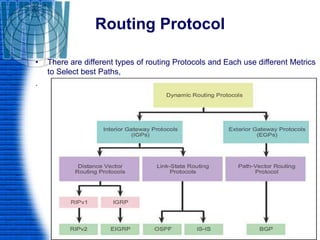
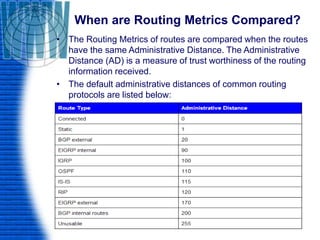
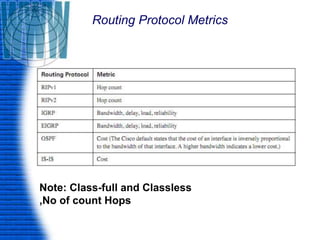
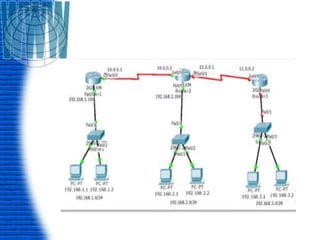
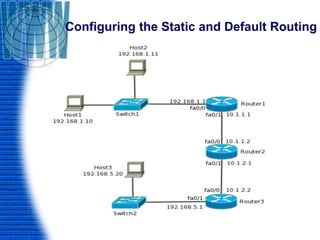
A router is a networking device that connects different networks and selects the best path to forward packets between them. It operates at the network layer and uses routing tables to determine the best path. Major router vendors include Cisco, Juniper, and Huawei. Routers have different types of ports including LAN ports to connect to local networks, WAN ports to connect between routers, and administrative ports for management. Routers also run an operating system like Cisco IOS to perform routing functions.



































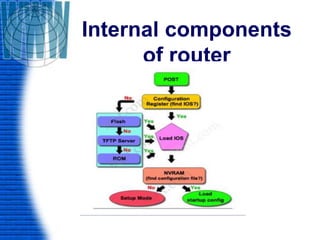
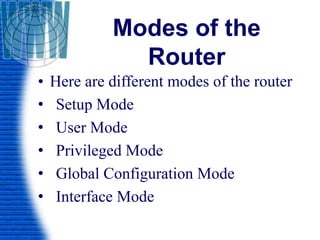
![• Setup Mode
• The router enters in to the setup mode if the
NVRAM is empty.
Continue with configuration dialog[yes/no]
Answer with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.
• User Mode
• Only some basic monitoring
• Limited show commands ping, trace,
• Router>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routerandrouting-150105121120-conversion-gate01/85/Router-and-routing-38-320.jpg)


![Basic Commands
• Setup Mode
• Continue with configuration
dialog?[Yes/No]
• Answer ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.
• User Mode
• Router>
• Router>enable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routerandrouting-150105121120-conversion-gate01/85/Router-and-routing-41-320.jpg)