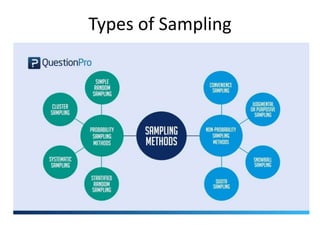
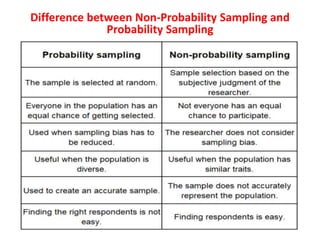
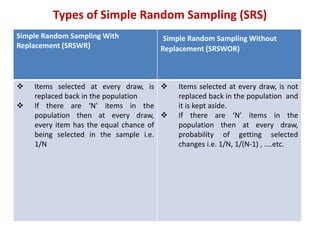
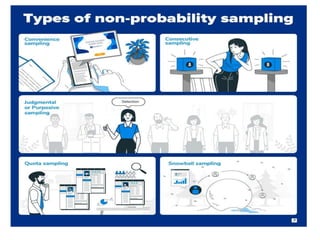
The document discusses various types of sampling methods in statistics, emphasizing the difference between probability and non-probability sampling techniques. It describes several specific sampling methods, such as simple random sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling, along with their applications and advantages. The information is aimed at providing practical insights for researchers to effectively gather data from populations.