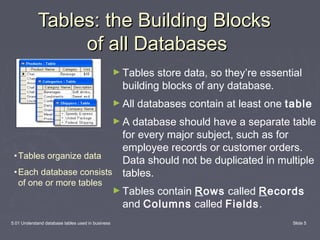
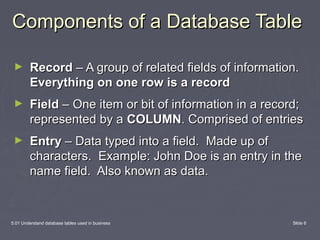
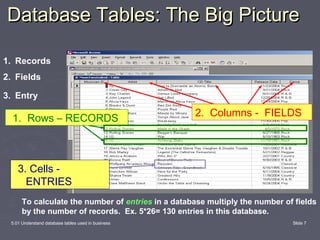
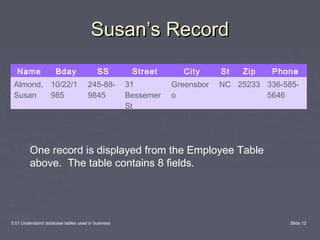
This document discusses database tables and their use in business. It defines a database as a tool for organizing, storing, retrieving, and communicating groups of similar information. Databases consist of tables, queries, forms, and reports. Tables are the essential building blocks of any database as they store the data in rows and columns. Each database contains at least one table to hold the different subjects of data, with each major subject stored in its own table to avoid duplication. The document provides examples of business databases and defines the components of a database table, including records, fields, and entries.