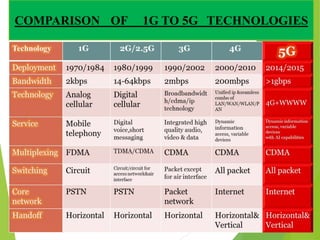
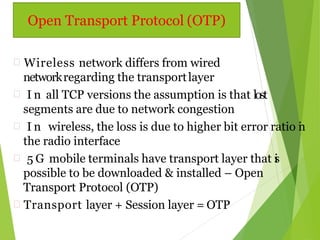
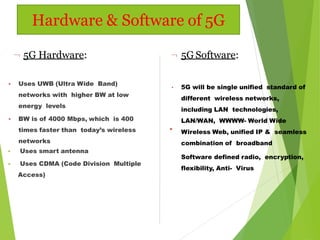
5G technology will offer speeds 10 times faster than 4G networks, providing up to 1 Gbps connectivity. It will feature widespread availability, ultra-low latency, and support for new applications through its unified global standard. 5G aims to enable a true wireless world with no limitations on access or location through technologies like smart antennas, software-defined networking, and virtualized infrastructure.