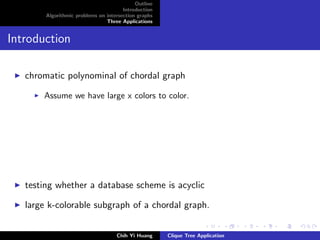
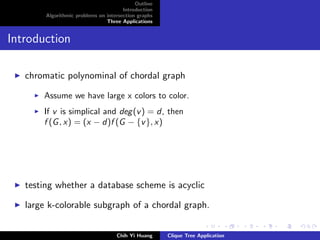
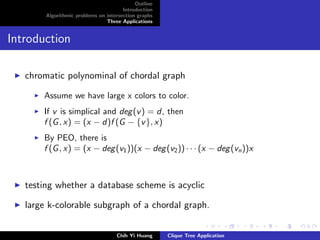
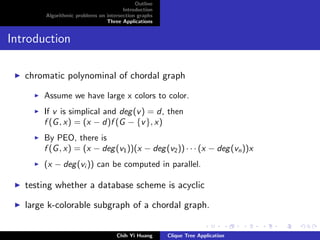
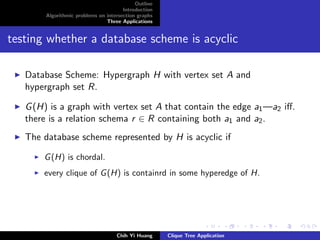
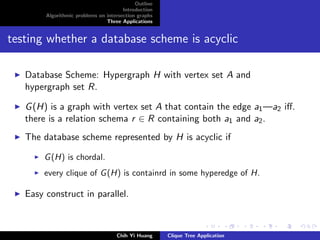
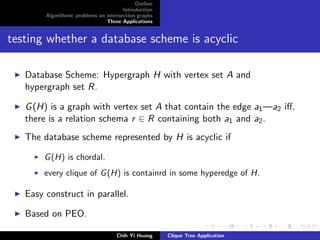
The document outlines an algorithmic problem on intersection graphs and discusses three applications. It introduces the concepts of perfect elimination scheme and independent set for chordal graphs. It then summarizes several papers on using clique trees for sparse matrix factorization, database systems, and graph theory problems like finding a maximum independent set in polynomial time on a parallel random access machine.










![Outline
Introduction
Algorithmic problems on intersection graphs
Three Applications
Introduction
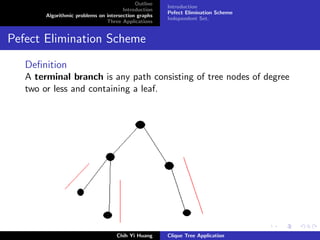
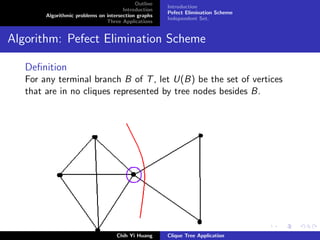
Pefect Elimination Scheme
Independent Set.
Results
For chordal graph, all following probelms can be sovled in
polylogarithmic time on a PRAM having polynominal many
processors:
all cliques and chromatic number [Da86]
clique repersentation [Da86]
optimal coloring
Pefect Elimination Scheme [Da86]
Unweighted max. Independent set.
Weighted max. Independent set.
Min. clique cover
[Da86]: Elias Dahlaus, Marek Karpinski, The Matching Problem
for Strongly Chordal Graph is in NC.
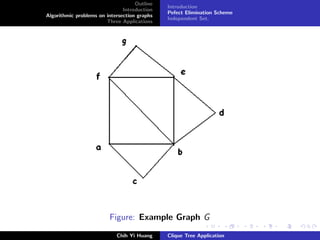
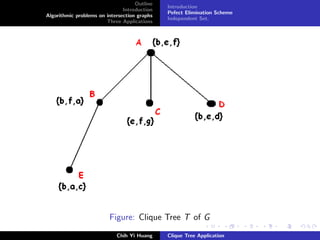
Chih Yi Huang Clique Tree Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20050921dgraph-1223730083229352-9-150607173402-lva1-app6892/85/Clip-Tree-Applications-11-320.jpg)

