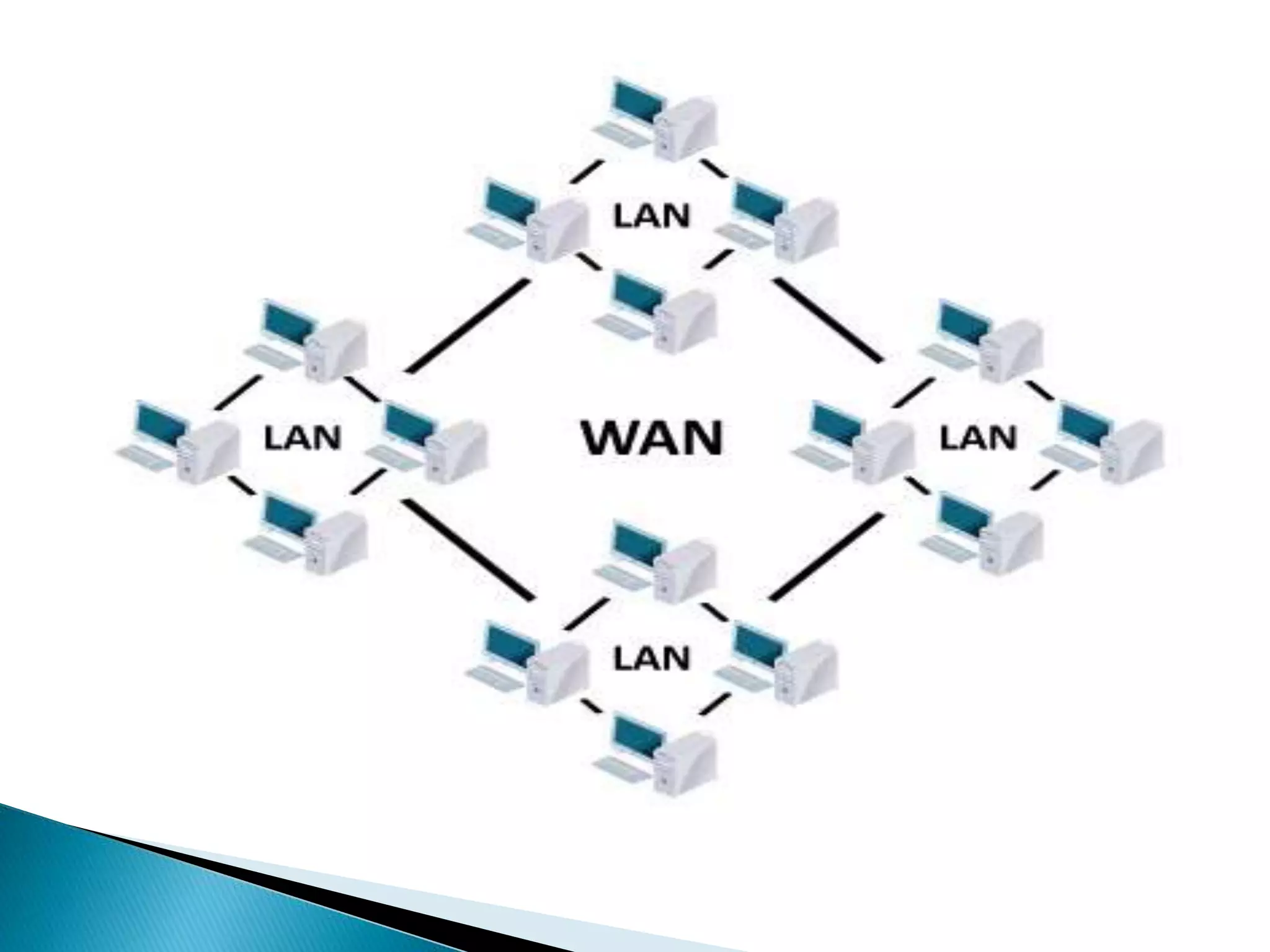
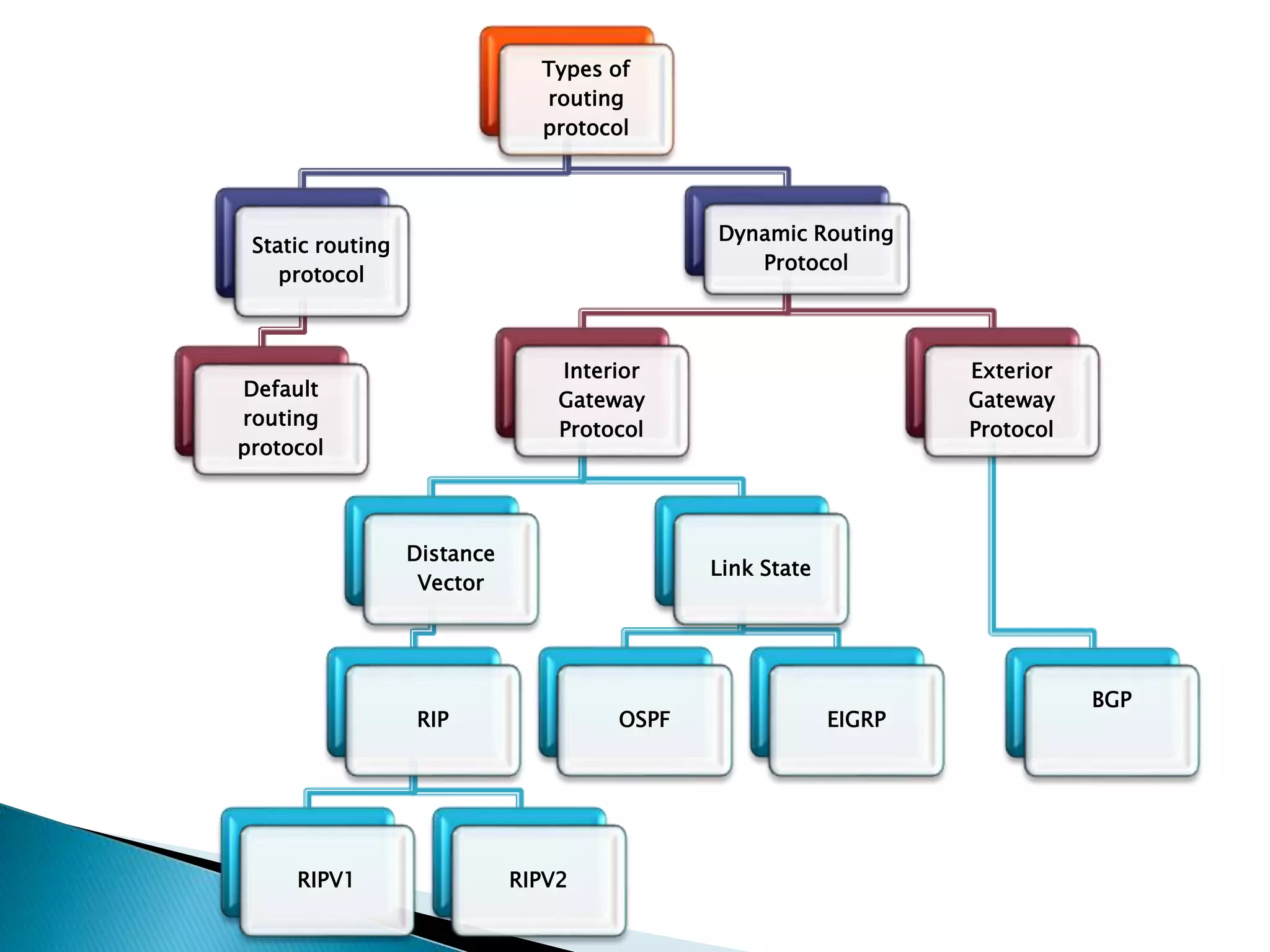
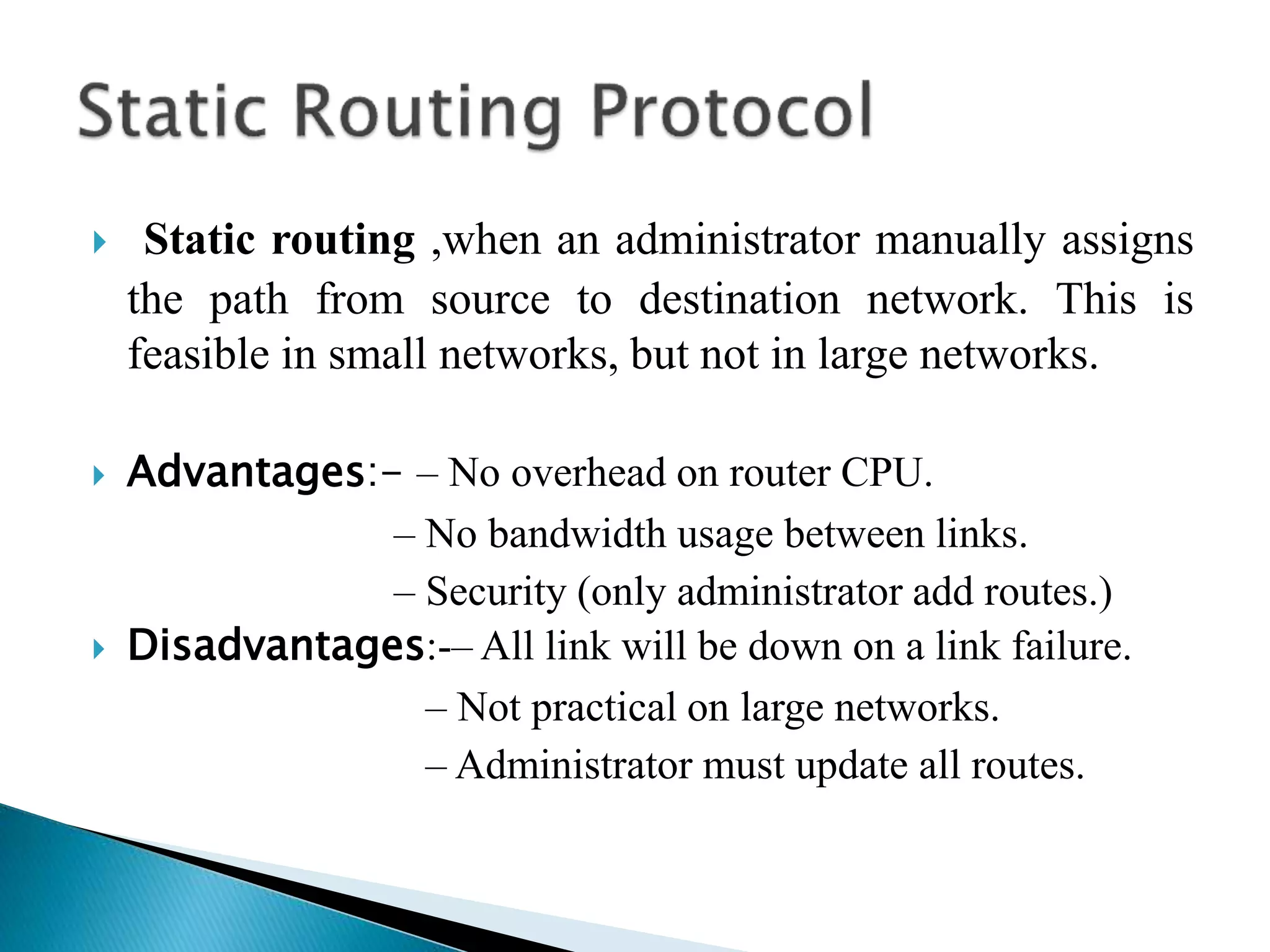
