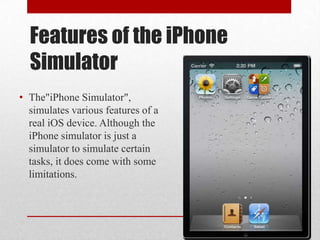
This document provides an introduction and overview of iOS development. It discusses prerequisites including previous programming experience, recommended resources for learning iOS development like Apple's developer site and books, and an introduction to the core concepts of iOS, Objective-C, and the Xcode integrated development environment. It also covers limitations of the iOS simulator and key tools like Instruments for debugging apps.