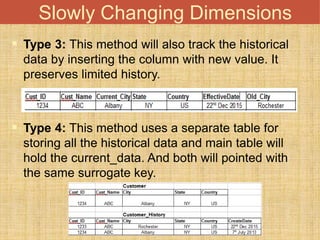
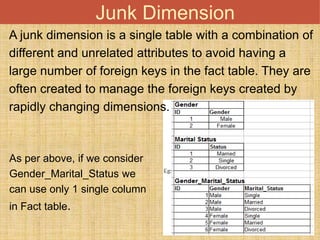
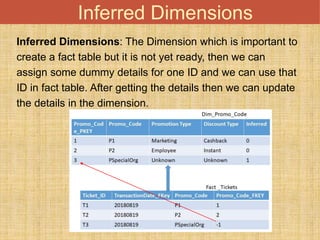
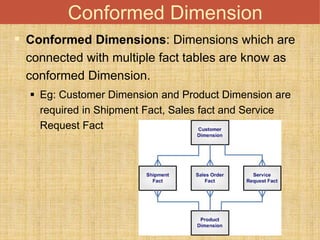
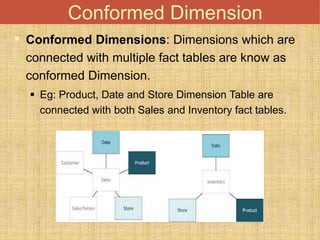
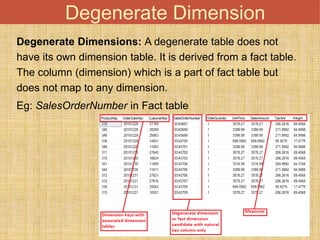
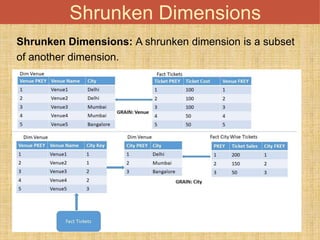
This document discusses different types of dimension tables commonly used in data warehouses. It describes slowly changing dimensions, rapidly changing dimensions, junk dimensions, inferred dimensions, conformed dimensions, degenerate dimensions, role playing dimensions, shrunken dimensions, and static dimensions. Dimension tables contain attributes and keys that provide context about measures in fact tables.