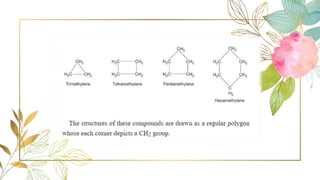
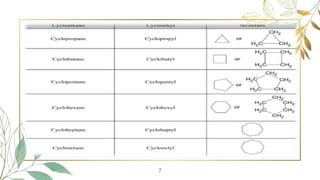
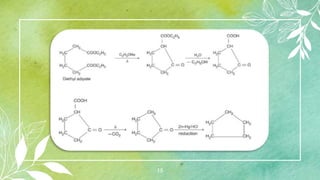
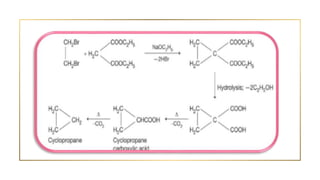
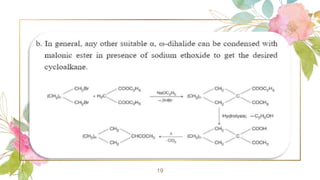
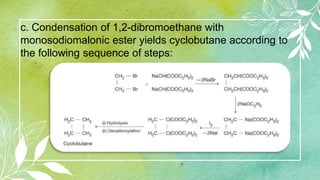
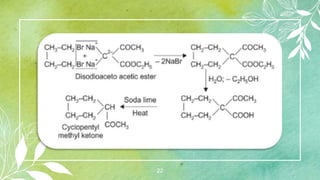
Cycloalkanes are cyclic hydrocarbons whose rings are formed entirely of carbon-carbon single bonds. They have the general formula CnH2n. There are several methods to prepare cycloalkanes, including Freund's method using α,ω-dihalides, the Wislicenus method using barium or calcium salts of dicarboxylic acids, and addition of carbenes to olefins to form cyclopropane derivatives. Cycloalkanes are named using IUPAC rules, which involve identifying the parent chain with the maximum number of carbons and using the prefix "cyclo-". They can be classified into groups based on ring size.
















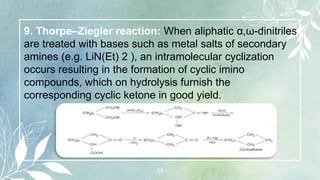
![25
10. Photochemical [2+2] cycloaddition reactions:
[2+2] Cycloaddition reaction refers to an addition of two
alkene molecules using two π electrons each to form a
cyclobutane ring. A convenient method for the synthesis
of cyclobutane derivatives is photodimerization reaction
between two alkenes. These reactions take place in a
concerted manner involving a cyclic transition state.
Some suitable substituted alkenes such as R 2 C = CF 2
or CH 2 = CH — X (X = —COR, —CN, —COOR, etc.)
yield cyclobutane derivatives under thermal conditions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycloalkanes-230830130531-497c9cda/85/CYCLOALKANES-pptx-25-320.jpg)
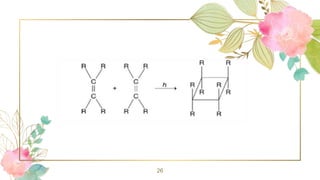
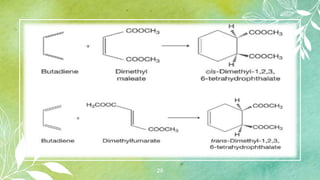
![27
11. Diels–Alder reaction [4+2] Cycloaddition:
The [4+2] cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated
diene (4π-electron system) to form an adduct is known as
Diels–Alder reaction named after the two German
chemists, who received the noble Prize for chemistry in
1950. a typical example is the addition of 1,3-butadiene
with acrolein at 100°C to form tetrahydrobenz-aldehyde.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycloalkanes-230830130531-497c9cda/85/CYCLOALKANES-pptx-27-320.jpg)