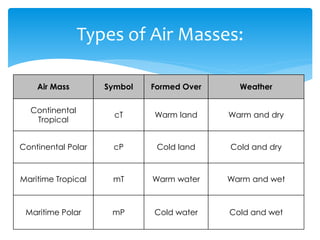
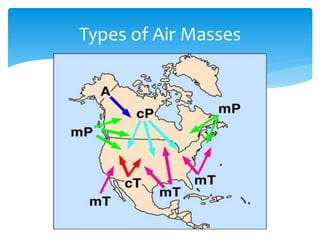
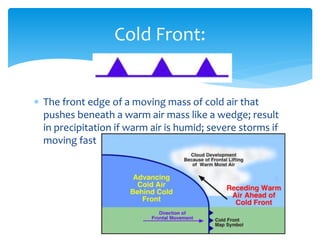
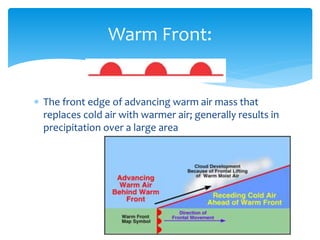
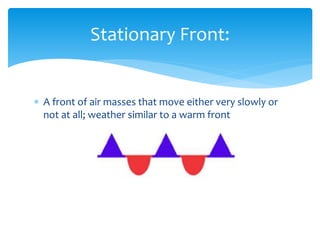
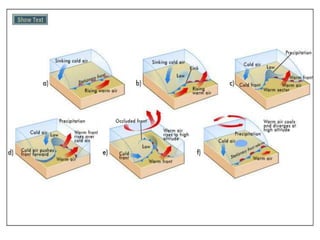
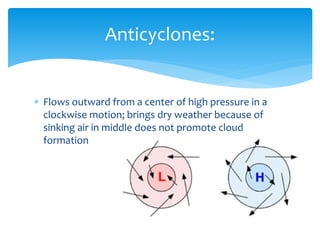
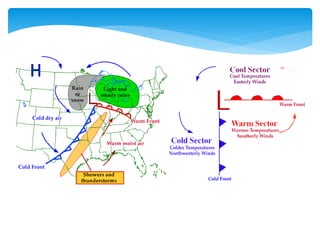
Air masses take on characteristics of the regions where they form and remain stationary. They are classified by temperature and moisture content as either continental, maritime, tropical, or polar. Fronts form boundaries between differing air masses and can cause precipitation. Cold fronts push warm air out of the way while warm fronts lift warm air over colder air. Stationary fronts move slowly and occluded fronts occur when a cold mass overtakes a warm one. Cyclones are low pressure storm systems that rotate counter-clockwise along storm tracks, while anticyclones bring dry weather with sinking air flowing outward clockwise from high pressure centers.