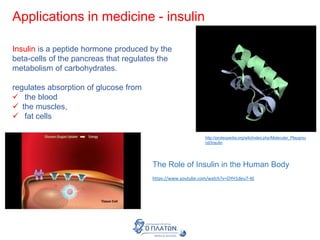
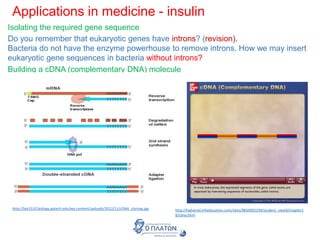
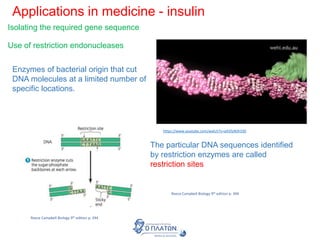
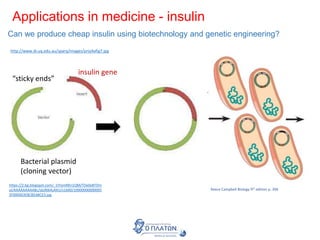
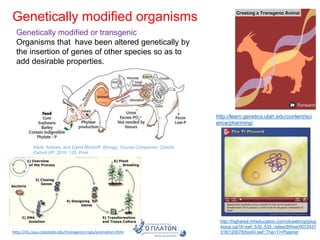
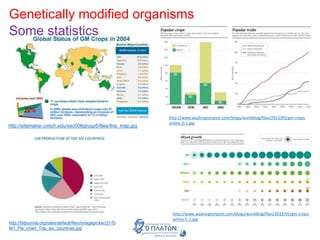
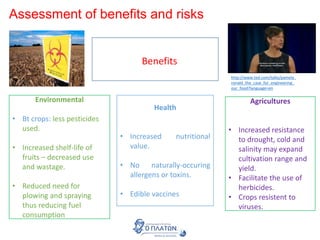
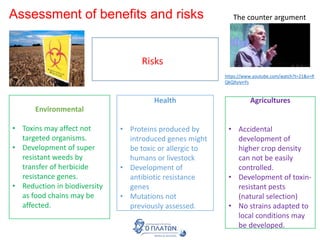
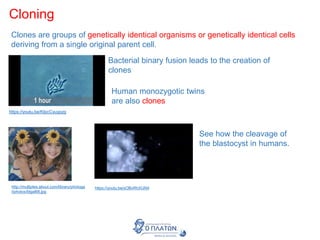
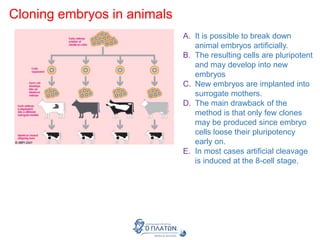
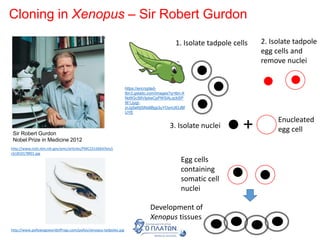
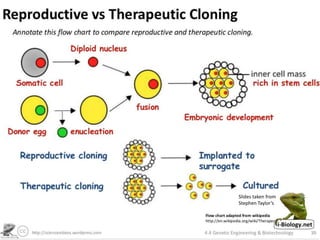
The document discusses genetic modification, biotechnology, and cloning. It begins by defining genetic modification as the transfer of genes between species, allowing the recipient to gain new properties. It then discusses applications in medicine like using genetic engineering to produce insulin in bacteria to treat diabetes. The document also addresses genetically modified organisms and both the potential benefits and risks of genetic modification, which are still an ongoing debate. It concludes by explaining natural and artificial methods of cloning plants and animals.