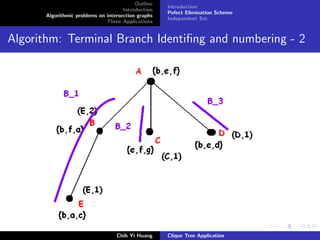


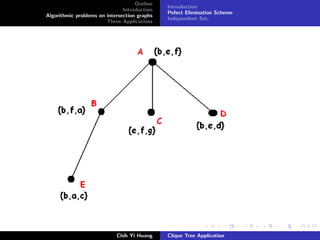
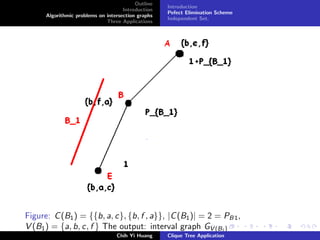
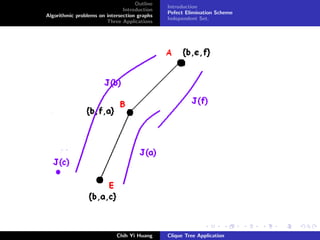
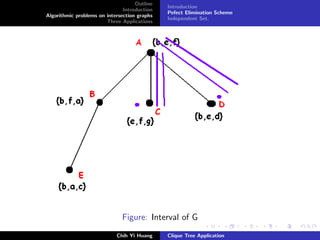







![Outline
Introduction
Algorithmic problems on intersection graphs
Three Applications
Introduction
Pefect Elimination Scheme
Independent Set.
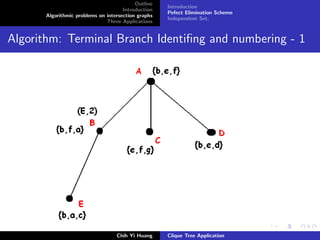
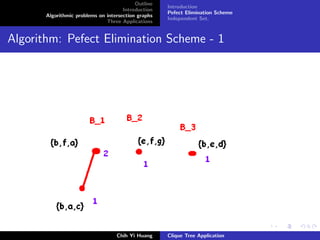
Unweighted Max. Independent Set.
Use Lexicographic frist order([He86]) based on PEO.
This paper is unavialiable.
Chih Yi Huang Clique Tree Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20050921dgraph-1223730083229352-9-150607173402-lva1-app6892/85/Clip-Tree-Applications-34-320.jpg)
![Outline
Introduction
Algorithmic problems on intersection graphs
Three Applications
Introduction
Pefect Elimination Scheme
Independent Set.
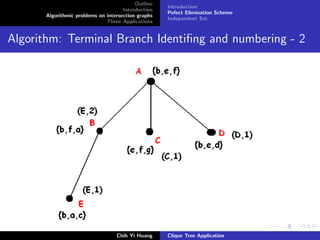
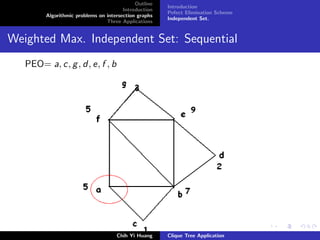
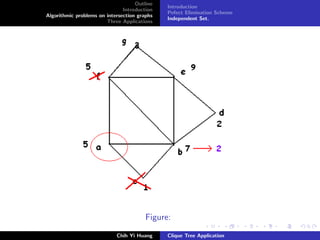
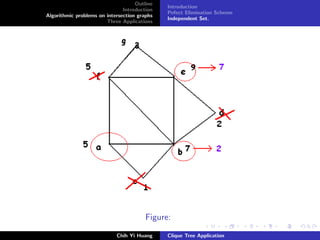
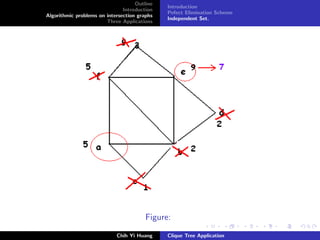
Weighted Max. Independent Set: Parallel
Proof: refer [He86]
Ref.: Observation: A vertex in U(Bi ) can never be adjance to a
vertex in U(Bj ) if Bi = Bj
Chih Yi Huang Clique Tree Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20050921dgraph-1223730083229352-9-150607173402-lva1-app6892/85/Clip-Tree-Applications-39-320.jpg)