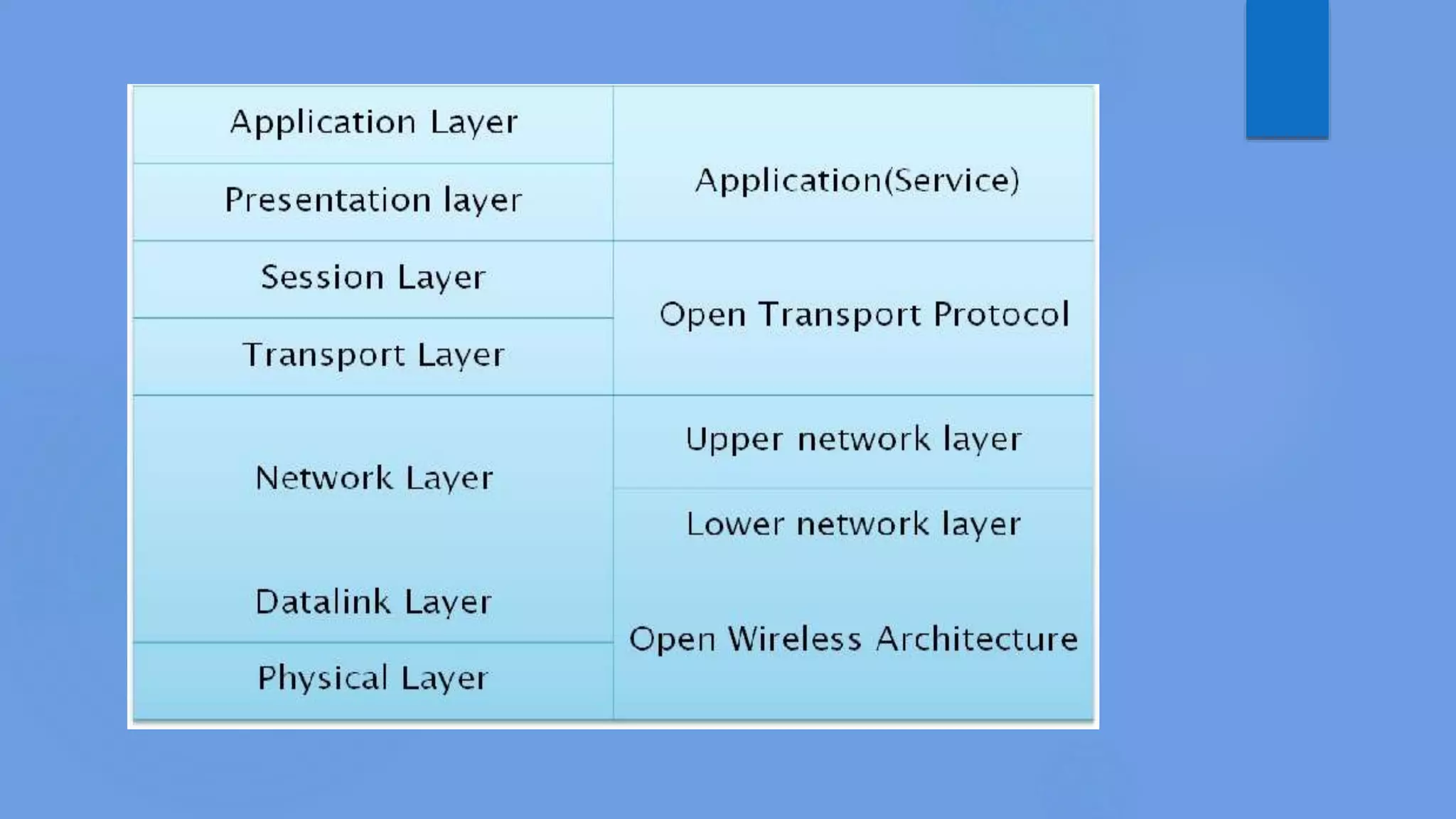
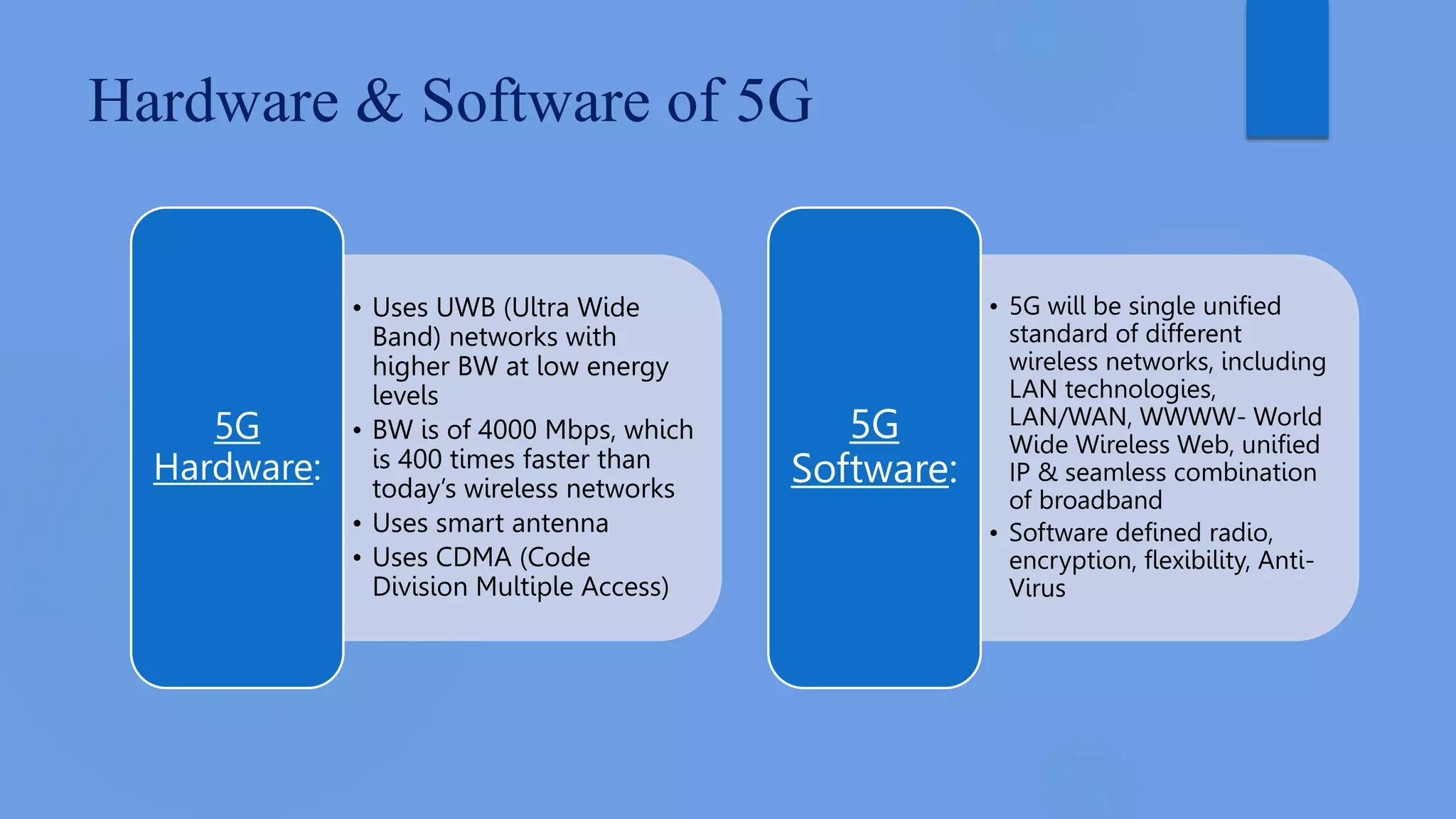
5G wireless technology will provide unprecedented wireless connectivity with speeds over 1 Gbps. It evolved from 1G analog cellular networks through 2G digital networks, 3G broadband networks, and 4G LTE networks. 5G will utilize new technologies like ultra-wideband, smart antennas, and software-defined networking to allow seamless connectivity between devices and access to dynamic information with applications in areas like wearable devices, media streaming, and smart homes. The open architecture of 5G is designed to be globally accessible at high speeds yet low cost to create a true wireless world with no connectivity limitations.