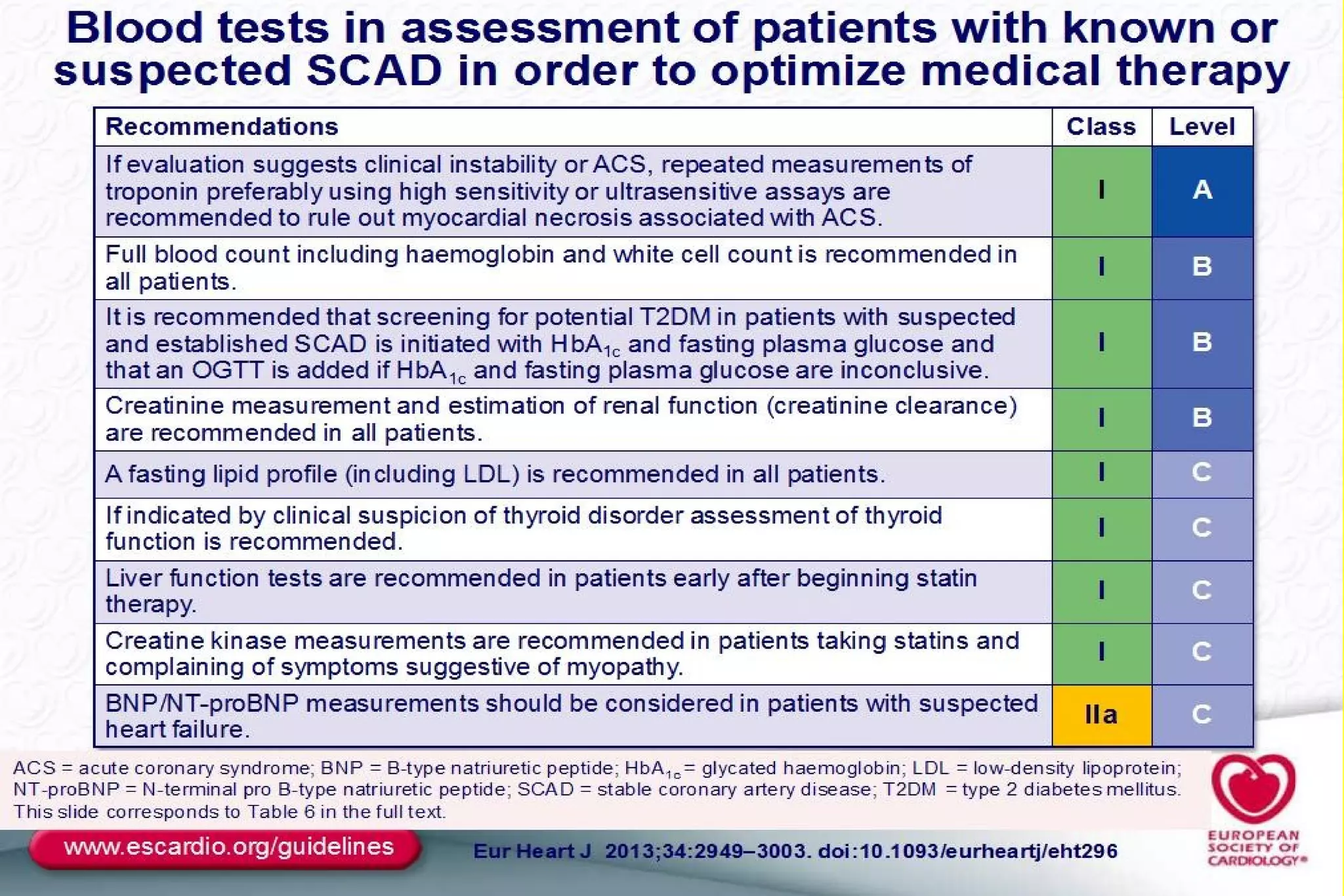
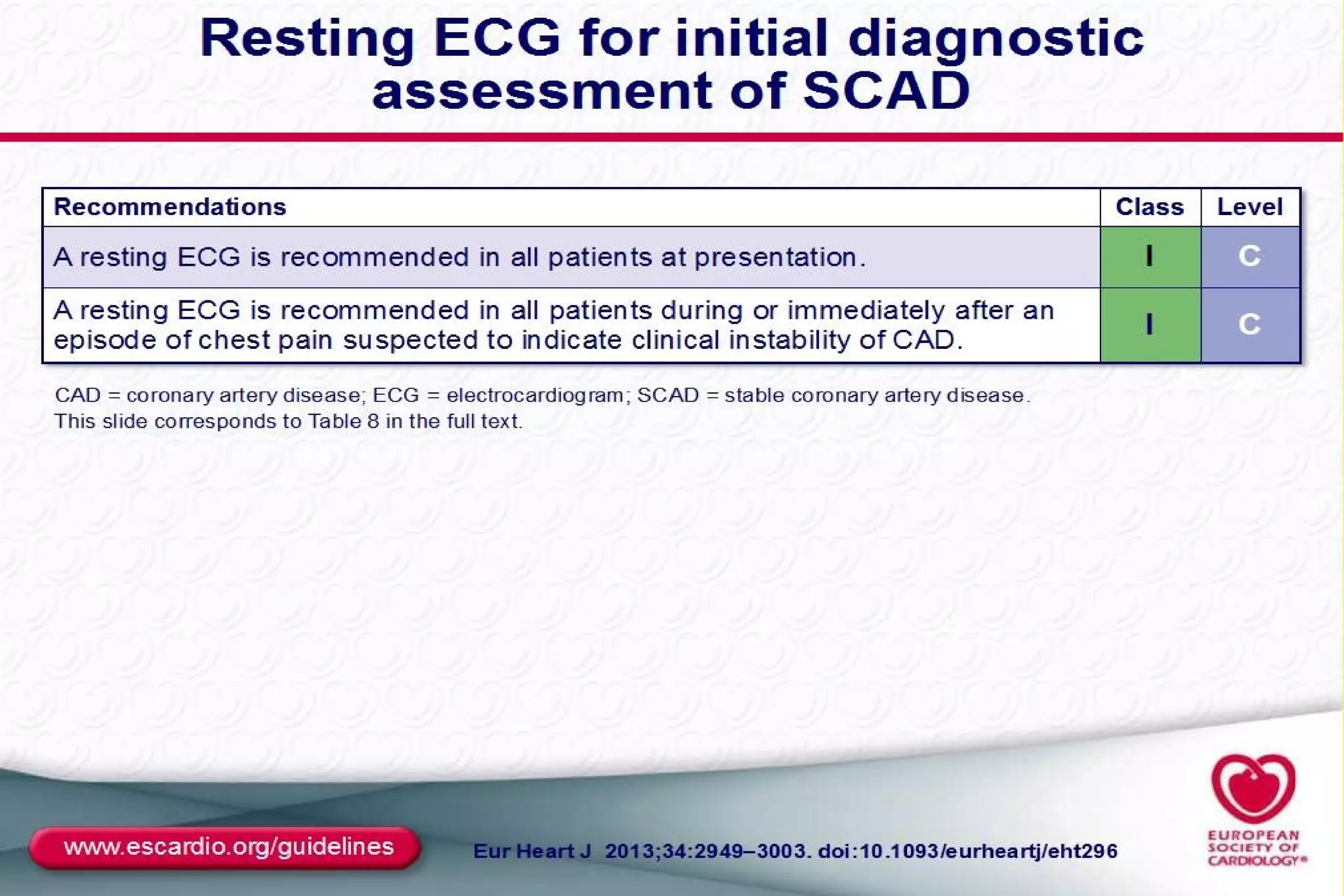
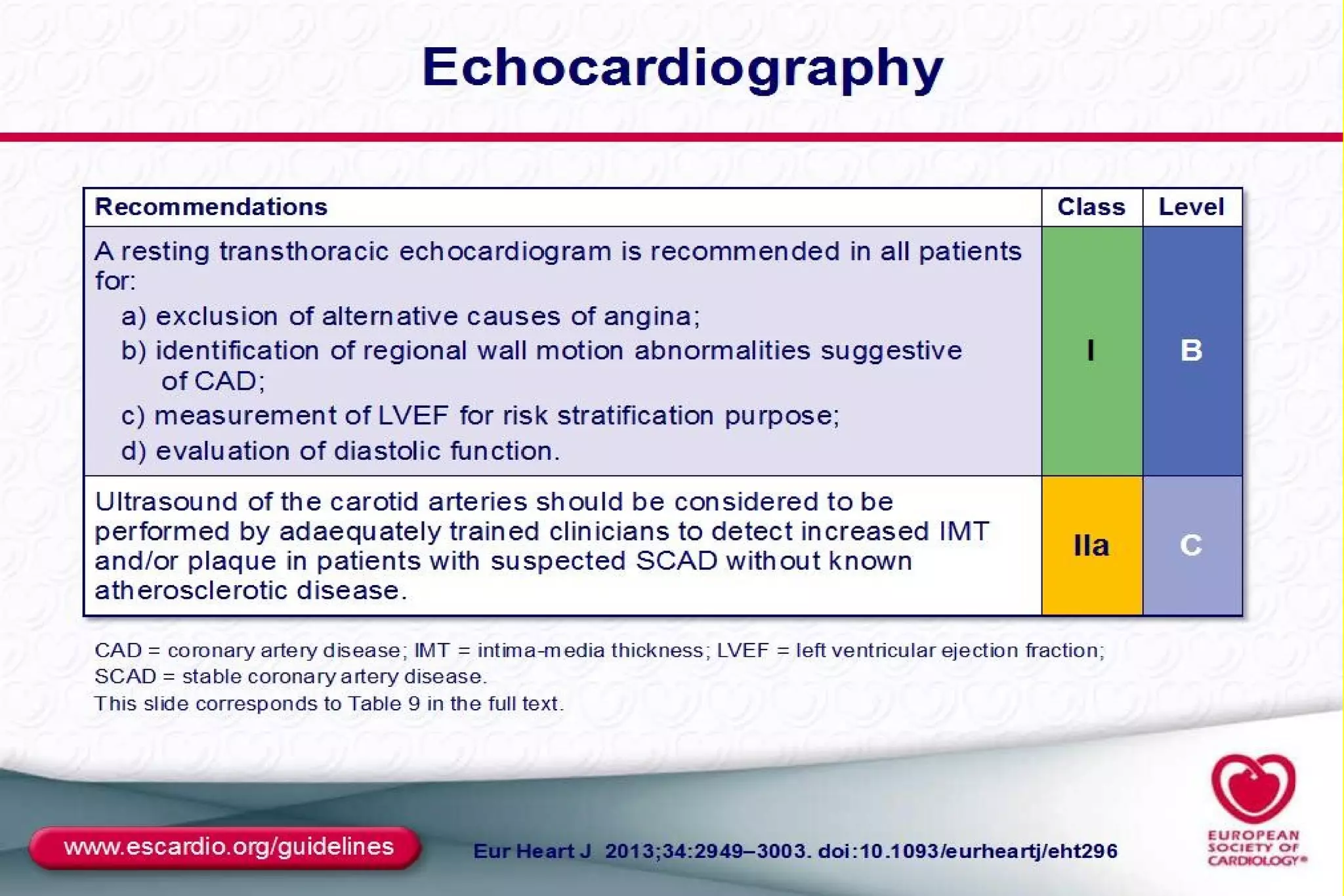
This document discusses the assessment, investigation, and treatment of chronic stable angina. It defines chronic stable angina as chest pain or discomfort that is reproducibly associated with exertion or stress and relieved by rest. The document outlines how to evaluate patients presenting with chest pain through history, physical exam, risk factor assessment, and probability estimation models. It recommends initial tests like ECG, cardiac biomarkers, and stress testing. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, medications like aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and revascularization if needed. Regular patient follow up and education are also emphasized.