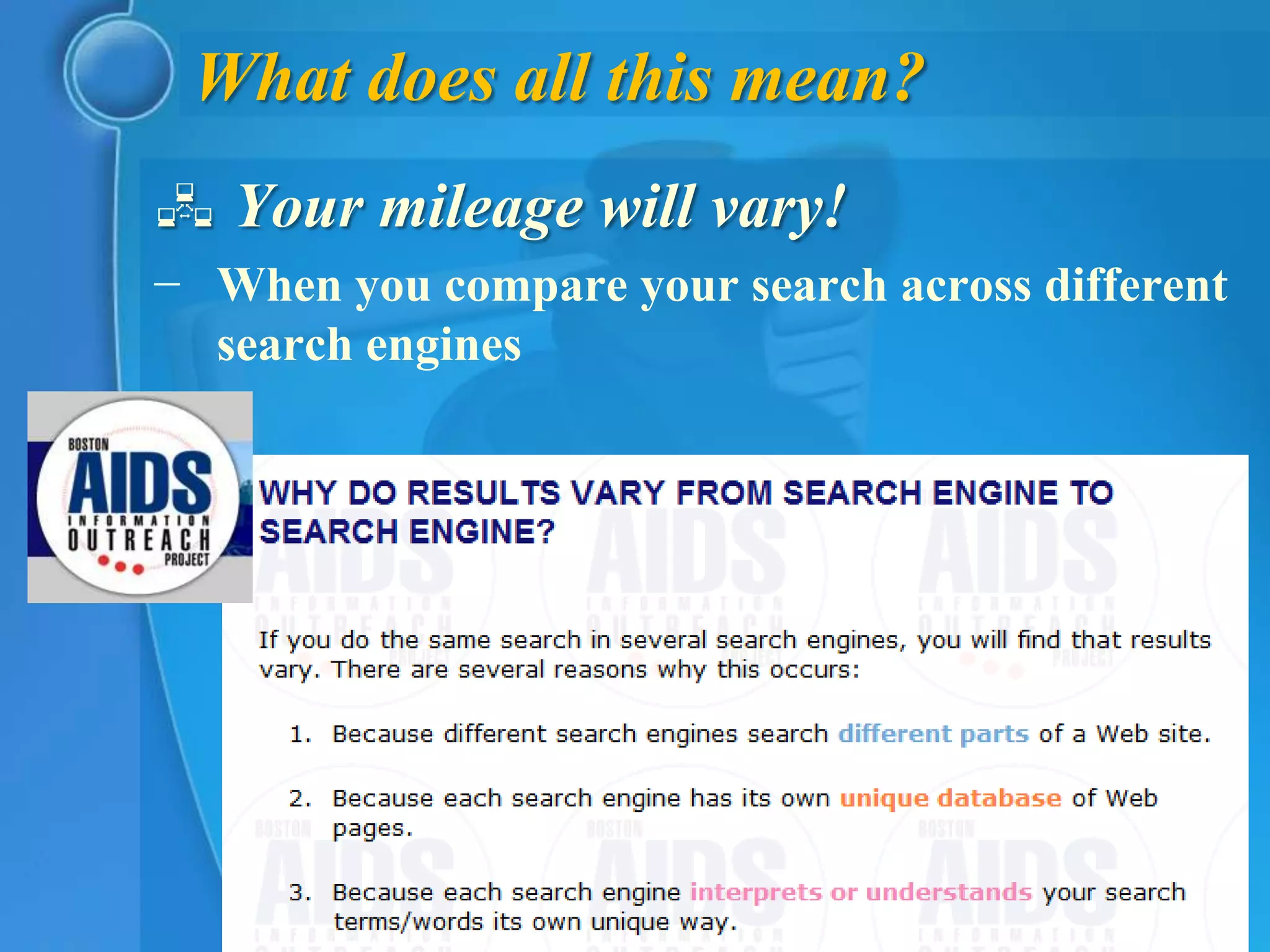
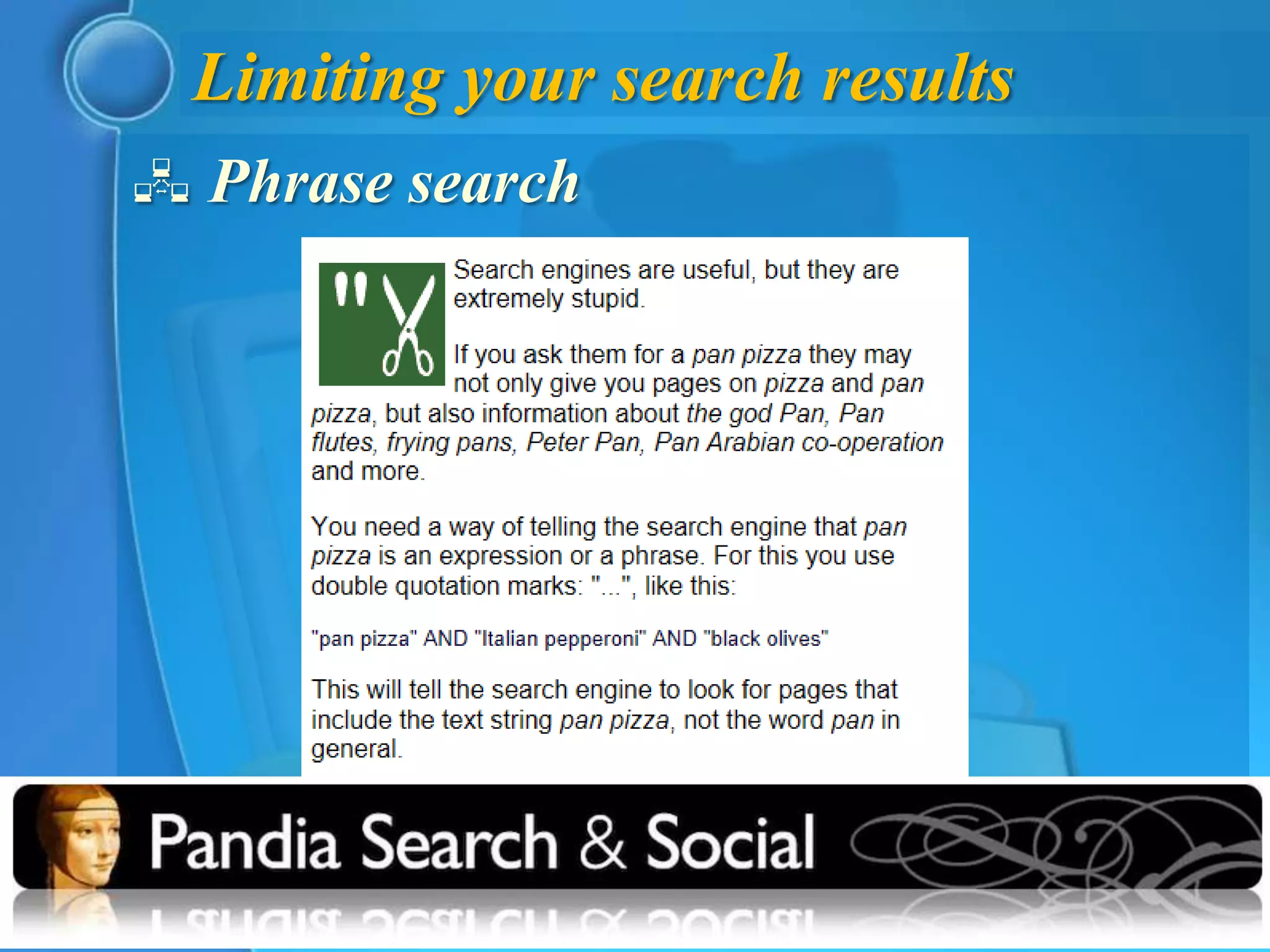
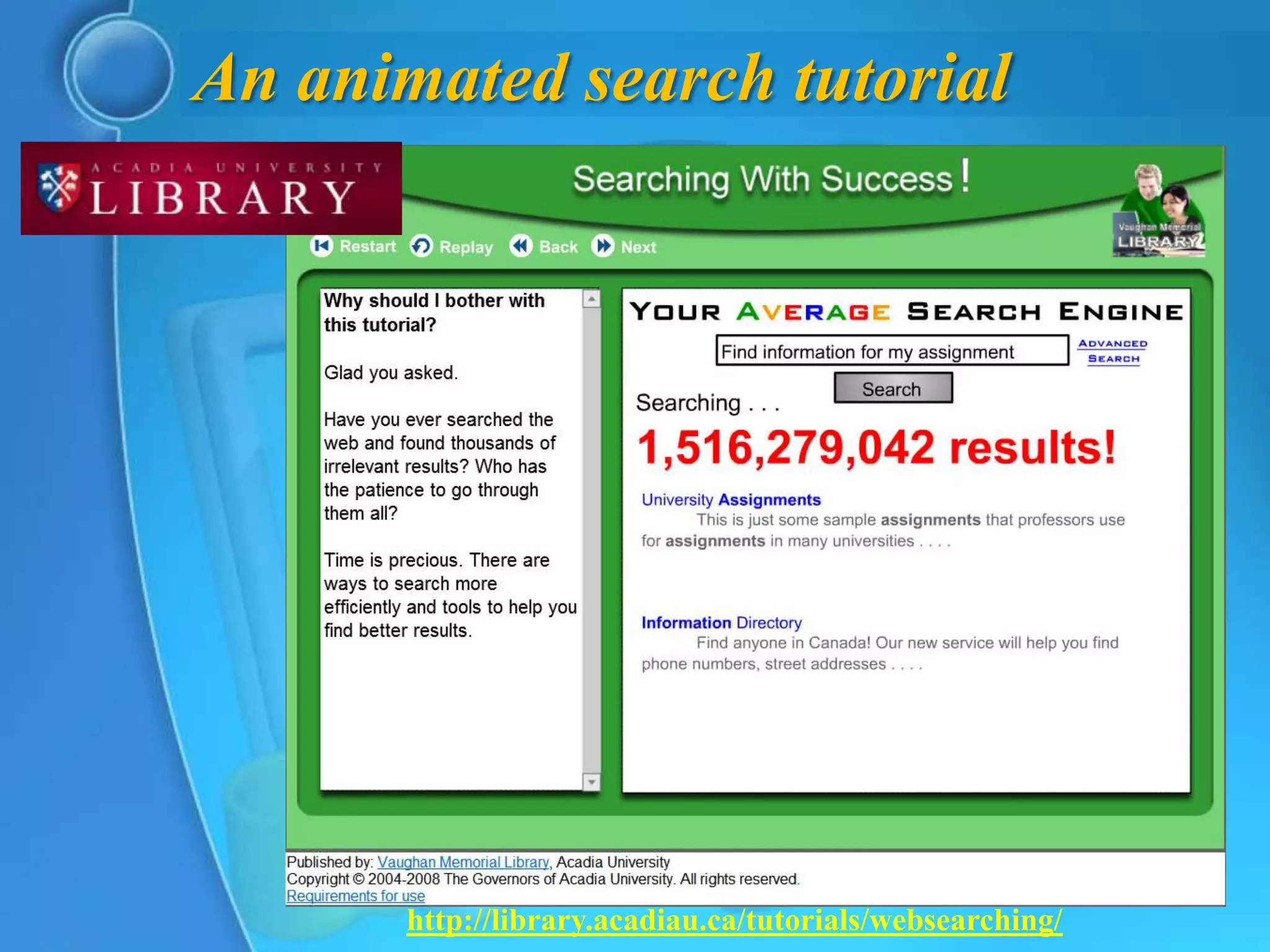
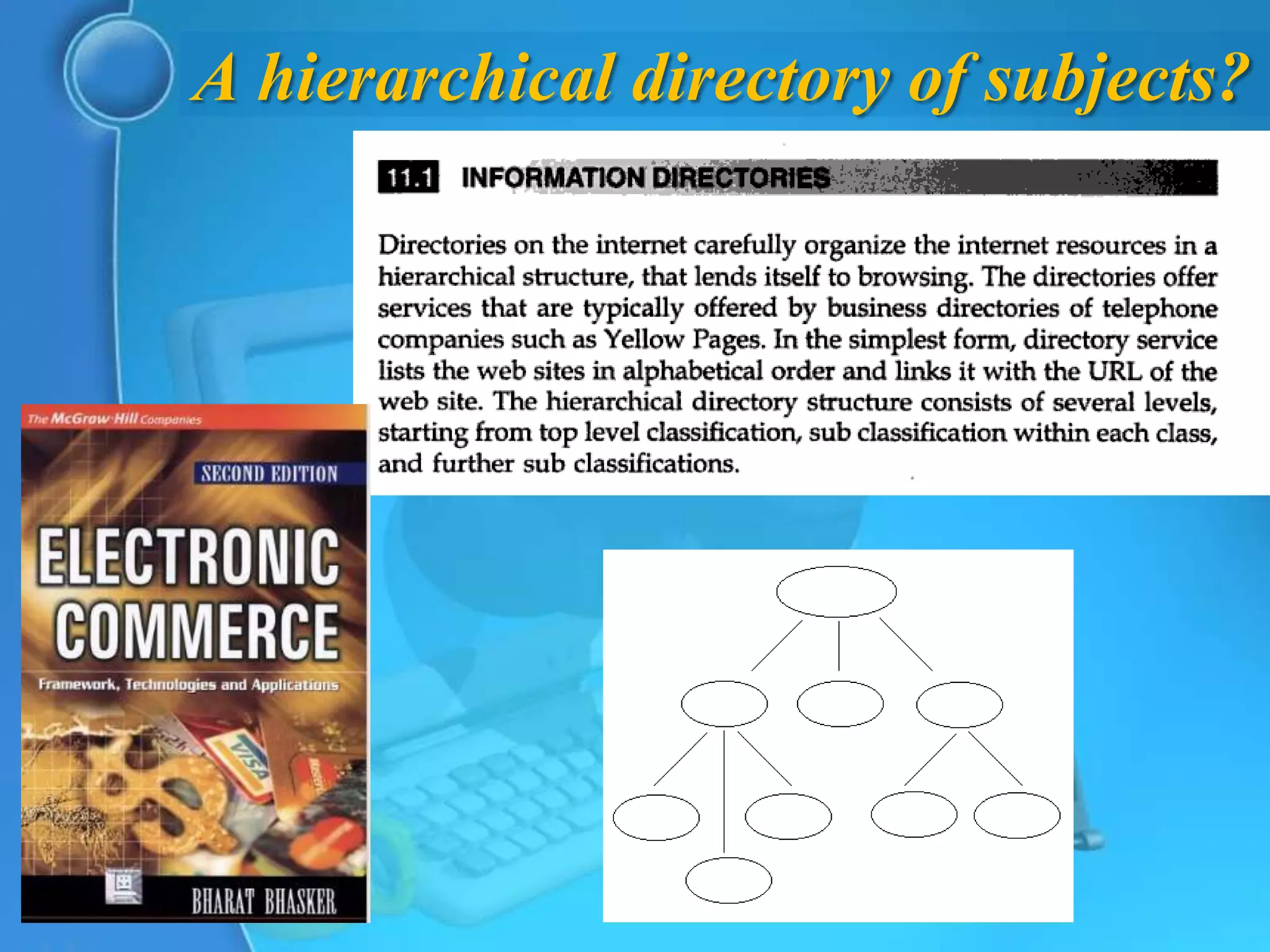
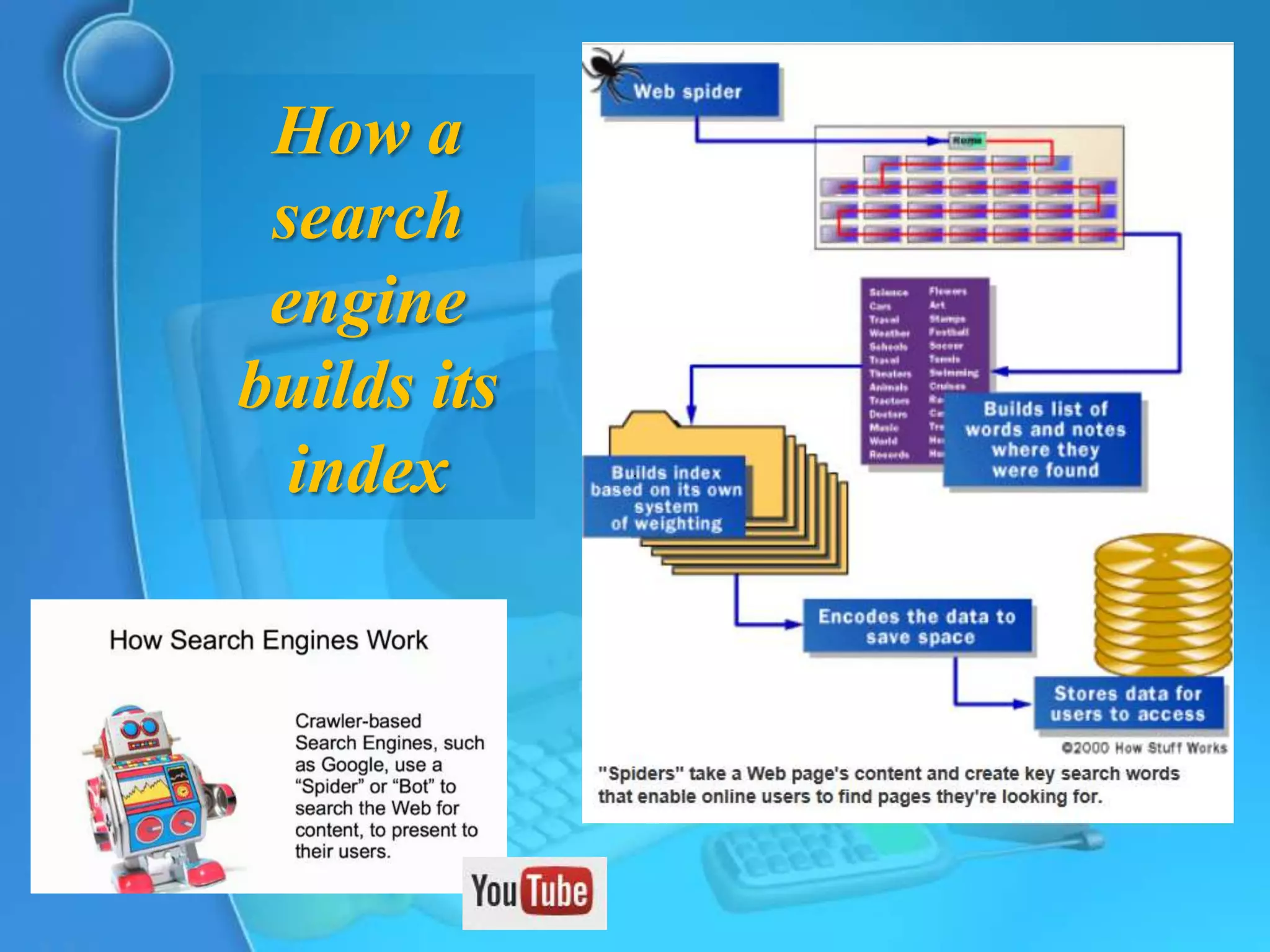
This document provides an overview of key concepts for understanding how search engines work. It defines search engines as computer programs that use clusters of computers to search the web and index pages based on important