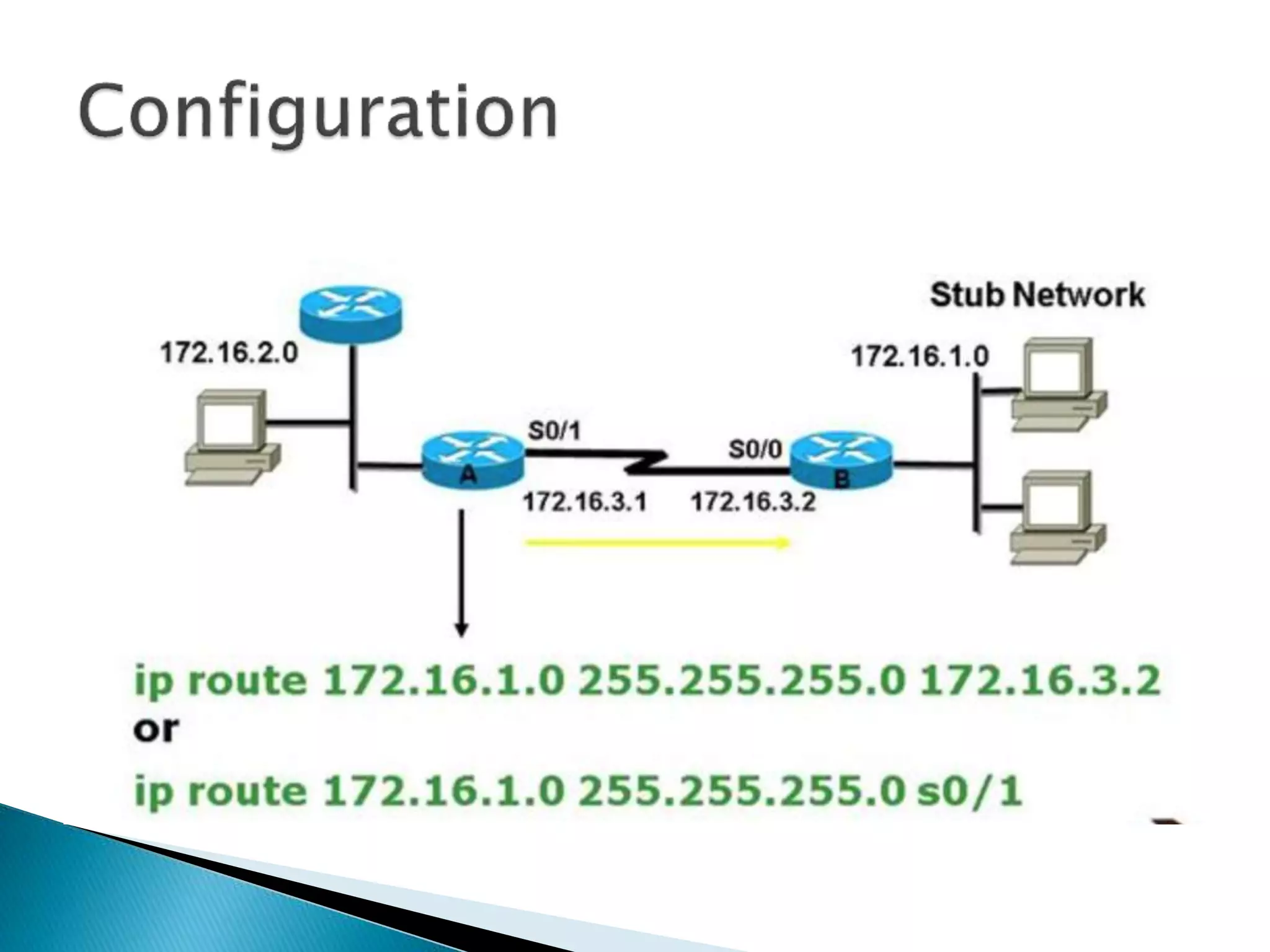
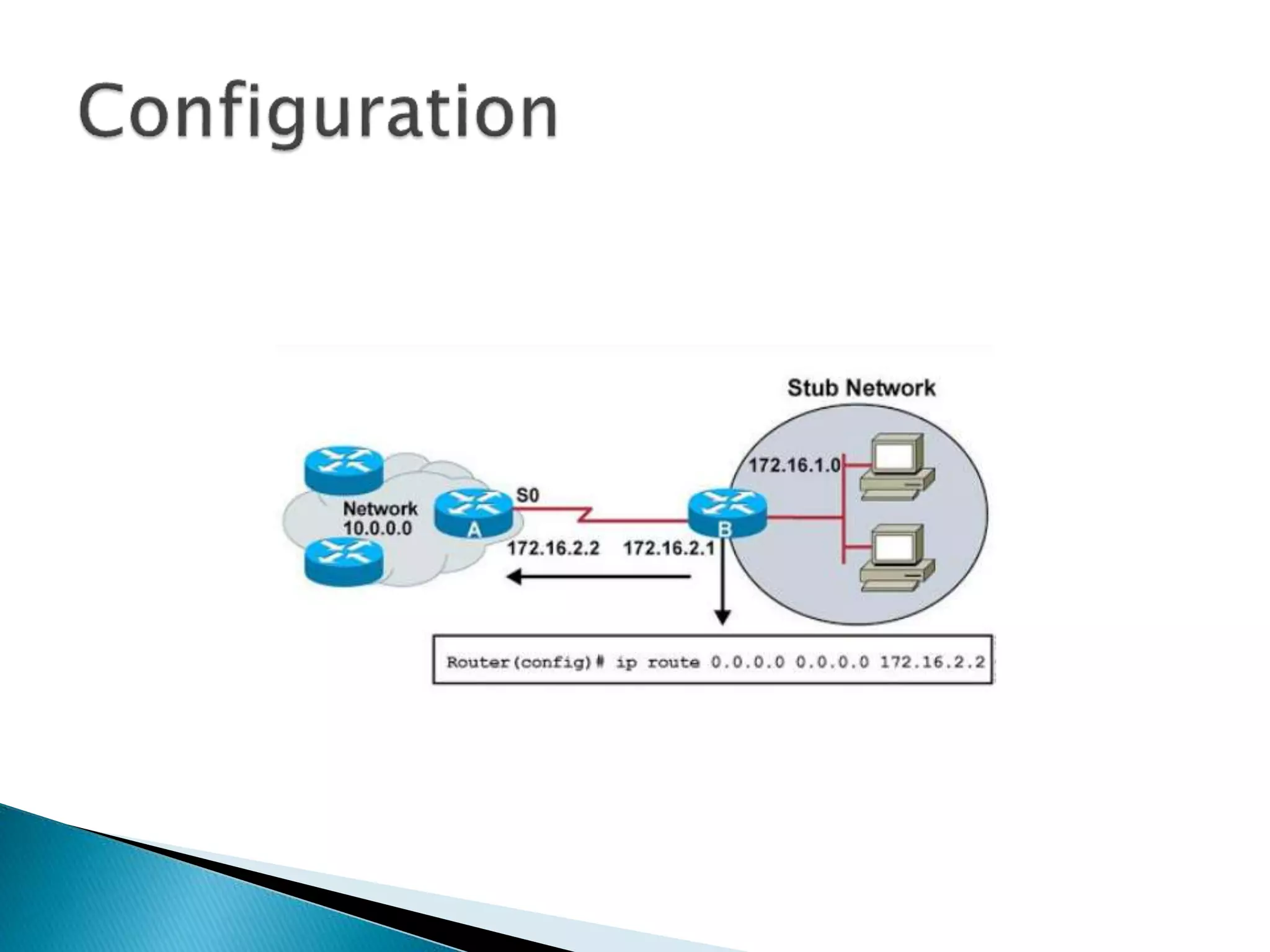
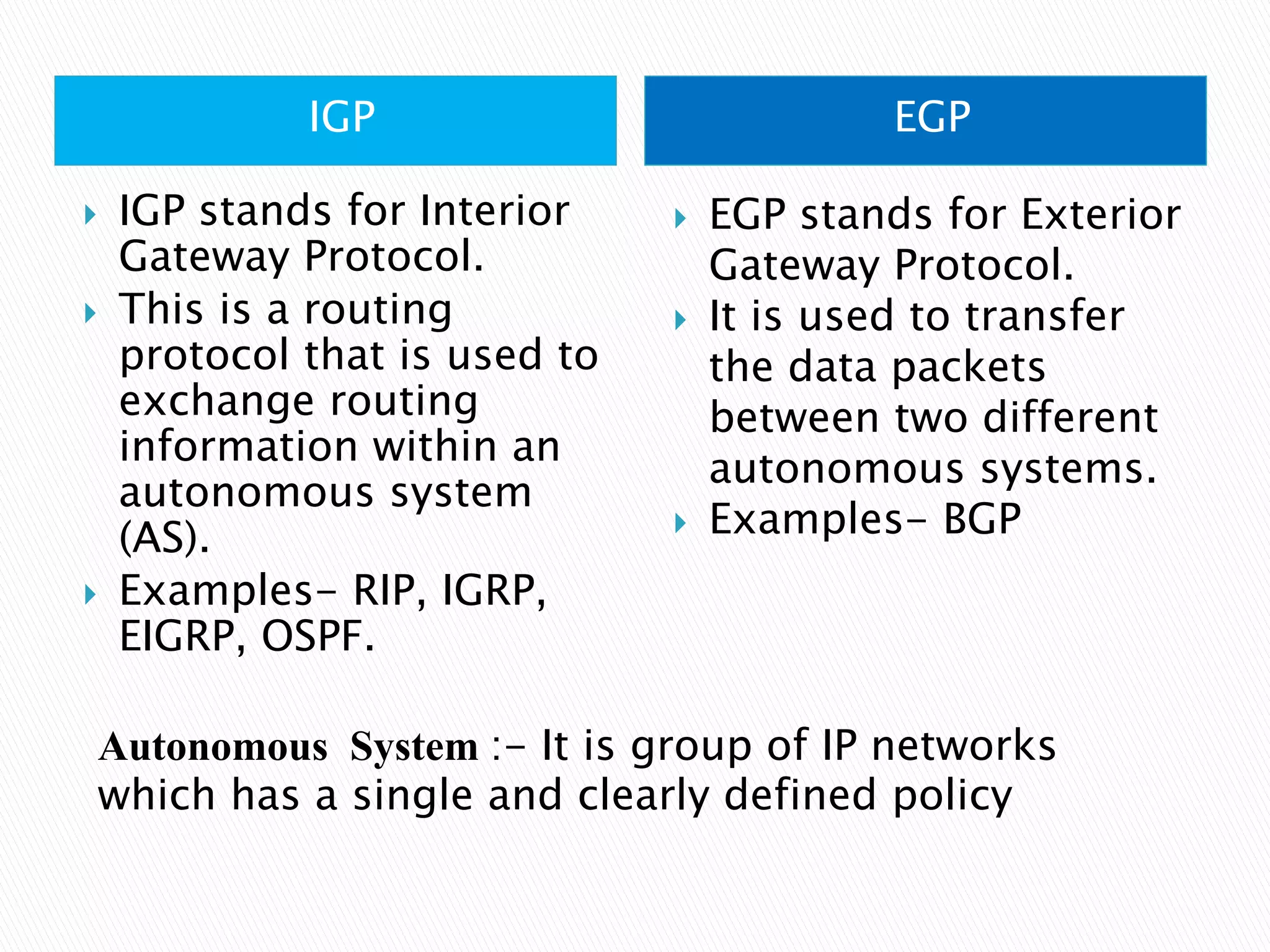
