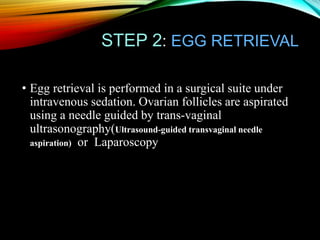
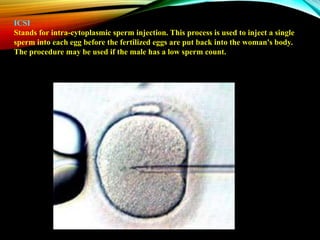
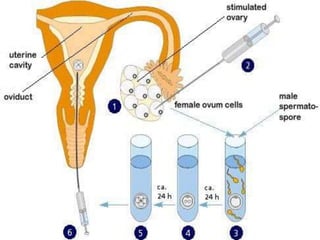
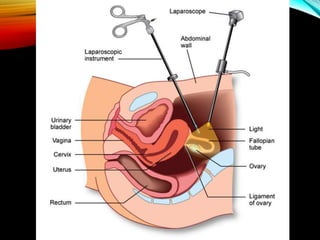
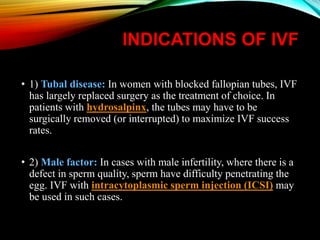
This document provides an overview of in vitro fertilization (IVF). It discusses that IVF involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside of the body in a laboratory dish. The first successful IVF birth was in 1978 in England. The document outlines the basic IVF process which includes hormonal treatment of the female, egg retrieval, fertilization and embryo culture, and embryo transfer. It also discusses the history of IVF, indications for IVF including tubal disease and male factor infertility, factors that affect IVF success rates like maternal age, and potential side effects and risks of IVF treatment.