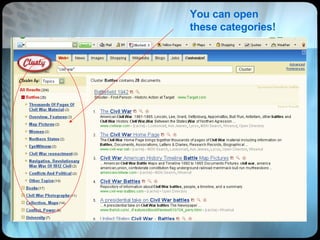
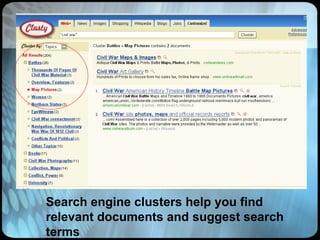
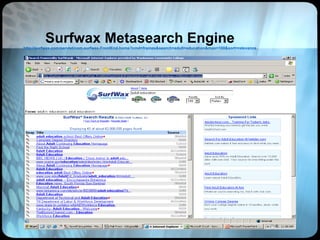
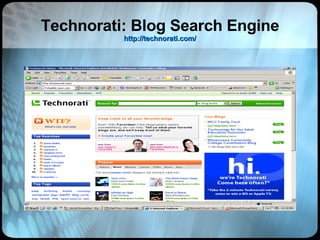
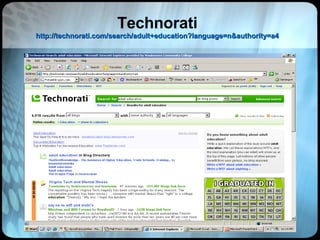
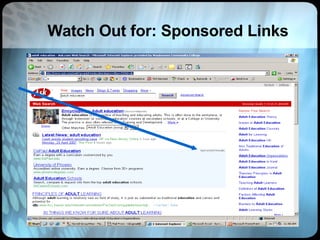
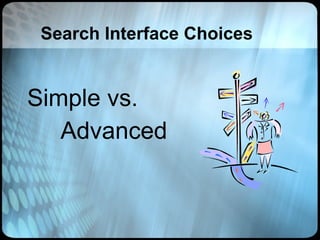
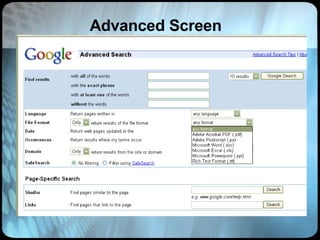
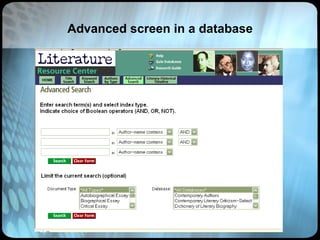
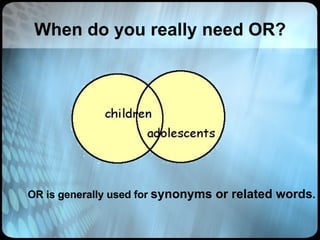
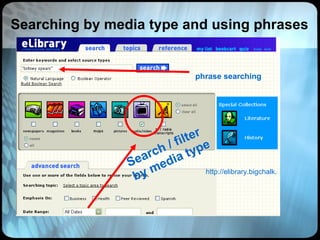
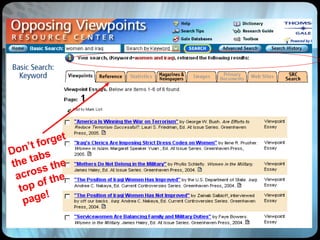
The document provides an overview of effective search strategies, discussing the pros and cons of different search engines and tools. It emphasizes that choosing the right search engine and using advanced features like Boolean operators, phrase searching and subject directories can help users find more relevant information. Meta-search engines and social search engines that gather results from multiple sources are presented as valuable options for comprehensive searching.



























![Need Help ? Judith Sotir, AELC Manager WCC Aurora Campus, Room 312 630-801-7900 x 4128 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/search-engine-strategies-1242160583-phpapp02/85/Search-Engine-Strategies-37-320.jpg)