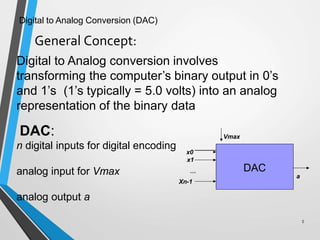
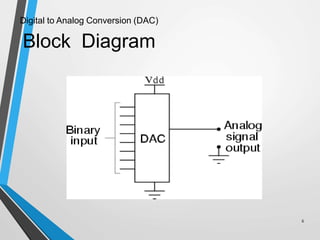
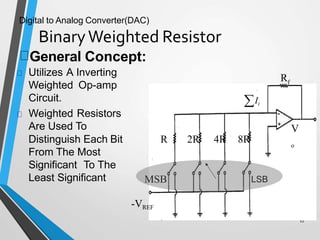
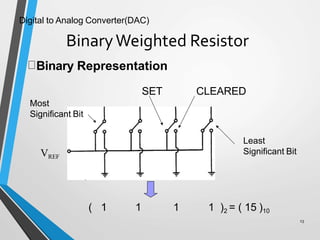
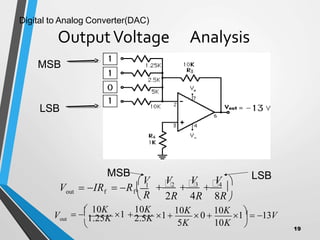
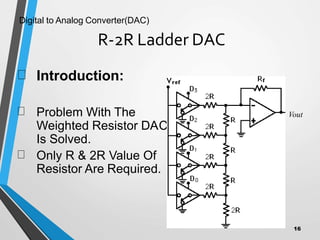
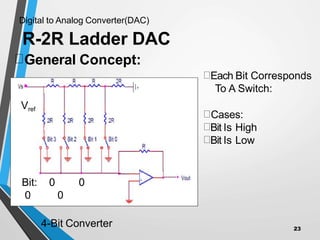
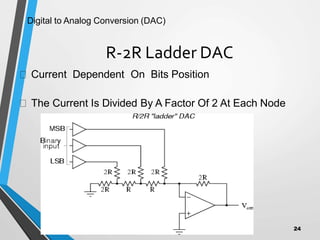
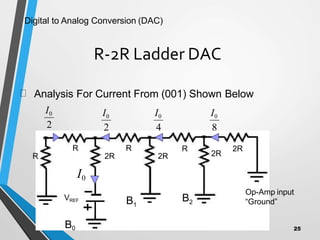
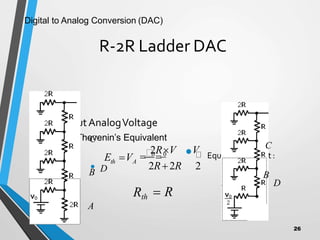
This document discusses digital to analog converters (DACs). It begins by defining analog and digital signals and what a DAC is. It then describes two common types of DACs: (1) weighted resistor DACs, which use a series of weighted resistors to convert digital codes to analog voltages; and (2) R-2R ladder DACs, which only require two resistor values and are easier to implement accurately. The document concludes by listing some applications of DACs such as digital audio players, signal generators, and motor controllers.