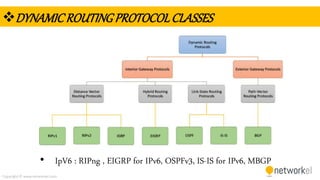
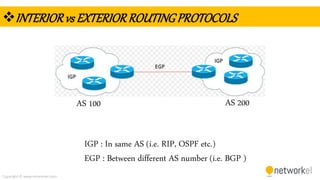
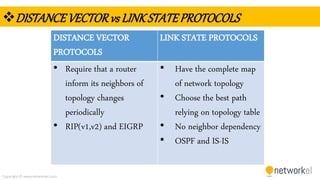
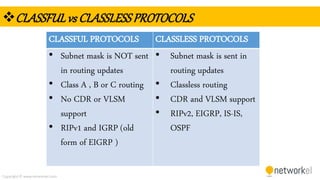
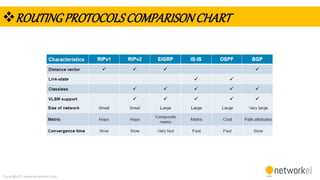
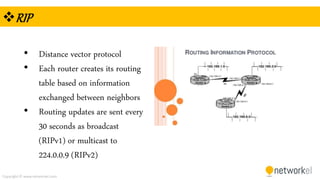
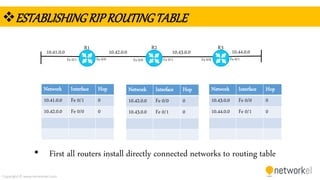
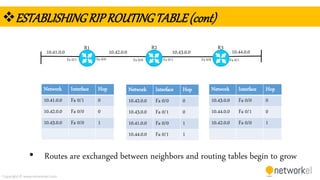
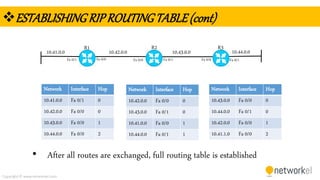
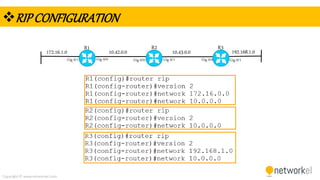
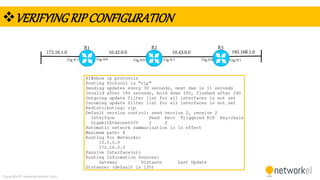
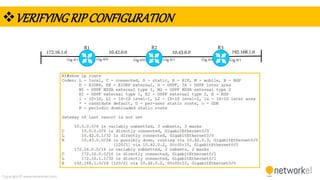
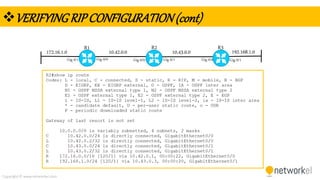
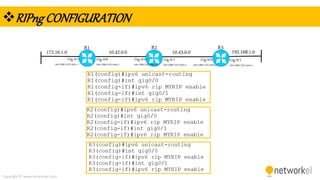
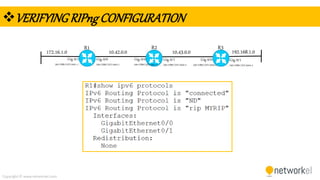
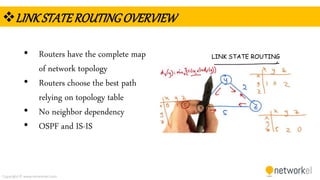
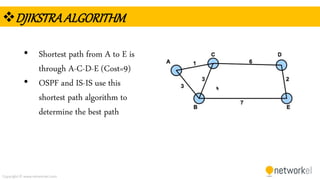
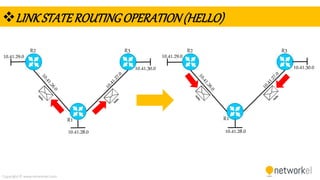
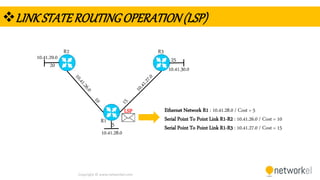
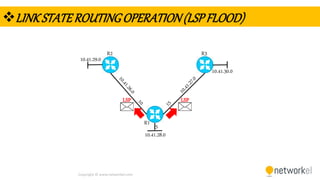
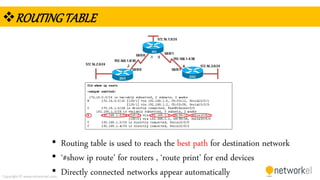
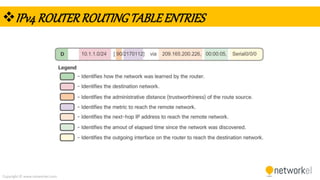
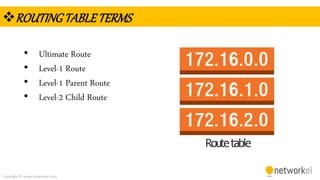
The document provides a comprehensive overview of dynamic routing protocols, contrasting static and dynamic routing, and detailing protocols such as RIP, RIPng, and OSPF. It highlights the mechanisms of distance vector and link state protocols, their configurations, and the processes involved in establishing routing tables. The document also discusses the metrics and algorithms used for determining the best routing paths, along with the significance of routing tables in network management.