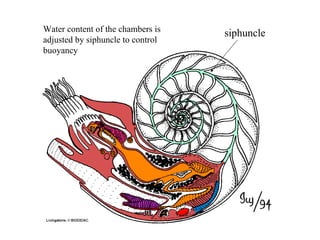
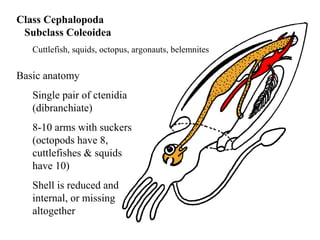
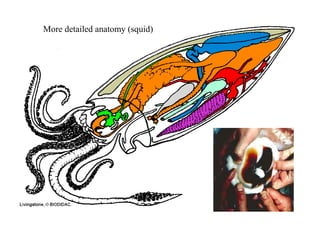
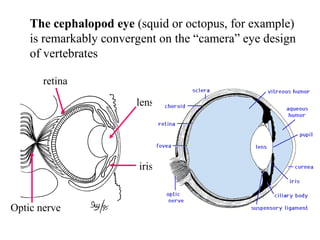
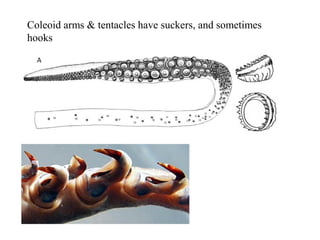
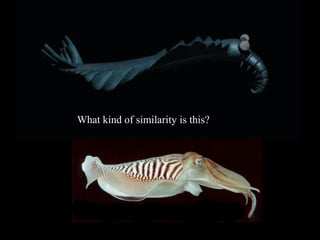
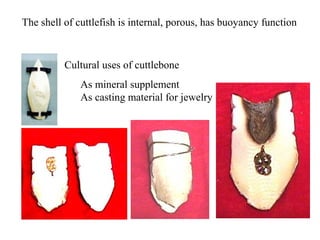
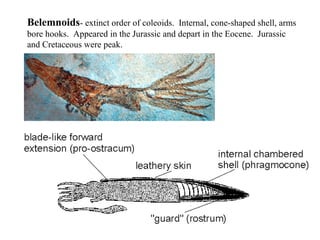
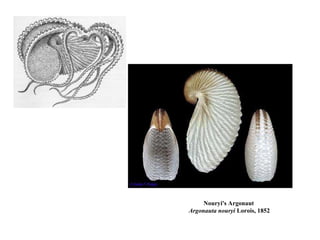
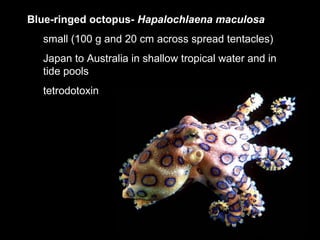
The document summarizes the class Cephalopoda, including their key anatomical features and subclasses. It describes the two living subclasses, Nautiloidea and Coleoidea. Nautiloidea contains the pouch-bearing nautilus, while Coleoidea contains cuttlefish, squids, octopuses, and extinct groups like ammonites and belemnites. Coleoideans have advanced sensory abilities and jet propulsion but internal or reduced shells. The document outlines the diversity of cephalopods past and present.