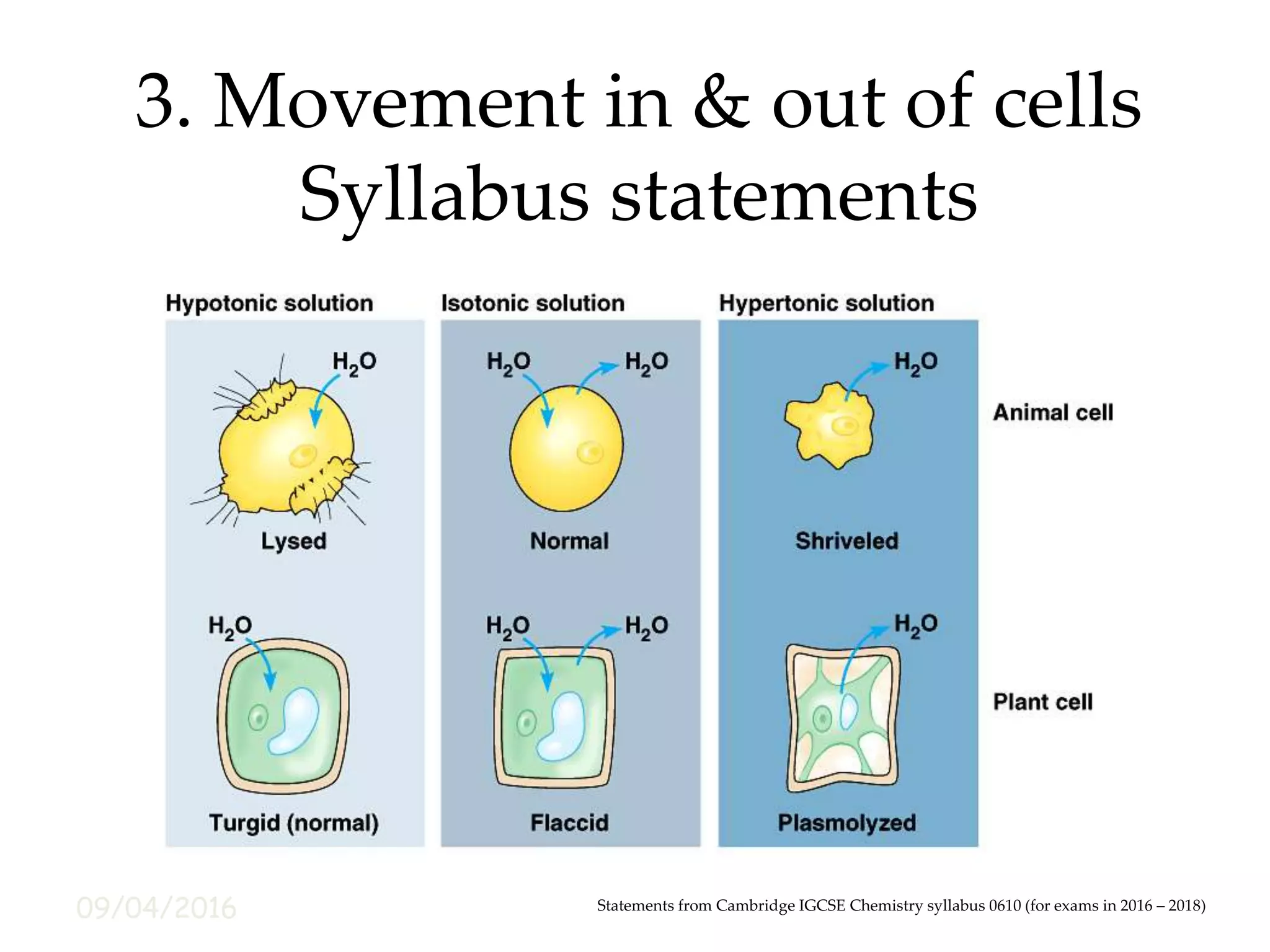
This document outlines statements from the Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry syllabus regarding movement in and out of cells. It discusses diffusion, the random movement of particles down a concentration gradient, and how substances diffuse through the cell membrane. Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water molecules through a partially permeable membrane from an area of higher water potential to lower. The effects of different solution concentrations on plant tissues are described. Active transport is defined as the movement of particles against a concentration gradient using energy from respiration, and examples of its importance are given.