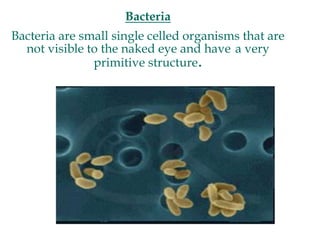
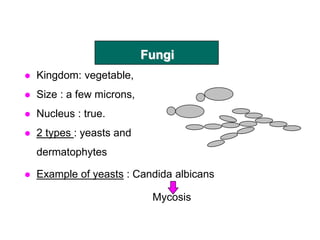
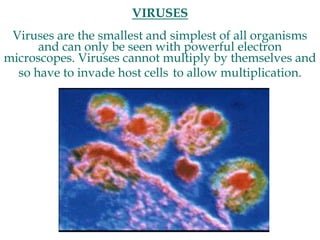
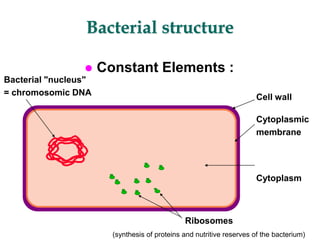
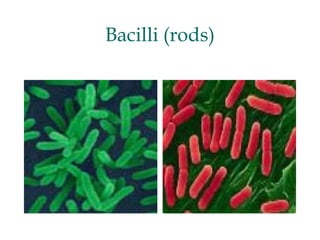
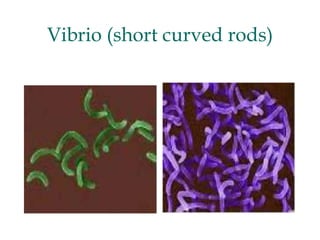
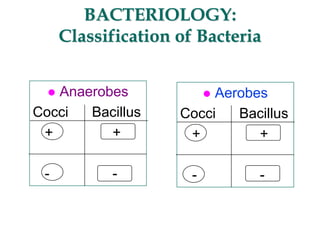
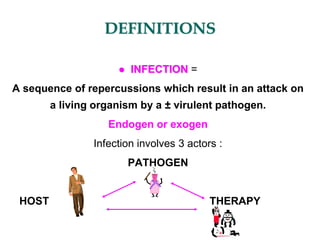
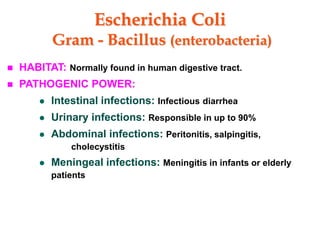
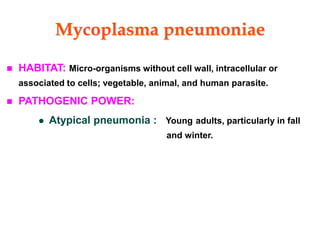
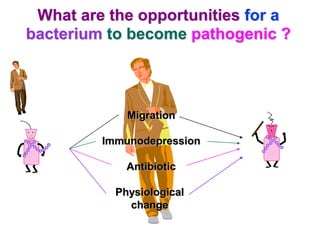
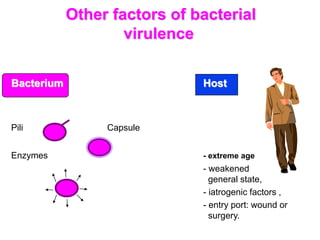
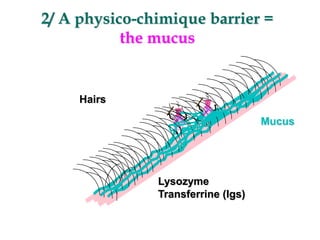
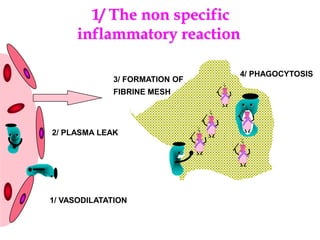
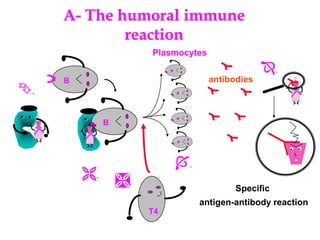
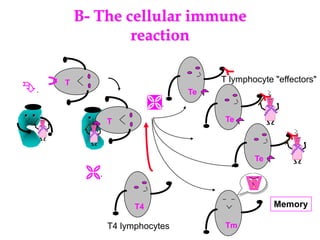
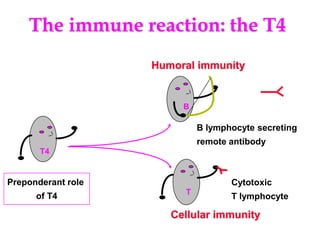
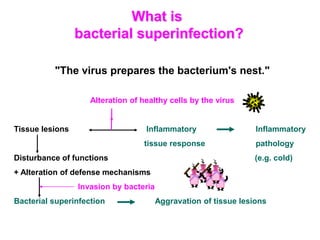
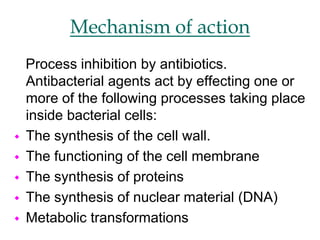
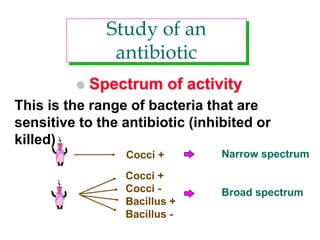
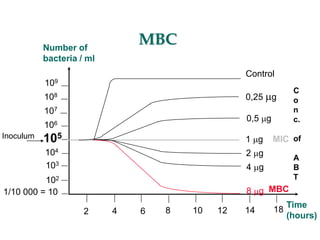
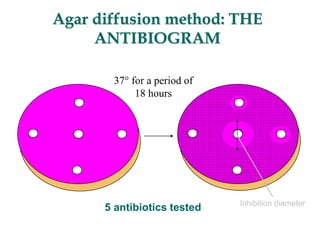
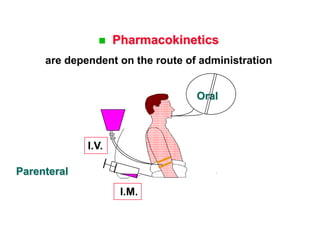
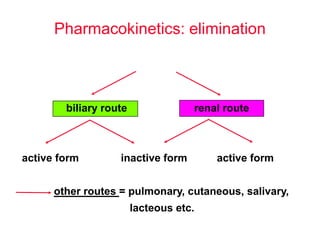
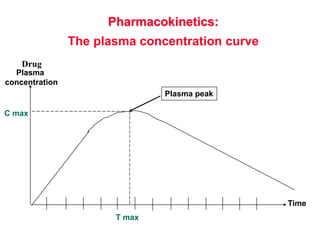
