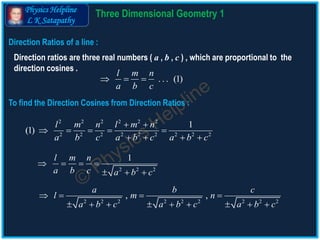
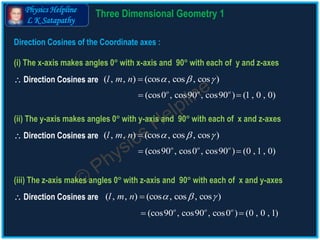
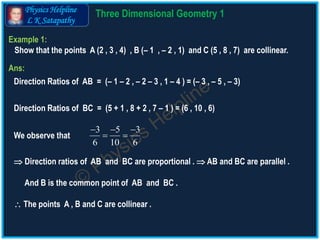
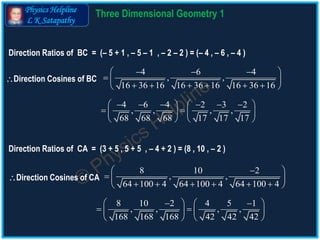
The document discusses the concepts of direction cosines and direction ratios in 3D geometry. It provides mathematical relations and examples to illustrate how to find these values for lines and points in space, including the conditions for collinearity of points. Additionally, it offers direction cosines for the coordinate axes and direction ratios for line segments connecting given points.

![Physics Helpline
L K Satapathy
( , , ) (cos , cos , cos )l m n
Direction Cosines of a line :
Cosines of the angles made by a line with the positive direction of X , Y and Z
axes are known as the direction cosines of the line , denoted by ( l , m , n ).
If , and be the angles made by the line with coordinate axes , then
Relation between the direction cosines : 2 2 2
1l m n
Also
2 2 2 2 2 2
sin sin sin (1 cos ) (1 cos ) (1 cos )
2 2 2
3 (cos cos cos )
2 2 2
3 ( ) 3 1 2l m n
[ Refer Theory of vectors 3 ]
3 D Geometry Theory 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometry3d-160406063253/85/3D-Geometry-Theory-1-2-320.jpg)