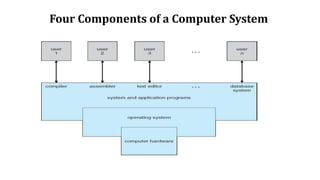
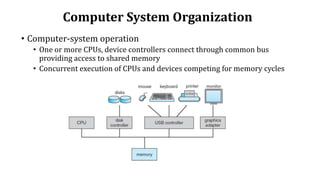
The document provides an overview of operating systems and system software. It discusses what system software is, the need for system software, types of system software including operating systems, device drivers, firmware, programming language translators, and utility software. It defines operating systems and describes their design goals. It also outlines the four main components of a computer system - hardware, operating system, application programs, and users. Finally, it discusses the key components of an operating system including process management, I/O device management, file management, memory management, and security management.