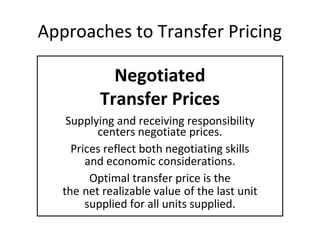
Transfer pricing refers to the prices charged for goods and services transferred between divisions within the same company. There are several approaches to setting transfer prices, including using market prices, cost-based prices, negotiated prices, or administered prices set by a rule. The objectives of transfer pricing are to provide accurate performance measurement for each division, encourage goal congruence between divisions, and mimic external market prices. Key considerations include using transfer prices that motivate optimal sourcing and production decisions for the entire company.