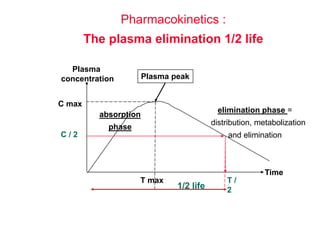
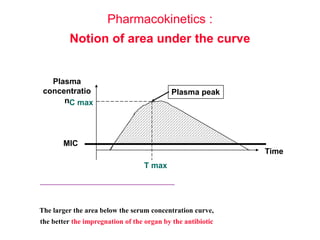
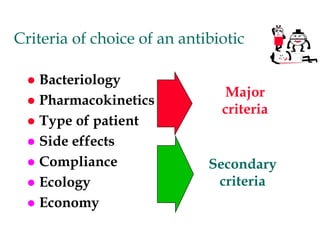
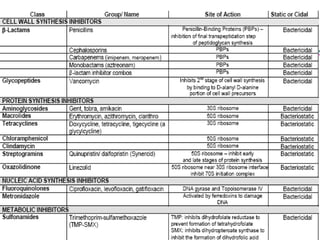
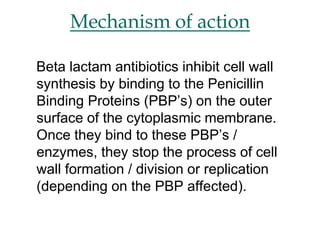
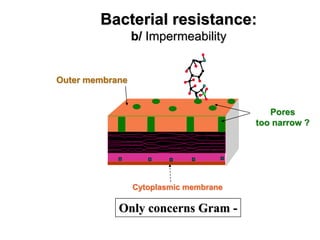
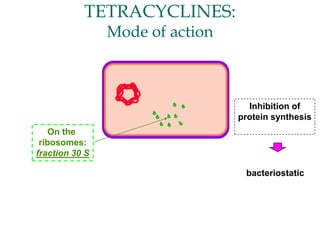
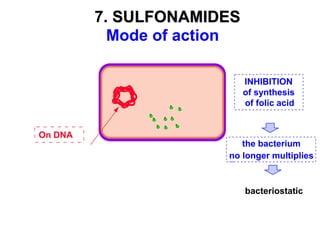
Micro-organisms can be divided into 4 main groups: bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and viruses. Bacteria are the smallest and most primitive of these microbes, lacking nuclei and existing as single cells or colonies. Viruses are even smaller and simpler, able to replicate only inside host cells. More complex microbes include protozoa, which have true nuclei, and fungi, which resemble primitive plants. An overview of bacterial structure, classification, and important pathogenic species is provided, highlighting bacteria's role in causing infectious disease. The document also discusses how bacteria can become pathogenic and how the human body defends against infection.