words found. Search engines allow users to search their indexes by entering keywords or browsing categorized directories. The document discusses how search engines build their indexes by crawling websites, and how they rank pages based on factors like keyword frequency, location, and link popularity. It also notes that search results vary between engines and are personalized based on individual search histories.








![What does this mean?
1. You are not searching the Web directly, and
not even a snapshot of the Web, either
2. You are not even searching all of the Web,
only the websites that have been crawled by
the search engine’s bots
3. The indexes do not distinguish the keywords
by their meaning—they’re simply a collection
of words with the links to where they occur
[not for nothing is one of the metasearch
engines called Dogpile!]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lostinthenet-120224163403-phpapp02/75/Lost-in-the-Net-Navigating-Search-Engines-11-2048.jpg)
![What about the order of appearance?
How Search Engines Rank Web Pages
1. Frequency of Keywords
• Search Engines look for the frequency of keyword
repeats in the content of the web page and the web
pages with the best keyword frequency stand a chance
to get to the top of search engine results. Low
keyword frequency may result in loss of ranking and
deliberate use of excessive keywords will end up being
penalized by search engines. SEO [Search Engine
Optimization] experts recommend keyword density of
3 to 5% of the whole content of the web page.
• January 4, 2012 By admin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lostinthenet-120224163403-phpapp02/75/Lost-in-the-Net-Navigating-Search-Engines-12-2048.jpg)