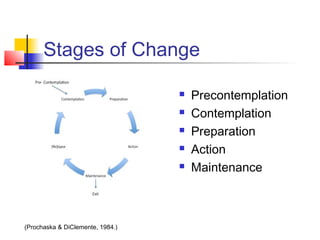
This document provides an overview of motivational interviewing (MI), including its key principles and communication skills. MI is a client-centered counseling approach that seeks to strengthen a person's own motivation and commitment to change. The four main principles discussed are expressing empathy, developing discrepancy, rolling with resistance, and supporting self-efficacy. Specific MI skills covered include using open-ended questions, affirmations, reflective listening, summarizing, and eliciting change talk. Examples are given throughout and the document concludes by discussing applying these techniques in home visitation settings.