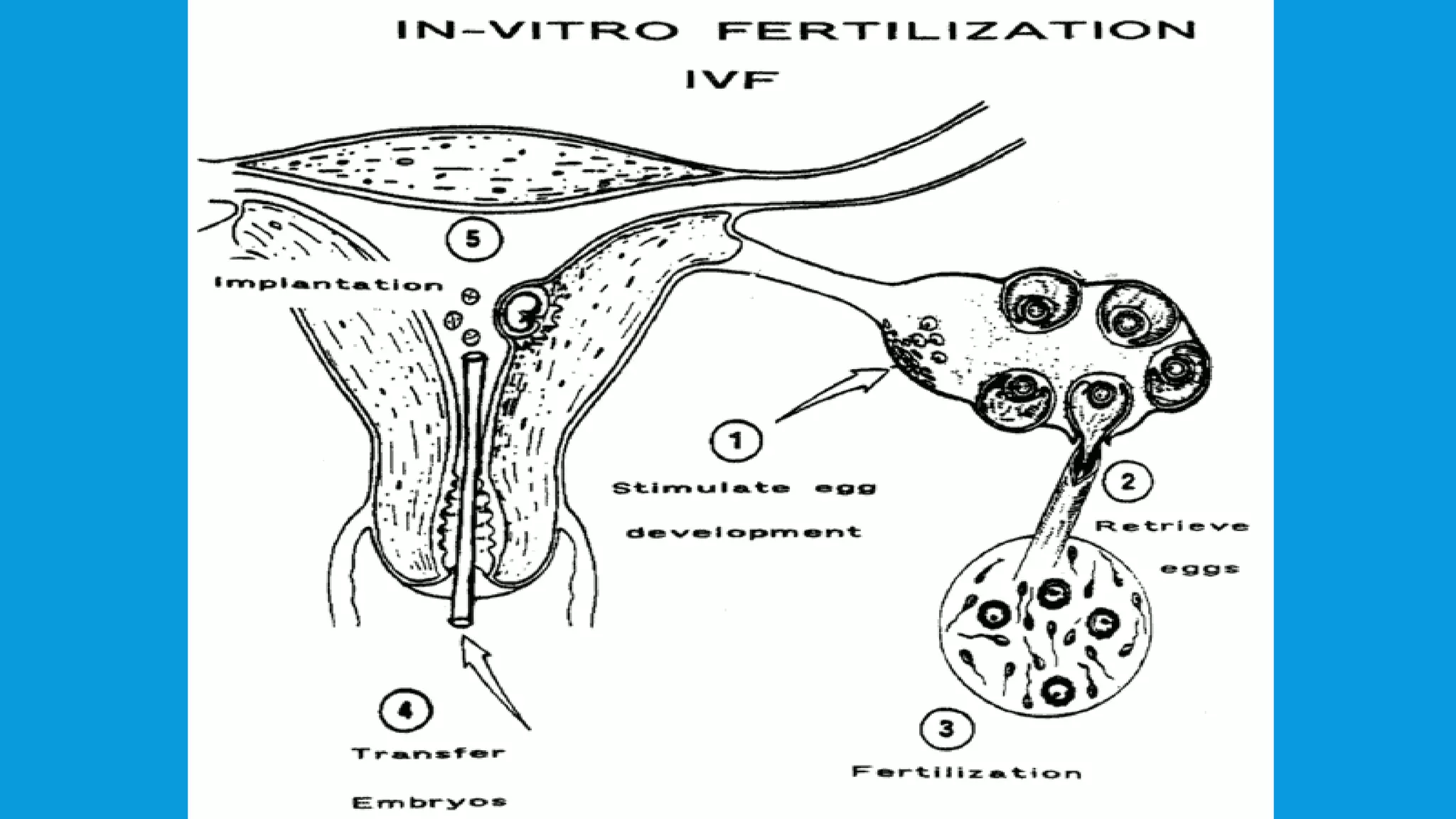
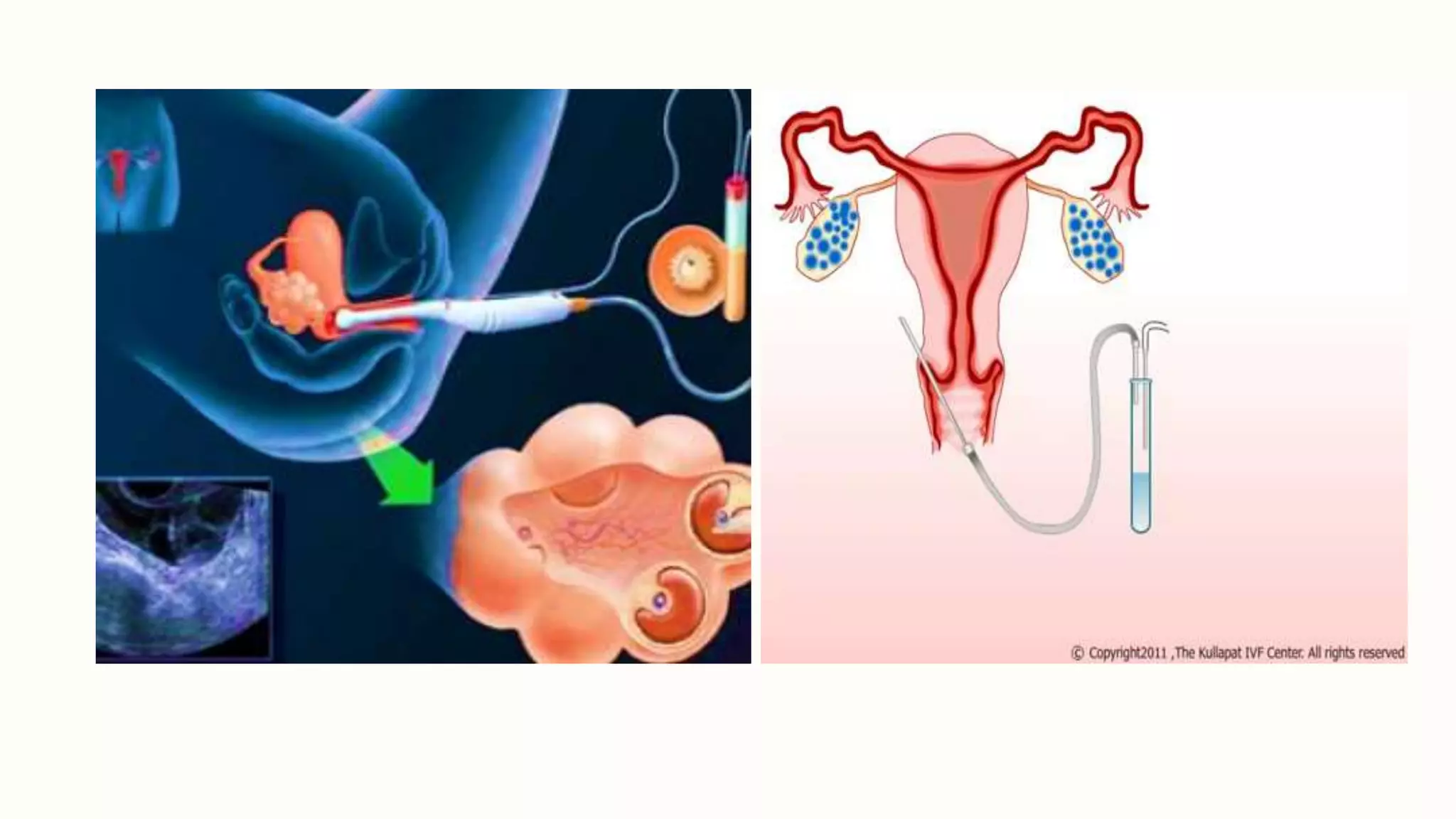
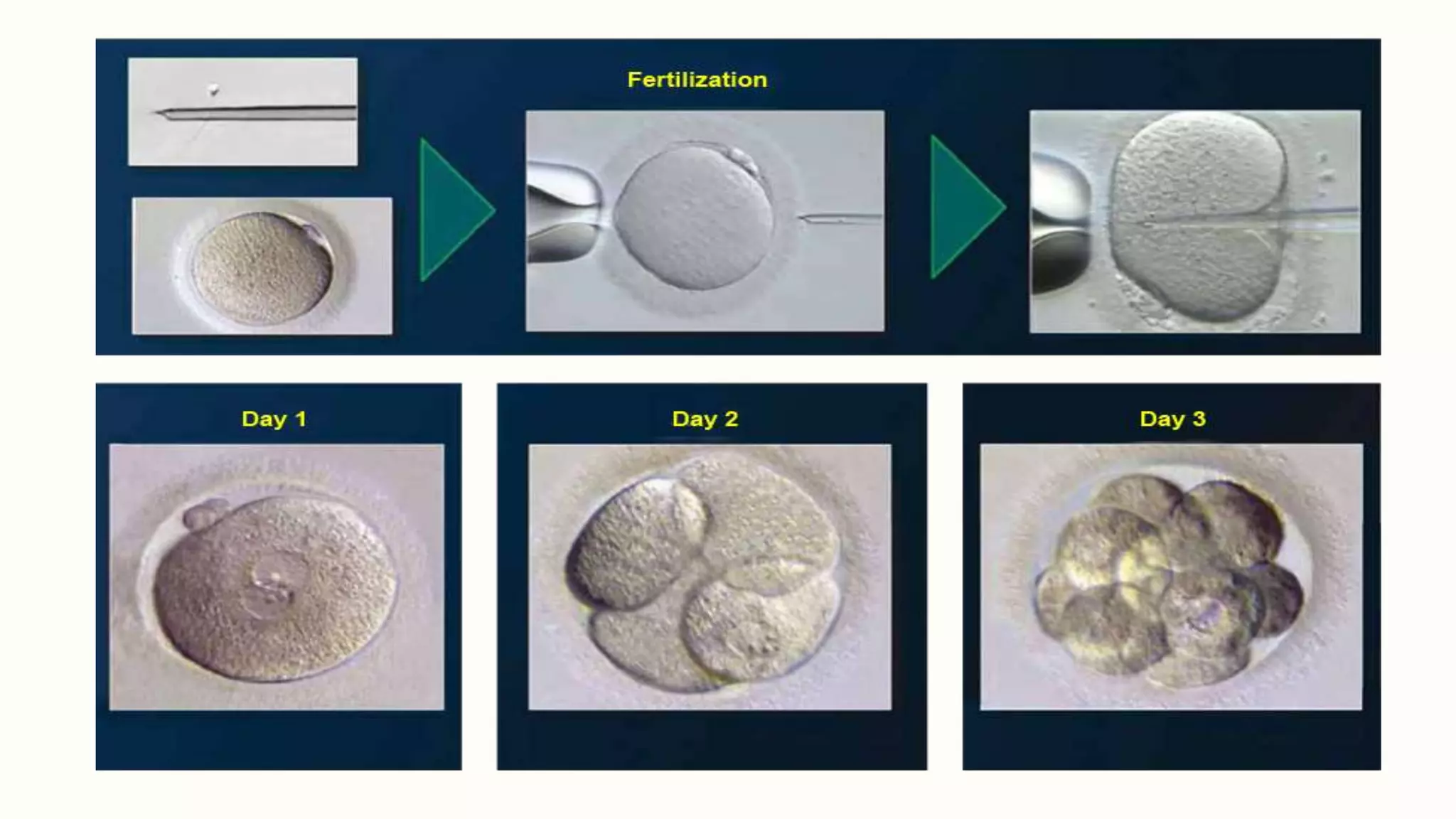
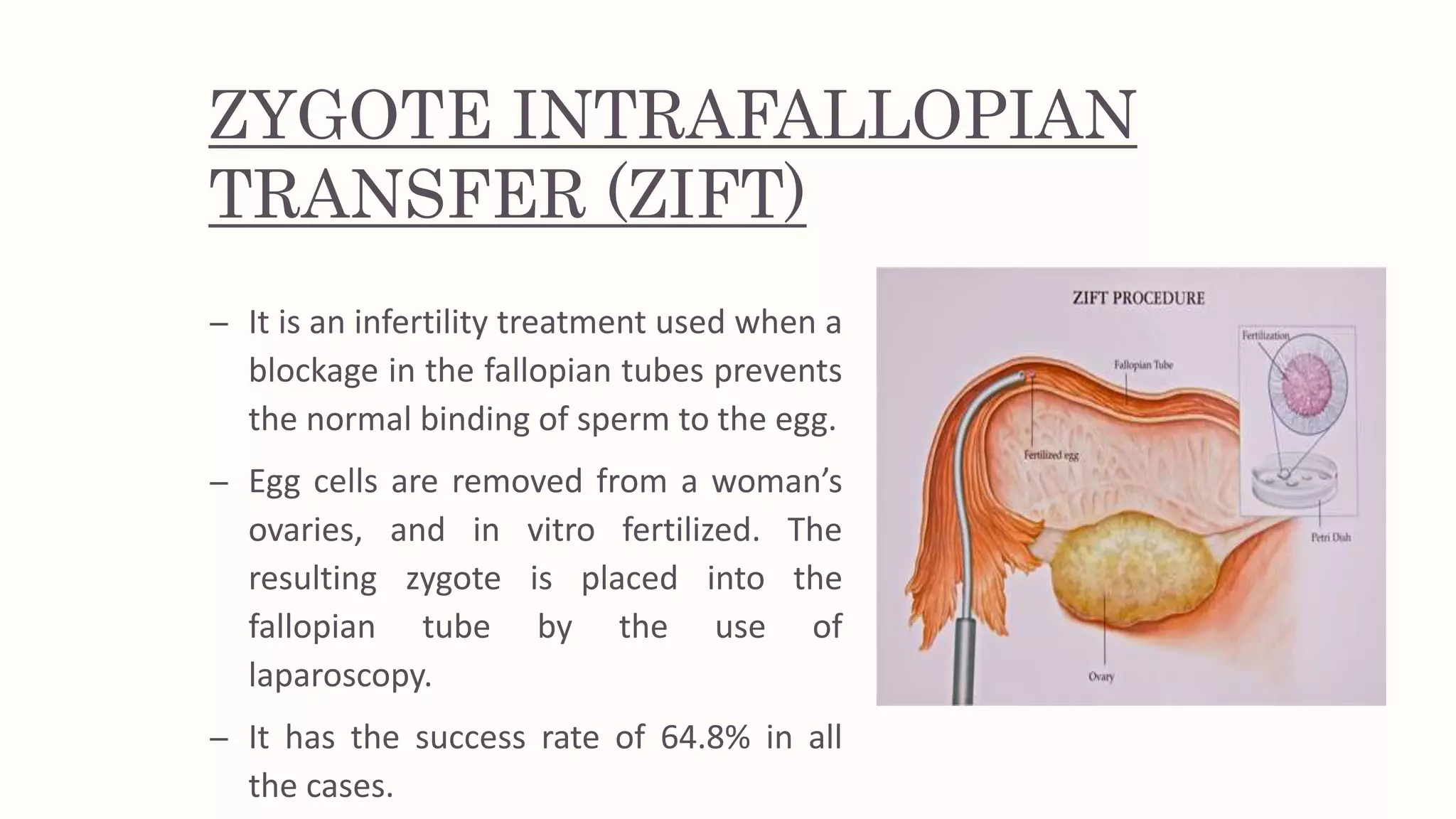
The document presents a seminar on infertility and assisted reproductive technology (ART), detailing various infertility causes in both males and females, including factors such as age and ovulation disorders. It discusses key ART techniques, such as artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization (IVF), and surrogacy, outlining their procedures, advantages, and drawbacks. The seminar concludes by emphasizing the ongoing advancements in ART that offer hope for childless couples, despite the associated risks and costs.