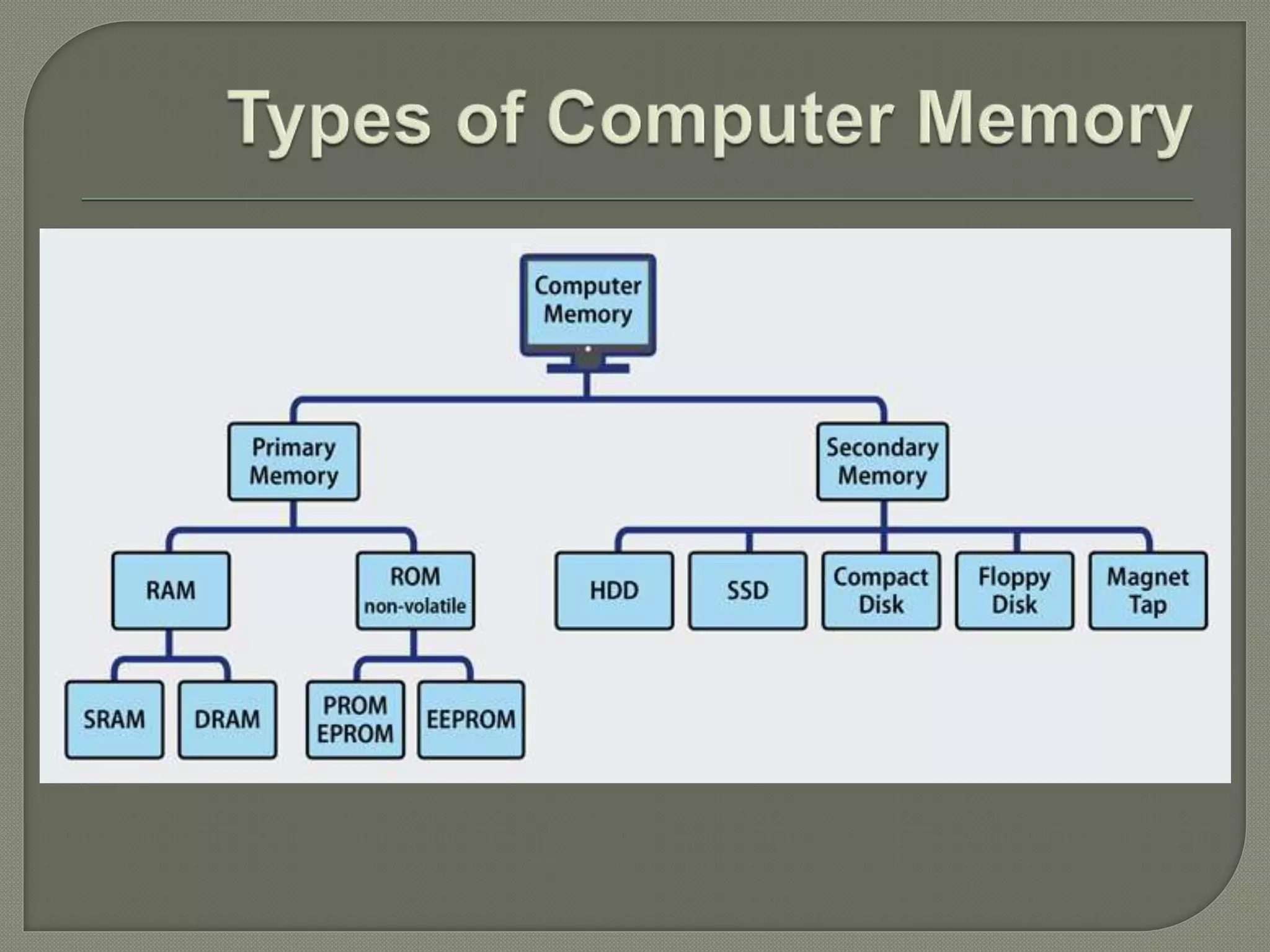
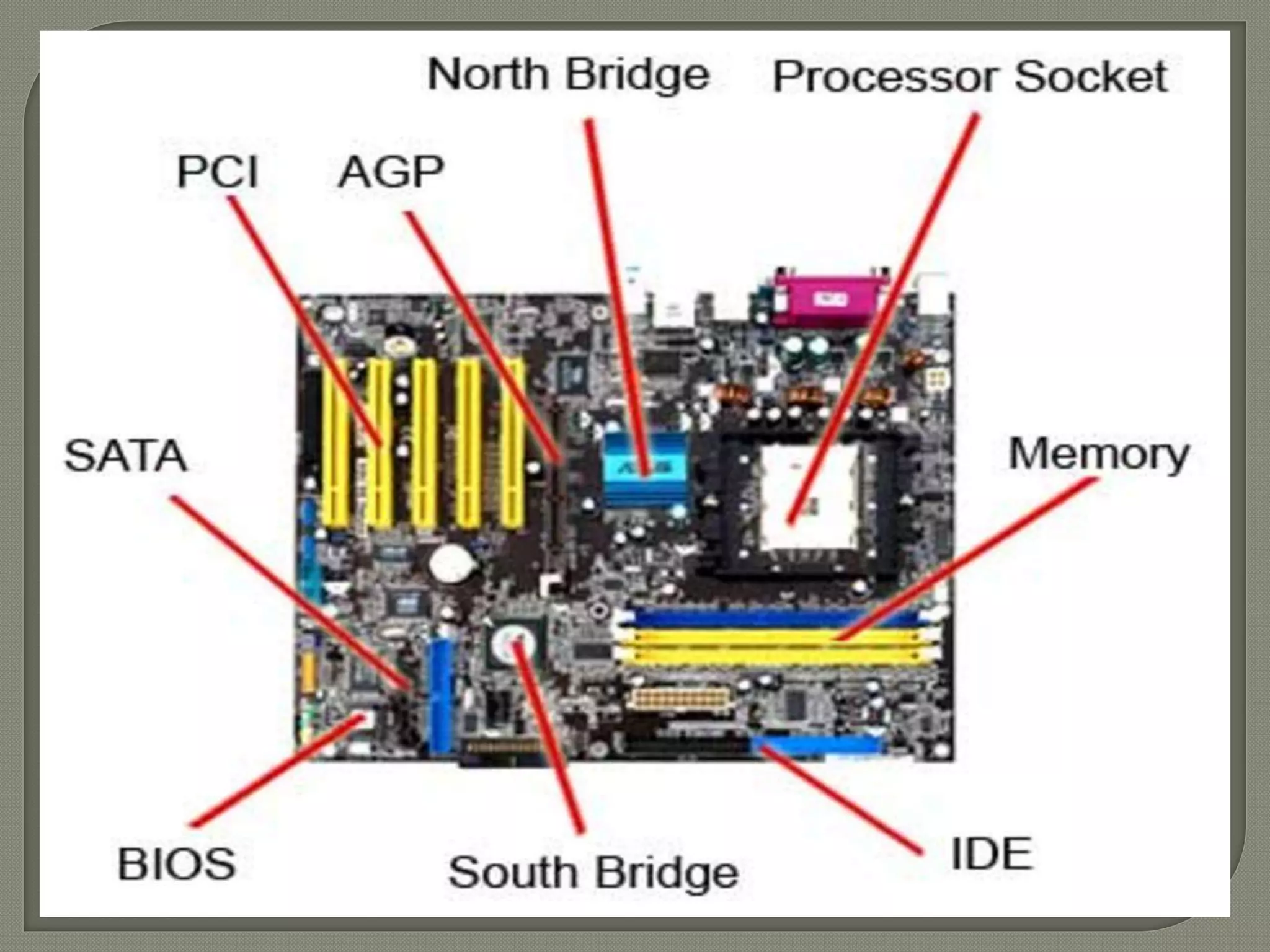
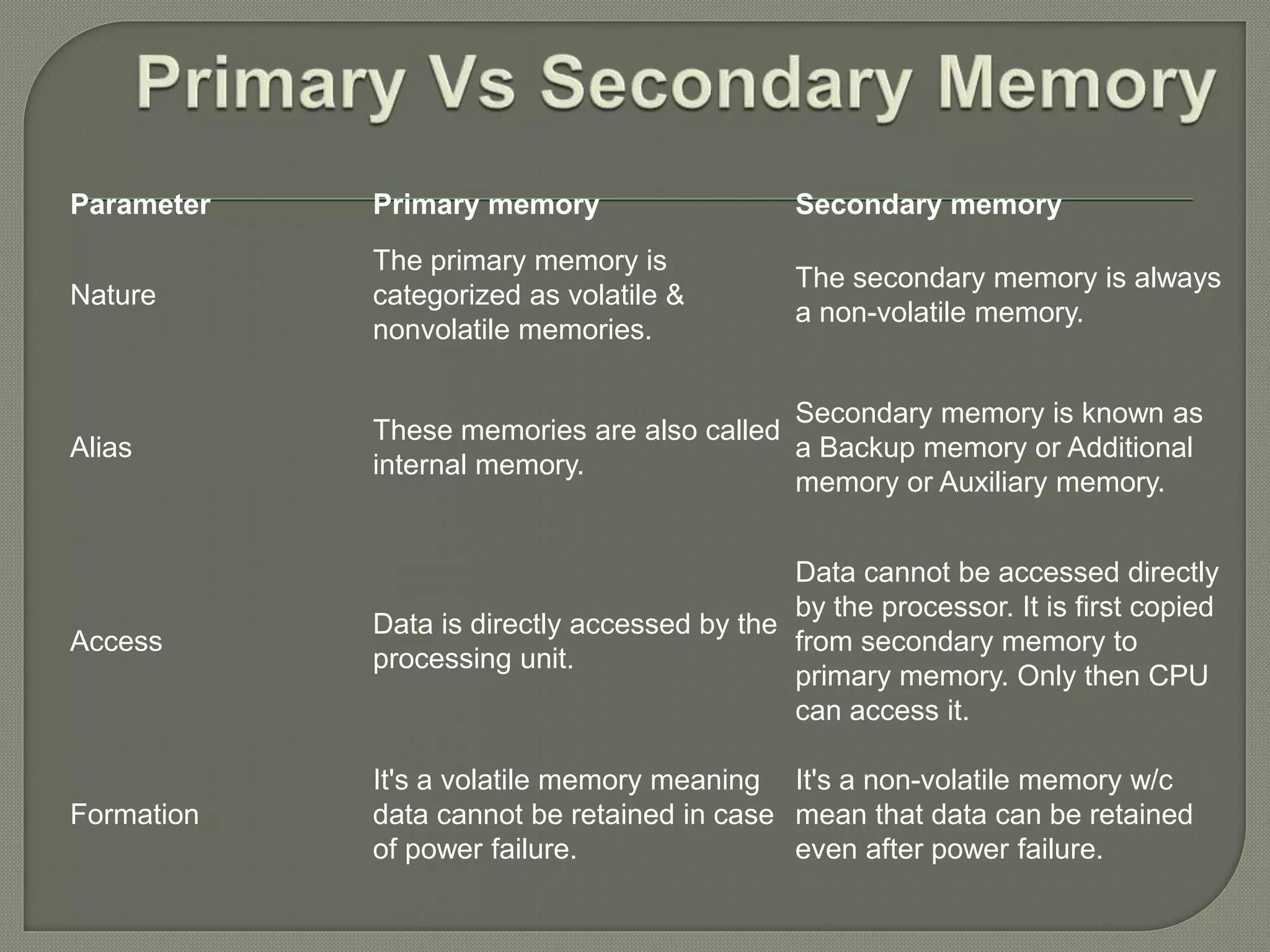
Computer memory temporarily stores data and instructions for processing by the CPU. Primary memory (RAM and ROM) allows direct CPU access but loses data when powered off, while secondary memory (hard disks, USB drives, etc.) permanently stores data but requires copying to primary memory for CPU access. Primary memory is volatile and internal, while secondary memory is non-volatile and external. Together they provide data storage and retrieval capabilities essential for computer functioning.