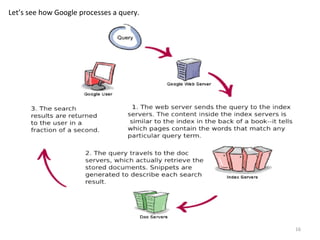
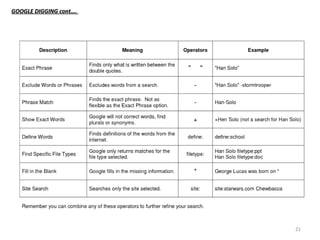
The document discusses the inner workings of the Google search engine. It begins with facts about Google's founding and history. It then explains the basic components of how any search engine works, including web crawlers that index pages, and how keywords are matched to search results. The bulk of the document focuses on Google's specific architecture, including its web crawler called Googlebot, its indexer that catalogs words in a database, and its query processor that matches searches to relevant pages based on factors like PageRank. It also discusses related topics like search engine optimization techniques and using "Google digging" to refine searches.