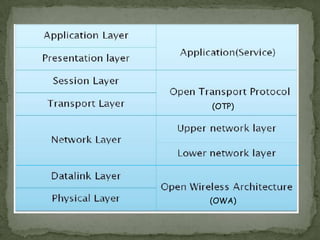
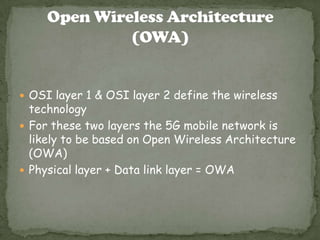
The document discusses the evolution of wireless technologies from 1G to 5G. It describes the key concepts, architecture, hardware and software components of 5G. 5G is expected to offer speeds up to 1 Gbps, lower latency, and better reliability than previous generations. It will allow simultaneous connectivity through multiple access technologies and provide intelligent quality of service management across networks. The document outlines some potential applications of 5G such as wearable devices with artificial intelligence capabilities and pervasive global connectivity.