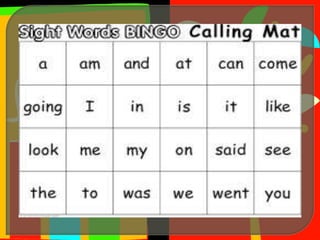
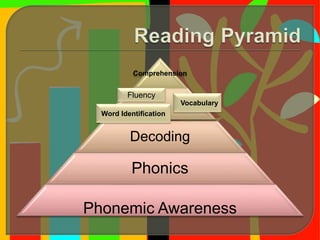
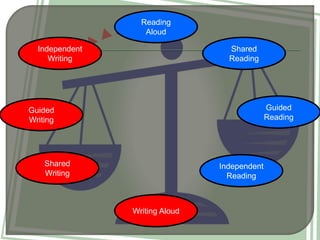
The document outlines a systematic reading instruction program aimed at developing students' reading skills and strategies while fostering a positive attitude towards reading. It details various levels of reading proficiency, from basic skills like print awareness and comprehension to advanced skills including critical reading and interpretation. The program emphasizes the role of teachers in guiding, observing, and supporting students as they progress through independent and collaborative writing and reading activities.