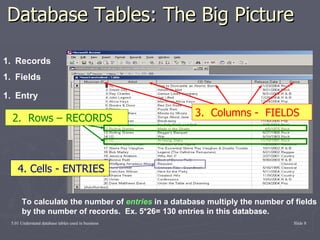
The document discusses database tables which are used by businesses to organize and store data. It defines what a database is and provides examples of common databases. It explains that tables are the basic building blocks of databases, with data stored in rows and columns. Each table contains records made up of related fields, with all the data in one row making up a single record.