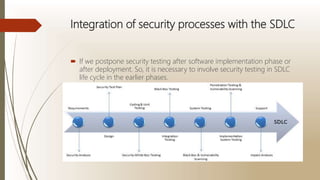
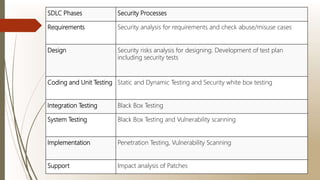
The document discusses software security testing. It defines software security testing as testing that aims to uncover vulnerabilities in a system and ensure data and resources are protected from intruders. The document then describes common security measures, approaches to security testing including functional and risk-based methods, and how security processes can be integrated into the software development lifecycle. It outlines how security testing is relevant at various stages including requirements, design, coding, integration, and system testing.