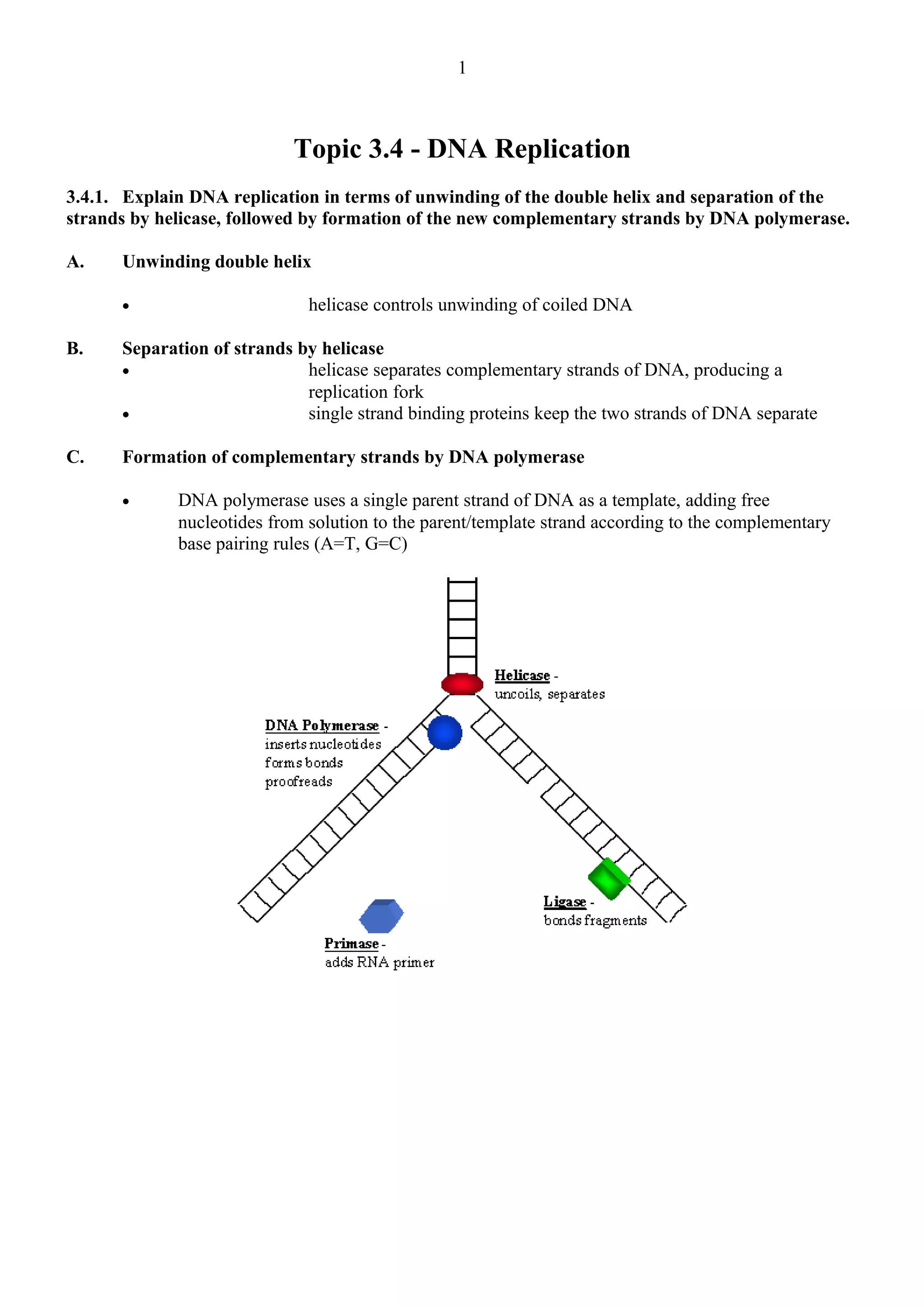
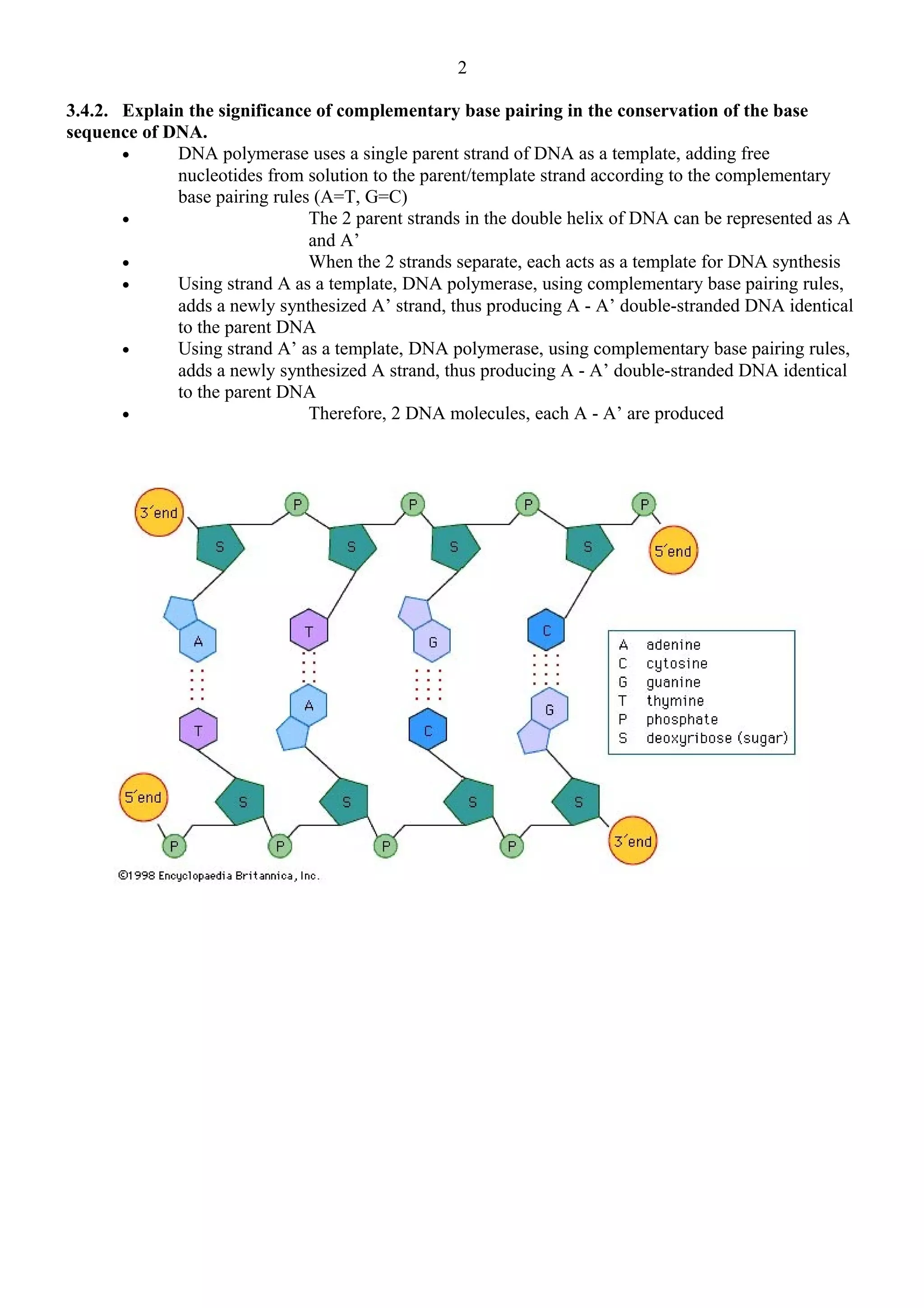
Helicase unwinds and separates the parental DNA strands at the replication fork. DNA polymerase then uses each parental strand as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides according to base pairing rules, thus precisely conserving the DNA sequence. This semi-conservative process produces two identical daughter DNA molecules each with one original parental strand and one newly synthesized strand.