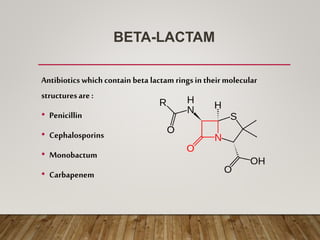
This document discusses beta-lactamase inhibitors which are used to combat bacteria that have developed resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins and cephalosporins. It explains that beta-lactamase enzymes produced by bacteria inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics by breaking the beta-lactam ring. The three main inhibitors discussed are clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam, which are commonly used in combination with other antibiotics. Clavulanic acid is well-absorbed orally and re-establishes activity against common resistant bacteria. Sulbactam has less potency than clavulanic acid and is preferably given parenter