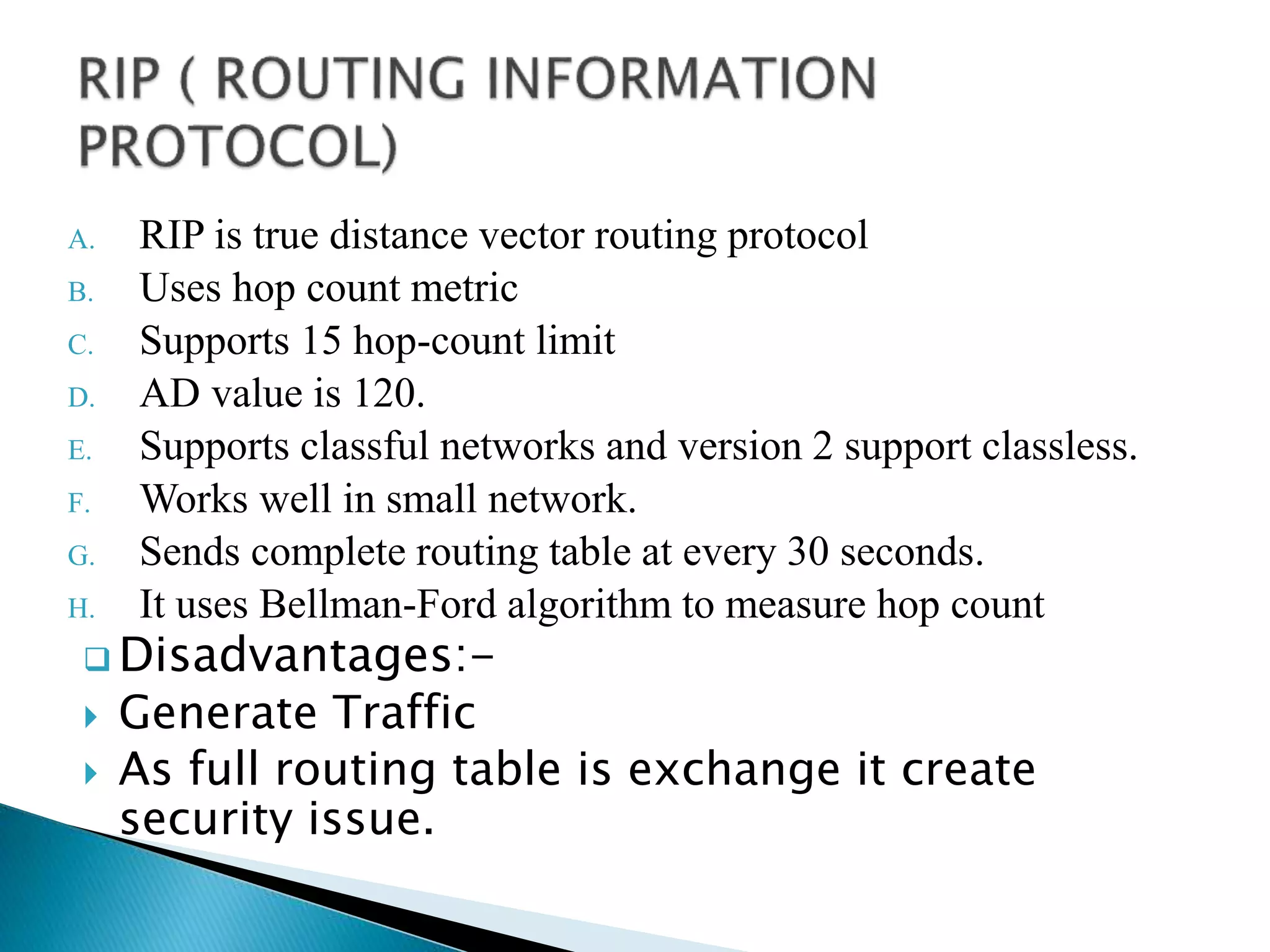
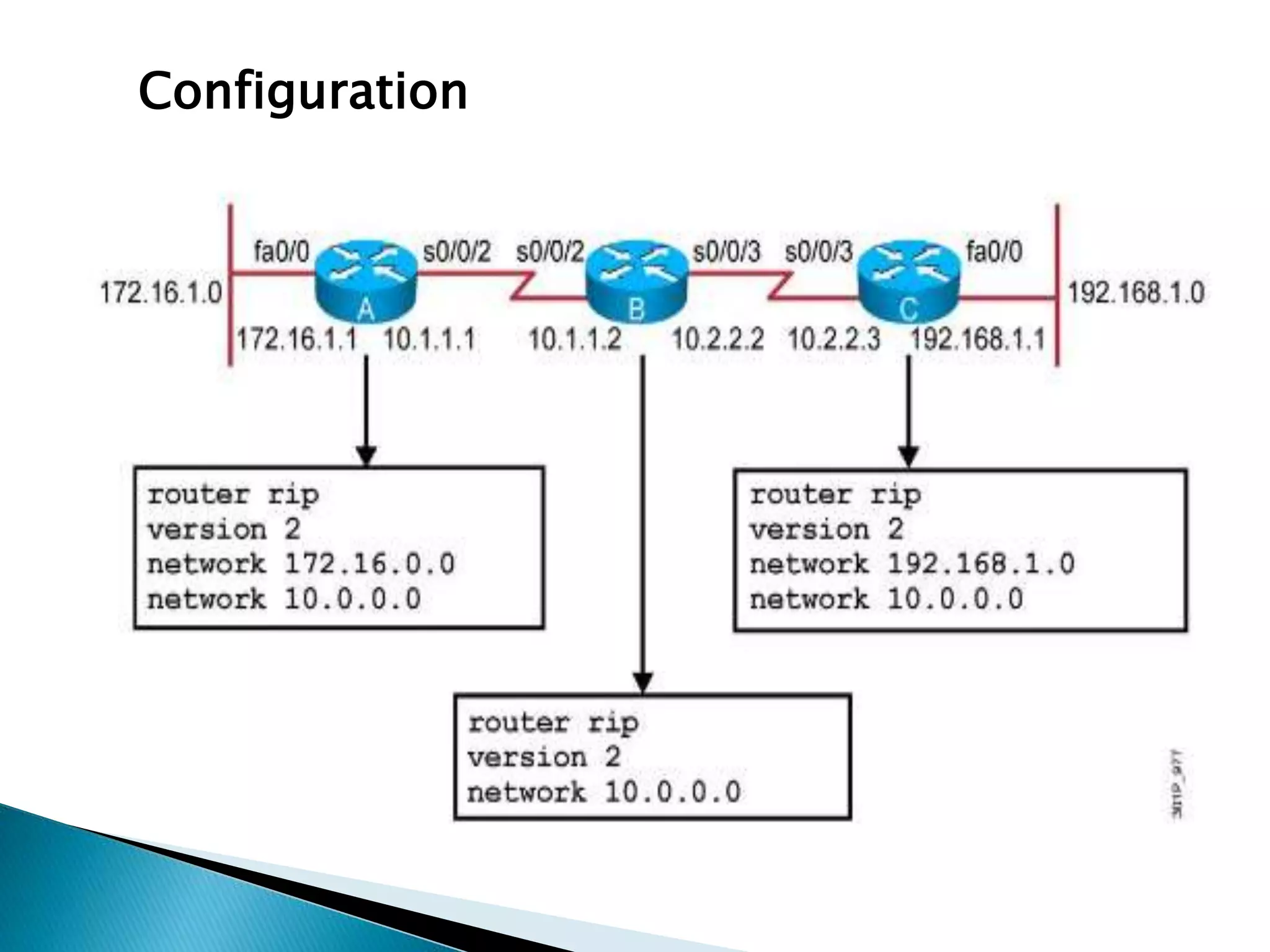
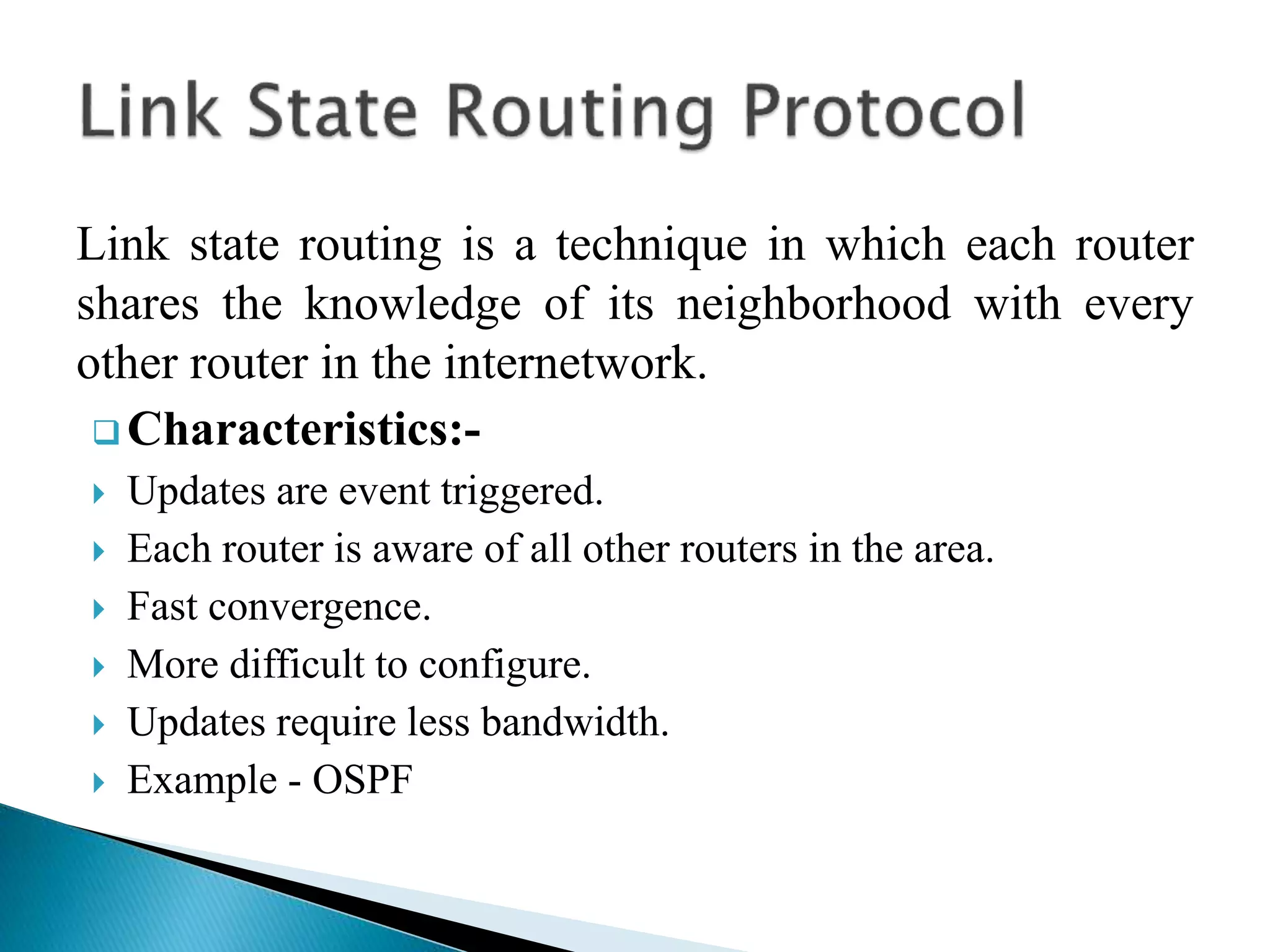
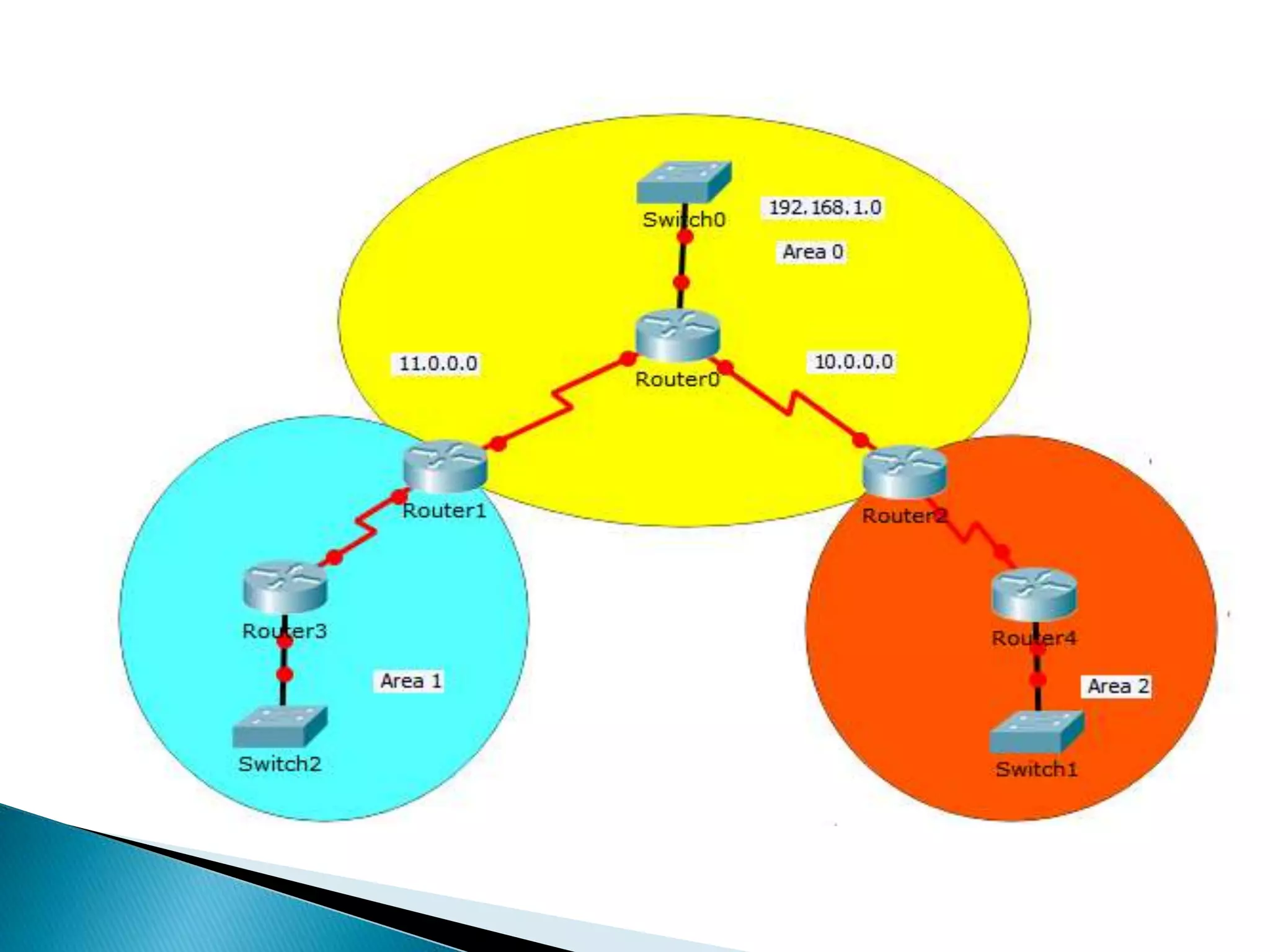
