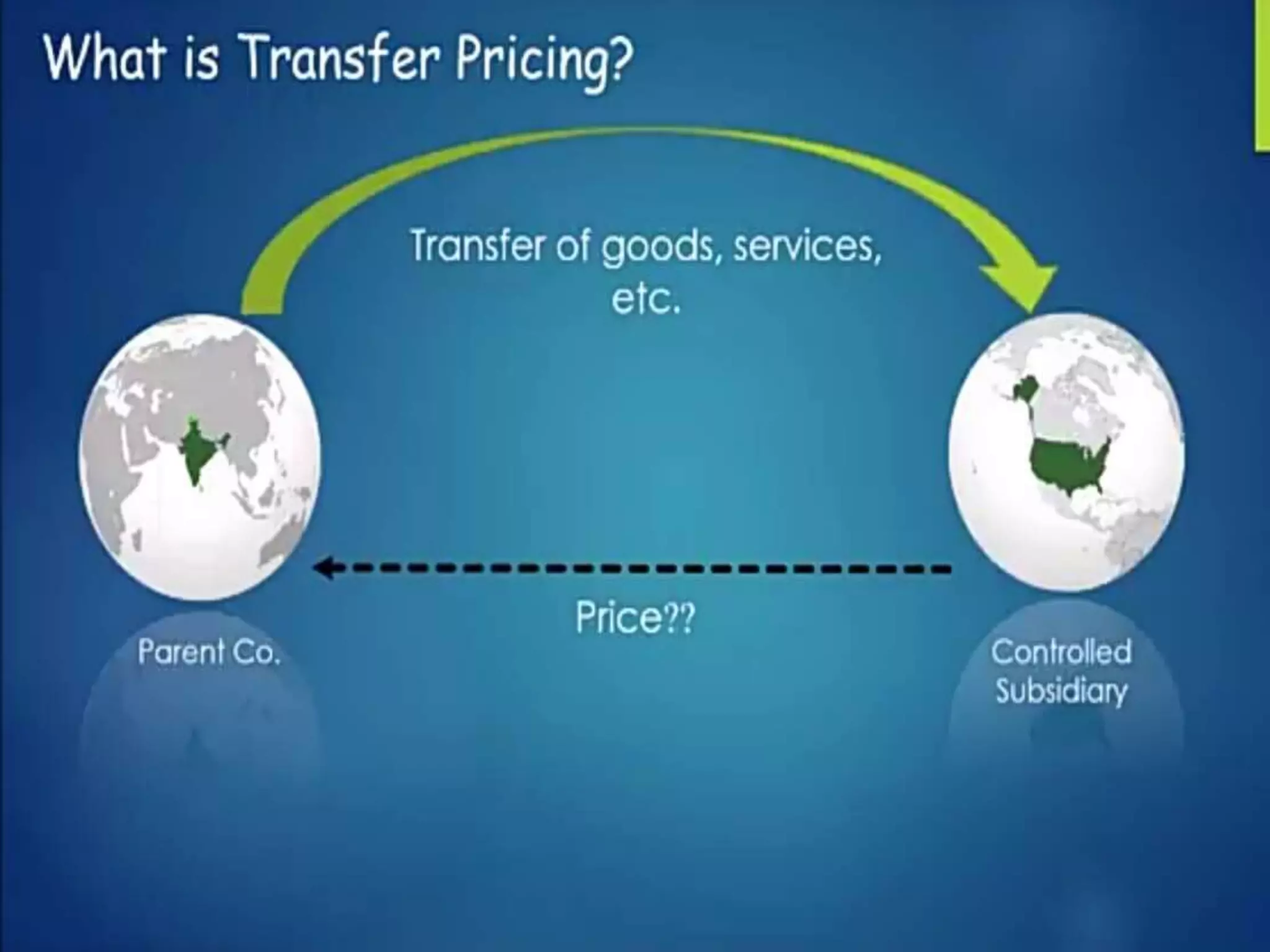
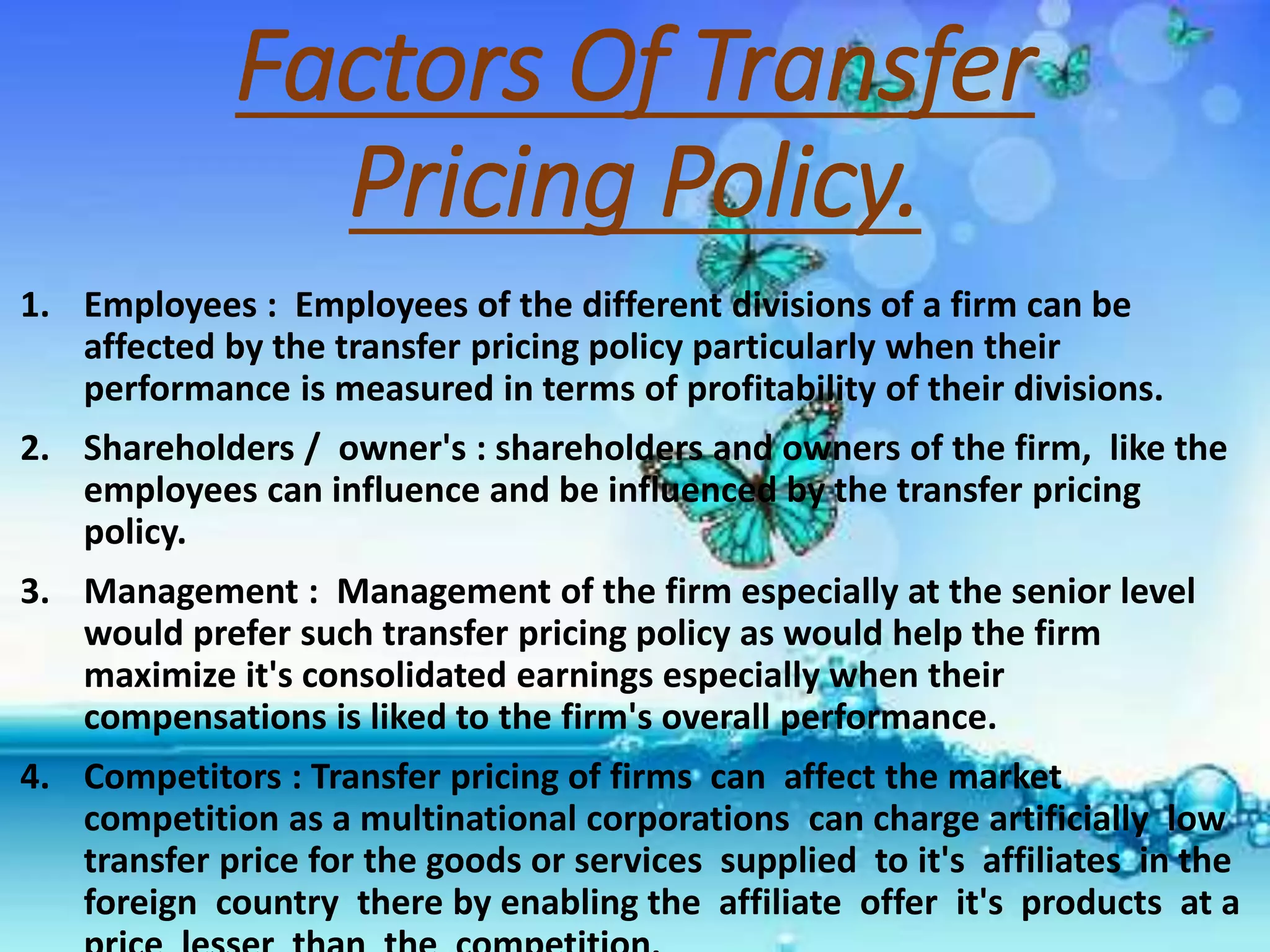
There are several methods for setting transfer prices between divisions of a company: cost-based transfer pricing uses costs of production; market-based transfer pricing uses market prices; and negotiated transfer pricing involves negotiation between divisions. Transfer pricing policies can affect employees, shareholders, management, and competitors by impacting divisional profits and market competition. The transfer price is an accounting expense and revenue used between divisions without cash flow changing hands.