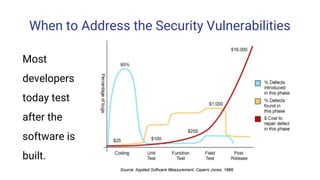
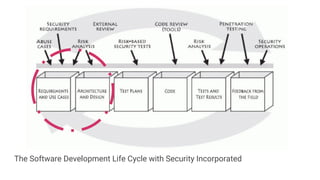
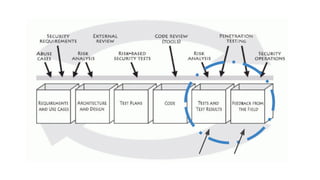
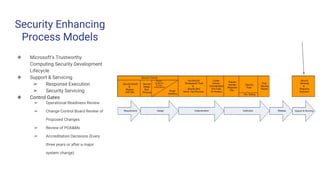
The document outlines the importance of incorporating security measures throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC), detailing phases such as planning, designing, implementation, testing, and maintenance. It emphasizes proactive risk management, secure design practices, and thorough testing methods to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards. The document also highlights the financial implications of software security, necessitating a strategic approach to minimize costs and enhance overall software quality.

![Phase 1
Frances
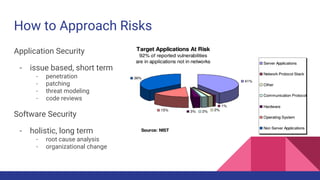
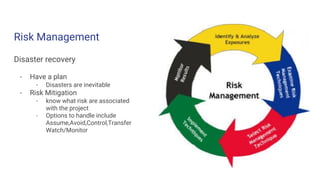
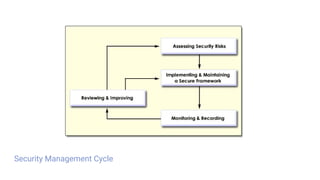
❖ Planning
❖ Analyzing Risk
❖ Cost Analysis
❖ Security Requirements
[1][2][3][4][5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-10-01securityinthesdlc-171102222250/85/Security-in-the-Software-Development-Life-Cycle-SDLC-3-320.jpg)





















![References
[1] R. Baskerville. Information systems security design methods: Implications for information systems development. ACM Computing
Surveys, 25(4):375–414, Dec. 1993.
[2] G. Brose. A typed access control model for CORBA. In F. Cuppens, Y. Deswarte, D. Gollmann, and M. Weidner, editors, Proc.
European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS), LNCS 1895, pages 88–105. Springer, 2000.
[3] G. Brose. Access Control Management in Distributed Object Systems. PhD thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, 2001.
[4] The Ten Best Practices for Secure Software Development: https://www.isc2.org/uploadedfiles/(isc)
2_public_content/certification_programs/csslp/isc2_wpiv.pdf
[5] Processes to Produce Secure Software: https://www.cigital.com/papers/download/secure_software_process.pdf
[6] Risk Mitigation Planning, Implementation, and Progress Monitoring: http://www.mitre.org/publications/systems-engineering-
guide/acquisition-systems-engineering/risk-management/risk-mitigation-planning-implementation-and-progress-monitoring](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-10-01securityinthesdlc-171102222250/85/Security-in-the-Software-Development-Life-Cycle-SDLC-34-320.jpg)
![[7] Disaster Recovery:Best Practices: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/collateral/tk869/tk769/white_paper_c11-
453495.html
[8] Eternal Sunshine Of The IS Mind: https://eternalsunshineoftheismind.wordpress.com/2013/03/10/sdlc-phase-5-maintenance/
[9] On Point : http://www.onpointcorp.com/uploads/1385/doc/SecurityandtheSystemDevelopmentLifestyle_TimSmith_OnPoint0.
pdf
[10] Nearly 1 million new malware attacks every day: http://money.cnn.com/2015/04/14/technology/security/cyber-attack-hacks-
security/
[11] Software Security Testing: https://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/xyzhang/fall07/Papers/sw-test.pdf
[12] Assuring Software Security Through Testing: https://www.isc2.org/uploadedfiles/(isc)
2_public_content/certification_programs/csslp/software%20security%20through%20testing.pdf
[13] Operation/Maintenance Phase: http://www.fedramp.net/operation-maintenance-phase
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-10-01securityinthesdlc-171102222250/85/Security-in-the-Software-Development-Life-Cycle-SDLC-35-320.jpg)