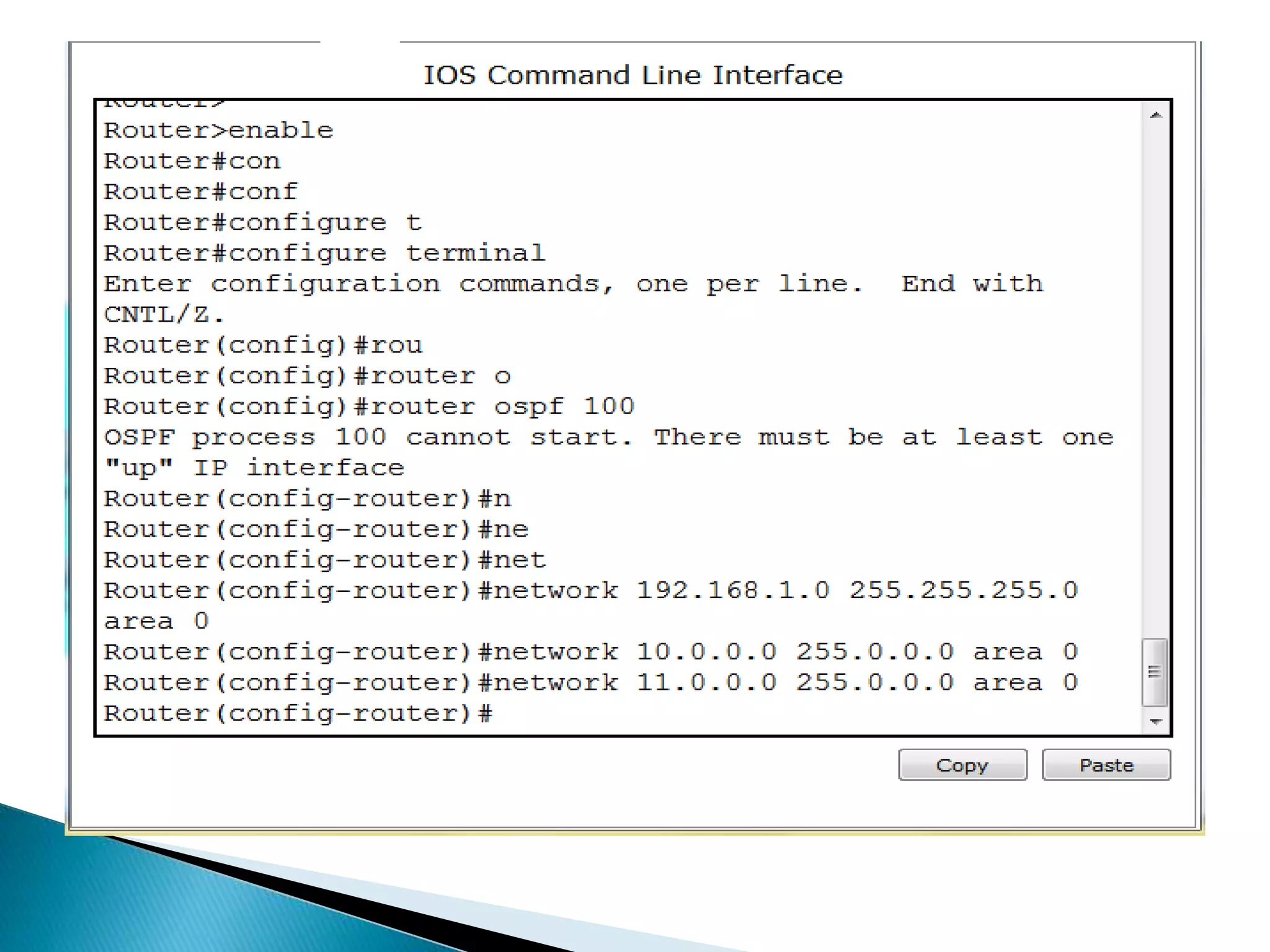
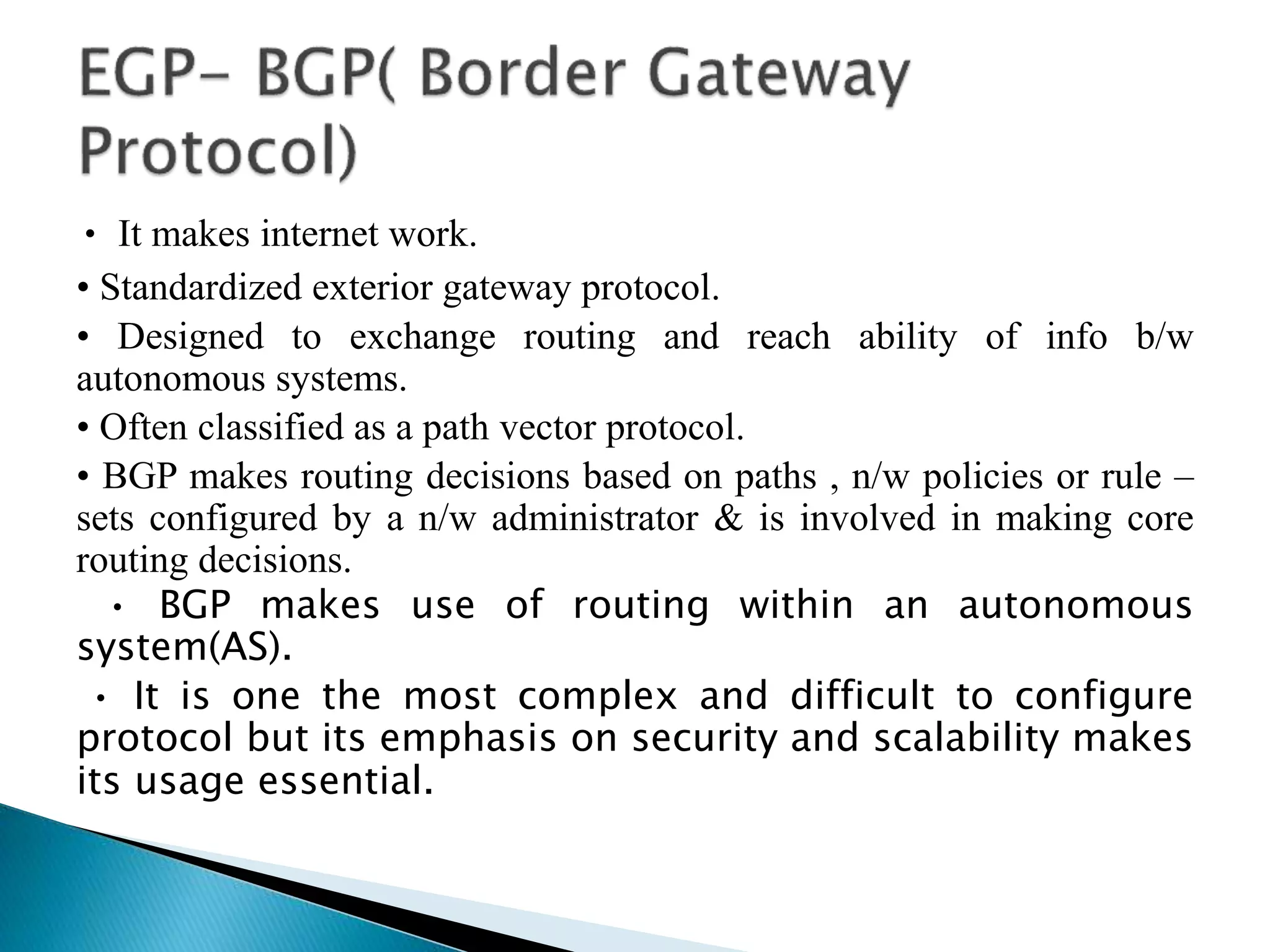
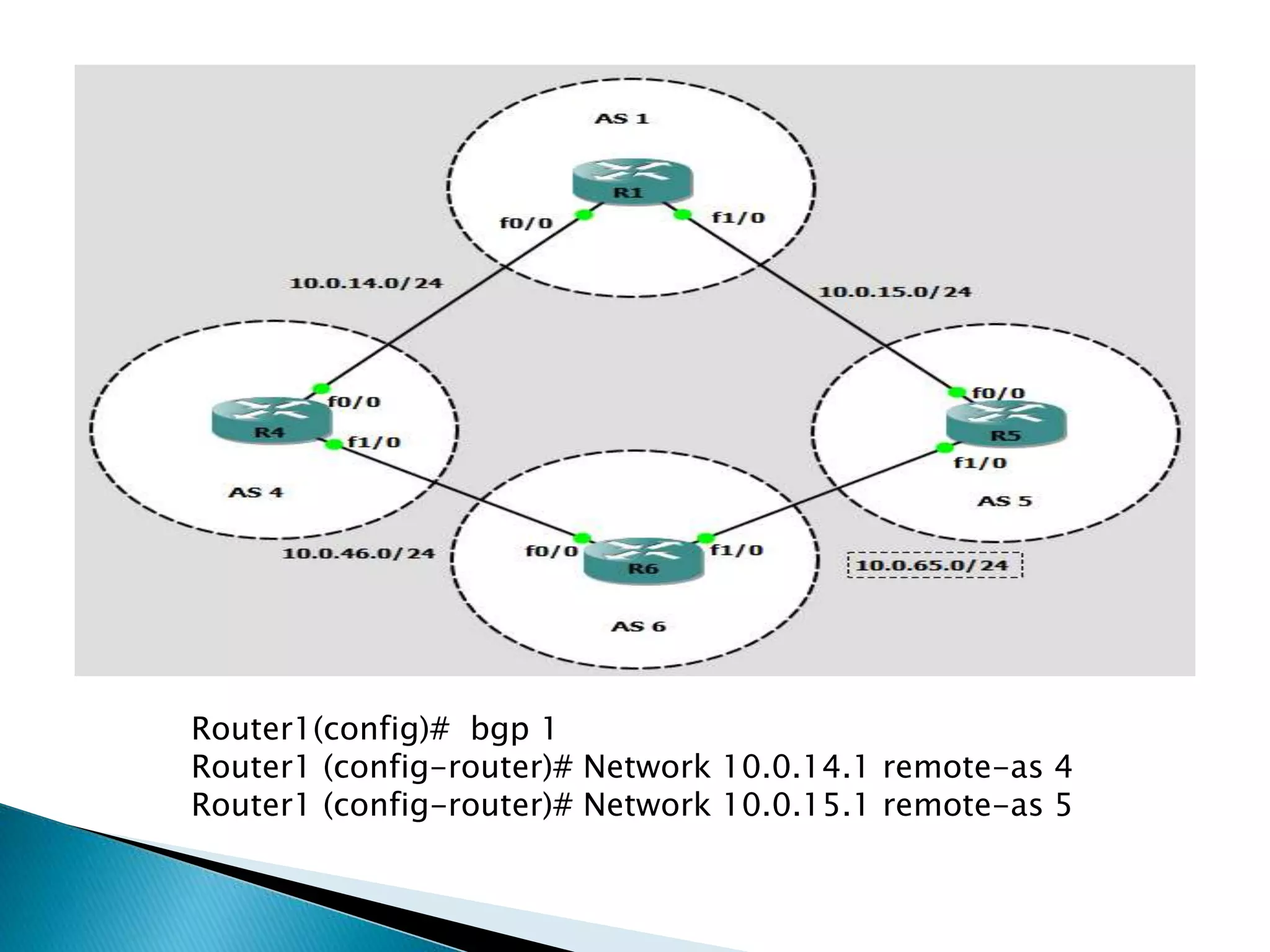
The document provides an overview of computer networks, IP addresses, and routing protocols, detailing the role of routers in forwarding data packets between networks. It explains different types of routing protocols, including static, dynamic, interior gateway protocols (IGP), and exterior gateway protocols (EGP), outlining their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it discusses specific protocols like RIP and OSPF, highlighting their characteristics, configuration details, and operational mechanisms.