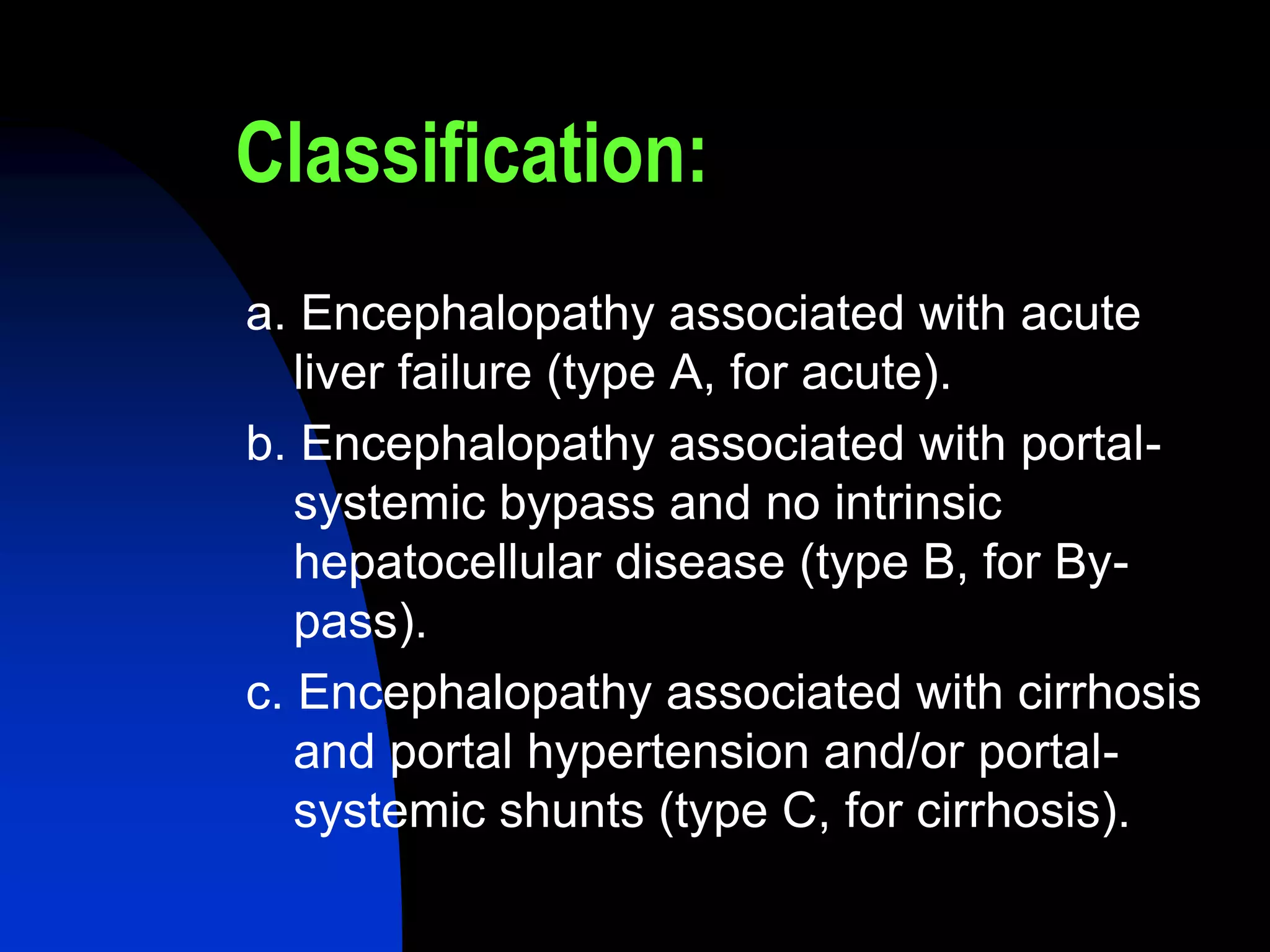
This document discusses hepatic encephalopathy, which is a potentially reversible disturbance in brain function caused by liver disease or portal-systemic shunting. It defines and classifies hepatic encephalopathy, discusses potential precipitating factors, describes methods of grading its severity including the West Haven criteria, and outlines treatment approaches including reducing nitrogenous toxins from the gut, improving extra-intestinal ammonia elimination, and counteracting abnormalities in central neurotransmission.