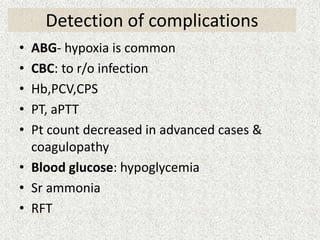
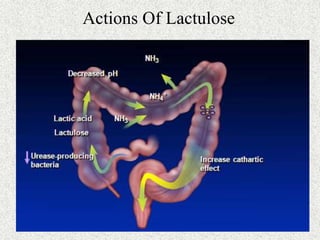
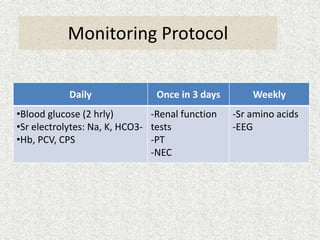
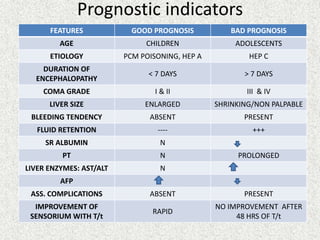
This document provides an overview of hepatic encephalopathy. It defines hepatic encephalopathy as a complex metabolic disorder seen in patients with liver dysfunction, characterized by disturbances in consciousness and behavior. It discusses the pathogenesis, including the ammonia and false neurotransmitter hypotheses. Precipitating factors and clinical manifestations ranging from mild cognitive changes to coma are described. Diagnosis involves ruling out other causes and elevated ammonia levels. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia through dietary changes, lactulose, antibiotics, and other supportive measures. Prognosis depends on the severity and underlying liver disease.