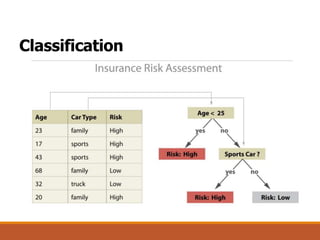
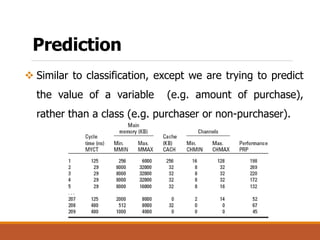
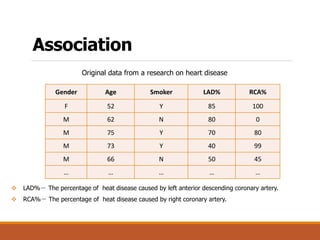
The document provides an introduction to data mining, outlining its definition, interdisciplinary nature, and main processes involved. It details various data mining tasks, including classification, prediction, association rules, clustering, and outlier analysis, while also discussing challenges such as scalability, data quality, and privacy concerns. Additionally, the document highlights diverse applications of data mining across sectors like science, business, and government.




![ Most famous data mining tasks:
Classification [Predictive]
Prediction [Predictive]
Association Rules [Descriptive]
Clustering [Descriptive]
Outlier Analysis [Descriptive]
Data Mining Tasks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3introduction-to-data-mininglecture3-180226114546/85/3-Data-Mining-Tasks-5-320.jpg)