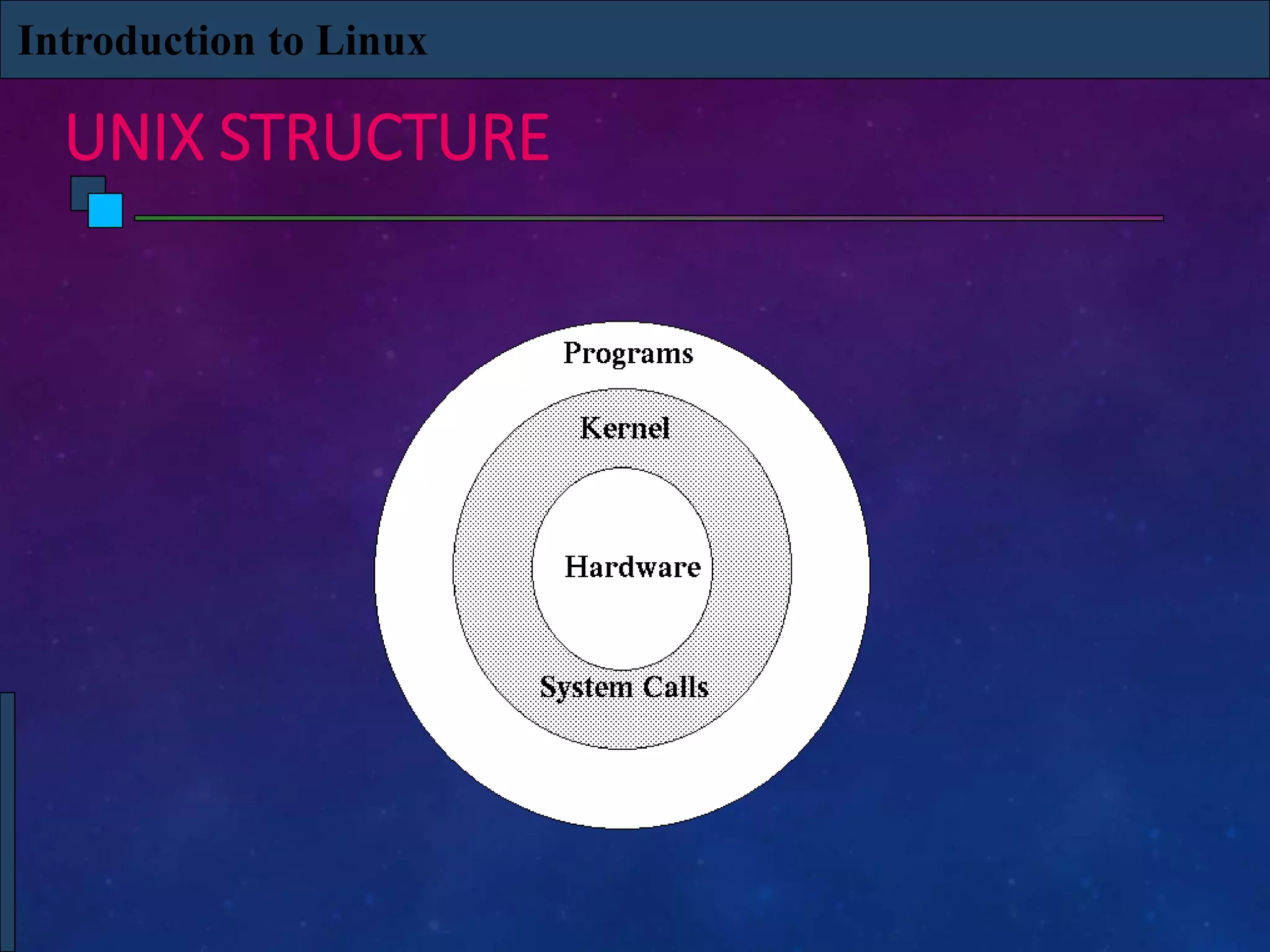
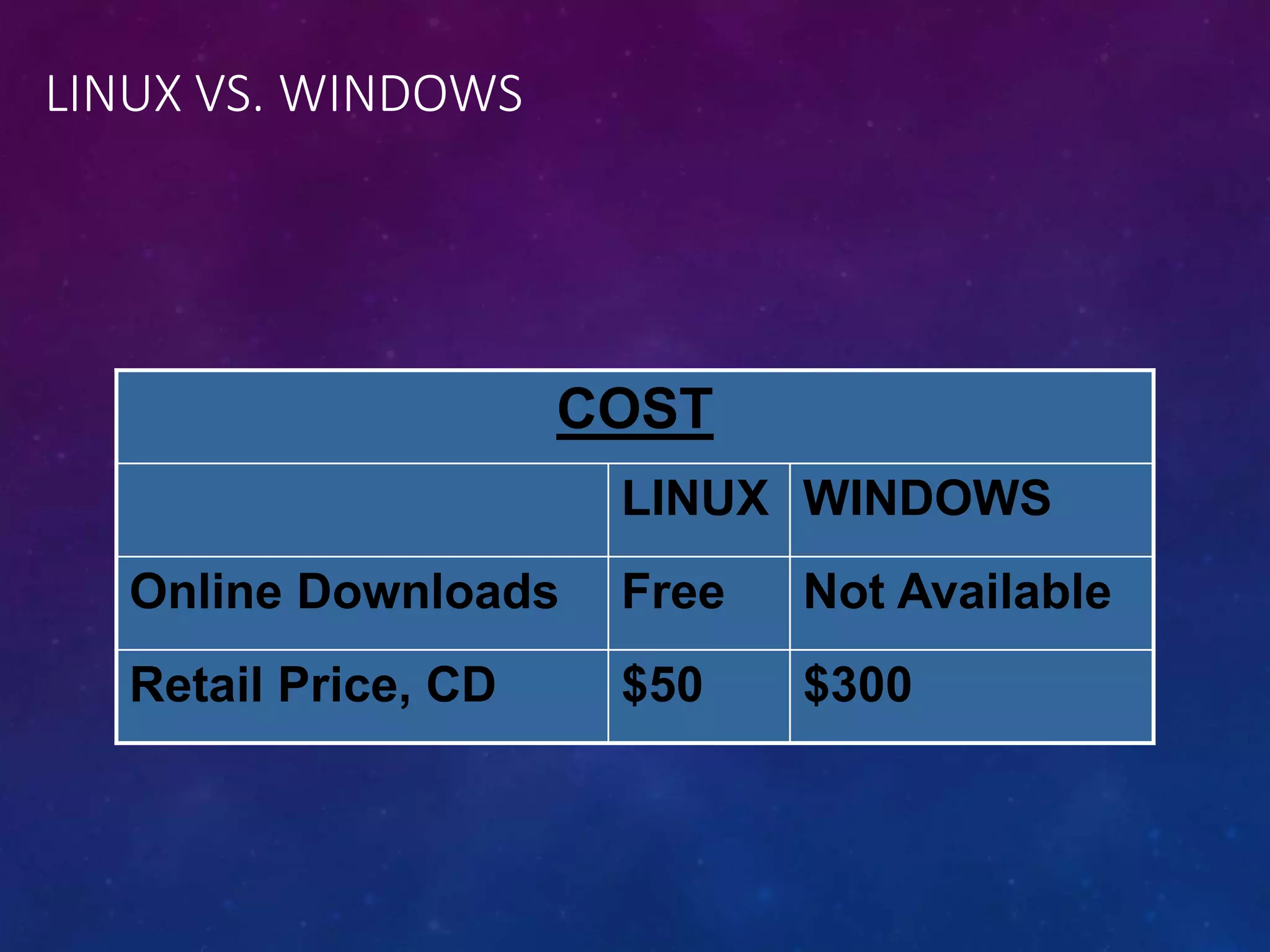
Unix is a multi-user, multi-tasking operating system that was first created in 1969 at Bell Labs. It allows many users to use the system simultaneously running multiple programs. Linux originated in 1991 as a personal project and is now a free, open source Unix-like operating system. It features multi-tasking, virtual memory, networking and more. Linux is widely used for servers, workstations, internet services and more due to its low cost, stability, and reliability compared to other operating systems.