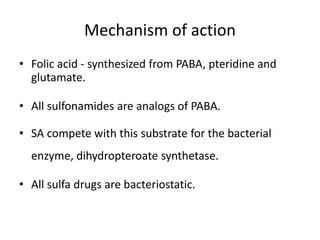
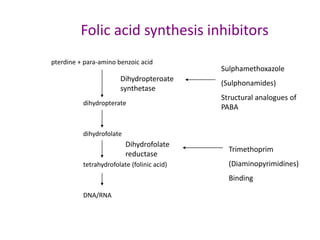
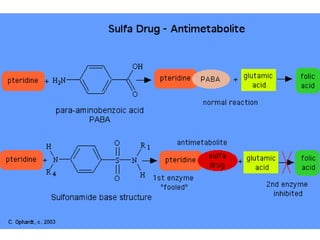
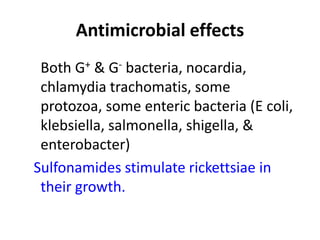
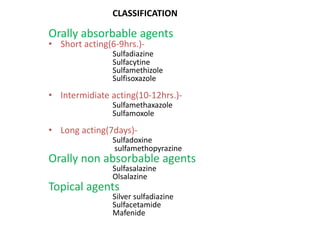
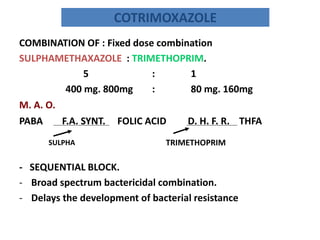
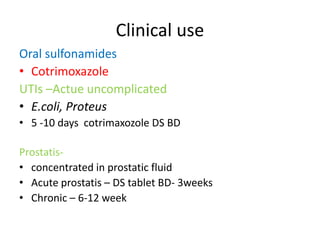
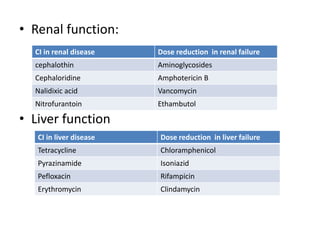
This document provides information on sulfonamides, which were the first antimicrobial agents effective against pyogenic bacterial infections. It discusses how sulfonamides work by competitively inhibiting the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, blocking the synthesis of folic acid. Various sulfonamides are described based on their absorption, duration of action, and clinical uses for infections like UTIs, respiratory infections, and travelers' diarrhea. Adverse effects include crystalluria, blood disorders, and hypersensitivity reactions. Sulfonamides remain important oral antibiotics but require monitoring for toxicity.











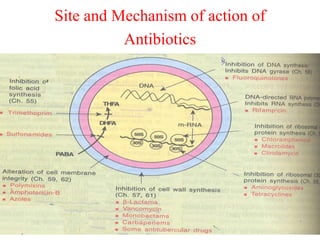






![The process of discovery for sulfonamides
SO2NH2
SO2NH2
NH
2
N N
CH3CONH
N
N
NaO3S
SO3Na
H2N
Prontosil Soluble
Prontosil
NH2
SO2NH2
N
N
H2N
inactive (in vitro)
SO2NH2
Liver
[H]
H2N
active(in vivo)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-131015051935-phpapp02/85/1-sulfonamide-final-24-320.jpg)